basic encryption and decryption
- 1. Basic Encryption and Decryption
- 2. • Encryption: a process of encoding a message so that its meaning is not obvious • Decryption: the reverse process
- 3. Encode(encipher) vs. Decode(decipher) • Encoding: the process of translating entire words or phrases to other words or phrases • Enciphering: translating letters or symbols individually • Encryption: the group term that covers both encoding and enciphering
- 4. Basic operations • plaintext to ciphertext: encryption C = E(P) • ciphertext to plaintext: decryption: P = D(C) requirement: P = D(E(P))
- 5. Classical Encryption Techniques • Symmetric key encryption • Asymmetric key encryption
- 6. Symmetric Key Encryption • Sender and recipient share a common key • Was the only type of cryptography, prior to invention of public-key in 1970’s • All traditional schemes are symmetric / single key / private-key encryption algorithms, with a single key, used for both encryption and decryption, since both sender and receiver are equivalent, either can encrypt or decrypt messages using that common key.
- 8. Requirements • Two requirements for secure use of symmetric encryption: – a strong encryption algorithm – a secret key known only to sender / receiver Y = EK(X) X = DK(Y) Here, plaintext X, ciphertext Y, key K, encryption algorithm Ek, decryption algorithm Dk. • Assume encryption algorithm is known • Implies a secure channel to distribute key
- 9. Types of Ciphers • Substitution ciphers • Permutation (or transposition) ciphers
- 10. Classical Substitution Ciphers • A substitution cipher replaces one symbol with another. • Substitution ciphers can be categorized as either monoalphabetic ciphers or polyalphabetic ciphers.
- 11. Monoalphabetic Ciphers • In monoalphabetic substitution, the relationship between a symbol in the plaintext to a symbol in the ciphertext is always one-to-one.
- 12. • The simplest monoalphabetic cipher is the additive cipher. This cipher is sometimes called a shift cipher and sometimes a Caesar cipher
- 13. Caesar Cipher • Earliest known substitution cipher • First attested use in military affairs • Replaces each letter by 3rd letter on • example: meet me after the toga party PHHW PH DIWHU WKH WRJD SDUWB
- 14. • Note: when letters are involved, the following conventions are used in this course: Plaintext is always in lowercase; ciphertext is in uppercase
- 15. • can define transformation as: a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z A B C • mathematically give each letter a number • then have Caesar cipher as: C = E(p) = (p + k) mod (26) p = D(C) = (C – k) mod (26)
- 16. When the cipher is additive, the plaintext, ciphertext, and key are integers in Z26
- 17. • This mathematical description uses modulo arithmetic (ie clock arithmetic). Here, when you reach Z you go back to A and start again. Mod 26 implies that when you reach 26, you use 0 instead (ie the letter after Z, or 25 + 1 goes to A or 0). • Example: howdy (7,14,22,3,24) encrypted using key f (5) is MTBID
- 18. Example • Use the additive cipher with key = 15 to encrypt the message “hello”.
- 19. • Use the additive cipher with key = 15 to decrypt the message “WTAAD”.
- 20. Cryptanalysis of Caesar Cipher • only have 26 possible keys, of which only 25 are of any use, since mapping A to A etc doesn't really obscure the message. • Advantage : easy to use • Disadvantage: simple structure and easy to break
- 21. Polyalphabetic Ciphers • another approach to improving security is to use multiple cipher alphabets • called polyalphabetic substitution ciphers • makes cryptanalysis harder with more alphabets to guess and flatter frequency distribution • use a key to select which alphabet is used for each letter of the message
- 22. Vigenere Cipher • Vigenere key stream does not depend on the plaintext characters; it depends only on the position of the character in the plaintext
- 24. Example • encrypt the message She is listening using the 6-character keyword “PASCAL”. • The initial key stream is (15, 0, 18, 2, 0, 11). The key stream is the repetition of this initial key stream (as many times as needed
- 26. TRANSPOSITION CIPHERS • A transposition cipher does not substitute one symbol for another, instead it changes the location of the symbols.
- 27. Keyless Transposition Ciphers • Simple transposition ciphers, which were used in the past, are keyless. • Text is written into a table column by column and then is transmitted row by row. • Text is written into a table and row by row, then is transmitted column by column.
- 28. Example: Rail fence cipher. • The ciphertext is created reading the pattern row by row. • For example, to send the message “Meet me at the park” to Bob, Alice writes She then creates the ciphertext “MEMATEAKETETHPR
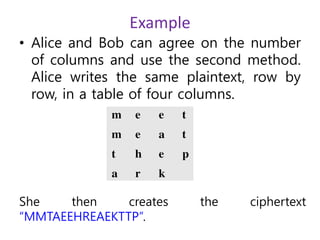
- 29. Example • Alice and Bob can agree on the number of columns and use the second method. Alice writes the same plaintext, row by row, in a table of four columns. She then creates the ciphertext “MMTAEEHREAEKTTP”.
- 30. Keyed Transposition Ciphers • Divide the plaintext into groups of predetermined size, called blocks, and then use a key to permute the characters in each block separately.
- 31. Steganography • an alternative to encryption • hides existence of message – using only a subset of letters/words in a longer message marked in some way – using invisible ink – hiding in LSB in graphic image or sound file • has drawbacks – high overhead to hide relatively few info bits
- 33. CONVENTIONAL ENCRYPTION ALGORITHMS • Triple DES • International Data Encryption Algorithm (IDEA) • Blowfish • RC5 • CAST-128 • RC2 • Characteristics of Advanced Symmetric Block Ciphers