Block Cipher modes of Operation
Last Updated :
11 Jul, 2025
Encryption algorithms are divided into two categories based on the input type: block cipher and stream cipher. A block cipher is an encryption algorithm that takes a fixed-size input (e.g., b bits) and produces a ciphertext of b bits. If the input is larger than b bits, it can be divided further. There are several modes of operation for a block cipher, each suited for different applications and uses.
What are Block Cipher Modes of Operation?
Block Cipher Modes of Operation define how to securely encrypt and decrypt large amounts of data using a block cipher. A block cipher is an encryption algorithm that processes data in fixed-size blocks (e.g., 128 bits) rather than one bit at a time. However, to encrypt data larger than a single block, different modes of operation are used to ensure both security and efficiency. Here are a few common modes. Here are a few common modes:
Electronic Code Book (ECB)
The electronic codebook is the easiest block cipher mode of functioning. It is easier because of the direct encryption of each block of input plaintext and output is in the form of blocks of encrypted ciphertext. Generally, if a message is larger than b bits in size, it can be broken down into a bunch of blocks and the procedure is repeated.
The procedure of ECB is illustrated below:
 Electronic Code Book
Electronic Code BookAdvantages of using ECB
- Parallel encryption of blocks of bits is possible, thus it is a faster way of encryption.
- Simple way of the block cipher.
Disadvantages of using ECB
- Prone to cryptanalysis since there is a direct relationship between plaintext and ciphertext.
- Identical plaintext blocks produce identical ciphertext blocks, which can reveal patterns.
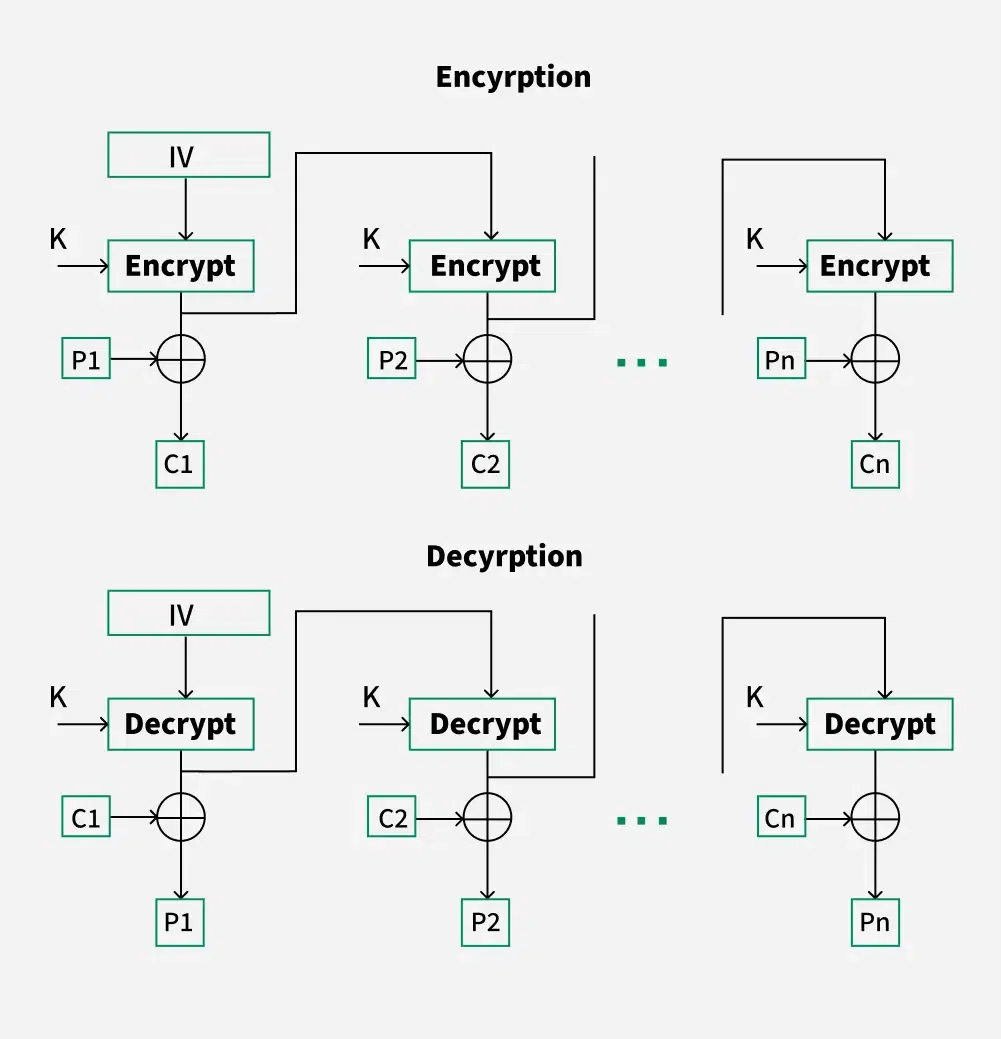
Cipher Block Chaining
Cipher block chaining or CBC is an advancement made on ECB since ECB compromises some security requirements. In CBC, the previous cipher block is given as input to the next encryption algorithm after XOR with the original plaintext block. In a nutshell here, a cipher block is produced by encrypting an XOR output of the previous cipher block and present plaintext block.
The process is illustrated here:
 Cipher Block Chaining
Cipher Block Chaining Advantages of CBC
- CBC works well for input greater than b bits.
- CBC is a good authentication mechanism.
- Better resistive nature towards cryptanalysis than ECB.
- More secure than ECB as it hides patterns.
Disadvantages of CBC
Cipher Feedback Mode (CFB)
In this mode the cipher is given as feedback to the next block of encryption with some new specifications: first, an initial vector IV is used for first encryption and output bits are divided as a set of s and b-s bits. The left-hand side s bits are selected along with plaintext bits to which an XOR operation is applied. The result is given as input to a shift register having b-s bits to lhs, s bits to rhs and the process continues. The encryption and decryption process for the same is shown below, both of them use encryption algorithms.
 Cipher Feedback Mode
Cipher Feedback ModeAdvantages of CFB
- Since, there is some data loss due to the use of shift register, thus it is difficult for applying cryptanalysis.
- Can handle data streams of any size.
Disadvantages of using CFB
- The drawbacks of CFB are the same as those of CBC mode. Both block losses and concurrent encryption of several blocks are not supported by the encryption. Decryption, however, is parallelizable and loss-tolerant.
- Slightly more complex and can propagate errors.
Output Feedback Mode
The output feedback mode follows nearly the same process as the Cipher Feedback mode except that it sends the encrypted output as feedback instead of the actual cipher which is XOR output. In this output feedback mode, all bits of the block are sent instead of sending selected s bits. The Output Feedback mode of block cipher holds great resistance towards bit transmission errors. It also decreases the dependency or relationship of the cipher on the plaintext.
 Output Feedback Mode
Output Feedback Mode Advantages of OFB
- In the case of CFB, a single bit error in a block is propagated to all subsequent blocks. This problem is solved by OFB as it is free from bit errors in the plaintext block. Thus errors in transmission don't propagate.
Disadvantages of OFB
- The drawback of OFB is that, because to its operational modes, it is more susceptible to a message stream modification attack than CFB.
- If the keystream is reused, security is compromised.
Counter Mode
The Counter Mode or CTR is a simple counter-based block cipher implementation. Every time a counter-initiated value is encrypted and given as input to XOR with plaintext which results in ciphertext block. The CTR mode is independent of feedback use and thus can be implemented in parallel.
Its simple implementation is shown below:
 Counter Mode
Counter Mode Advantages of Counter
- Since there is a different counter value for each block, the direct plaintext and ciphertext relationship is avoided. This means that the same plain text can map to different ciphertext.
- Parallel execution of encryption is possible as outputs from previous stages are not chained as in the case of CBC.
Disadvantages of Counter
- The fact that CTR mode requires a synchronous counter at both the transmitter and the receiver is a severe drawback. The recovery of plaintext is inaccurate when synchronization is lost.
Applications of Block Ciphers
- Data Encryption: Block Ciphers are widely used for the encryption of private and sensitive data such as passwords, credit card details and other information that is transmitted or stored for a communication. This encryption process converts a plain data into non-readable and complex form. Encrypted data can be decrypted only by the authorized person with the private keys.
- File and Disk Encryption: Block Ciphers are used for encryption of entire files and disks in order to protect their contents and restrict from unauthorized users. The disk encryption software such as BitLocker, TrueCrypt uses block cipher to encrypt data and make it secure.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPN): Virtual Private Networks use block cipher for the encryption of data that is being transmitted between the two communicating devices over the internet. This process makes sure that data is not accessed by unauthorized person when it is being transmitted to another user.
- Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS): SSL and TLS protocols use block ciphers for encryption of data that is transmitted between web browsers and servers over the internet. This encryption process provides security to confidential data such as login credentials, card information etc.
- Digital Signatures: Block ciphers are used in the digital signature algorithms, to provide authenticity and integrity to the digital documents. This encryption process generates the unique signature for each document that is used for verifying the authenticity and detecting if any malicious activity is detected.
Initialization Vector (IV)
Initialization Vector (IV) is a crucial concept in cryptography, especially when using block cipher modes of operation. It is a random or unique value used in combination with a secret key to initialize the encryption process. It ensures that the same plaintext encrypted multiple times will produce different ciphertexts, enhancing security by preventing patterns from emerging.
Importance of IV
- Initialization Vector (IV) is a non-secret, unique value used to ensure that encrypting the same plaintext with the same key results in different ciphertexts.
- IVs are essential for maintaining the security and integrity of encryption processes, especially in block cipher modes like CBC, CFB, OFB, and CTR.
- Proper generation and management of IVs ensures they are unique and unpredictable and are vital to preventing cryptographic vulnerabilities.
- IVs should be transmitted or stored alongside the ciphertext to enable successful decryption, but they must never be reused with the same key.
Other Modes of Operation
- GCM (Galois/Counter Mode)
- CCM (Counter with CBC-MAC)
- XTS (XEX Tweakable Block Cipher with Ciphertext Stealing)
- EAX Mode
- OCB (Offset Codebook Mode)
- PCBC (Propagating Cipher Block Chaining)
- LRW (Liskov, Rivest, Wagner) Mode
Conclusion
Block Cipher Modes of Operation are methods that determine how to encrypt and decrypt large amounts of data securely using block ciphers like AES. They ensure that the same plaintext doesn't always produce the same ciphertext by using techniques like chaining and counters. Common modes include ECB, CBC, CTR, and GCM, each offering different levels of security and performance. Choosing the right mode and properly managing elements like Initialization Vectors is essential for maintaining data confidentiality and protection against attacks.
Similar Reads
Cryptography Tutorial Cryptography is a technique of securing communication by converting plain text into unintelligible ciphertext. It involves various algorithms and protocols to ensure data confidentiality, integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation. The two primary types of cryptography are symmetric key cryptogr
7 min read
Cryptography Basic
Cryptography Algorithm
What is data encryption?
Classical Encryption Techniques
Block Cipher , DES and AES
Public Key Cryptography and RSA
What is Cryptanalysis?
Comman Cryptography
Custom Building Cryptography Algorithms (Hybrid Cryptography)Cryptography can be defined as an art of encoding and decoding the patterns (in the form of messages). Cryptography is a very straightforward concept which deals with manipulating the strings (or text) to make them unreadable for the intermediate person. It has a very effective way to encrypt or dec
15+ min read
An Overview of Cloud CryptographyCloud cryptography is a set of techniques used to secure data stored and processed in cloud computing environments. It provides data privacy, data integrity, and data confidentiality by using encryption and secure key management systems. Common methods used in cloud cryptography include:Symmetric en
4 min read
Quantum CryptographyThe uncertainty principle of quantum physics builds the earliest foundations for quantum cryptography. With quantum computers of the future being expected to solve discrete logarithmic problems and the popularly known cryptography methods such as AES, RSA, DES, quantum cryptography becomes the fores
7 min read
Image Steganography in CryptographyThe word Steganography is derived from two Greek words- 'stegos' meaning 'to cover' and 'grayfia', meaning 'writing', thus translating to 'covered writing', or 'hidden writing'. Steganography is a method of hiding secret data, by embedding it into an audio, video, image, or text file. It is one of t
8 min read
DNA CryptographyCryptography is the branch of science that deals with the encoding of information to hide messages. It plays a vital role in the infrastructure of communication security. The Pioneering work had been done by Ashish Gehani et al and Amin et al after Leonard Max Adleman had shown the capability of mol
12 min read
Caesar Cipher in CryptographyThe Caesar Cipher is one of the simplest and oldest methods of encrypting messages, named after Julius Caesar, who reportedly used it to protect his military communications. This technique involves shifting the letters of the alphabet by a fixed number of places. For example, with a shift of three,
11 min read
One Time Password (OTP) algorithm in CryptographyAuthentication, the process of identifying and validating an individual is the rudimentary step before granting access to any protected service (such as a personal account). Authentication has been built into the cyber security standards and offers to prevent unauthorized access to safeguarded resou
7 min read
Data Integrity in Cryptography