What is Semi-structured data?
Last Updated :
11 Jul, 2025
Semi-structured data is data that does not reside in a traditional relational database (like SQL) but still has some organizational properties, such as tags or markers, that make it easier to analyze than completely unstructured data.
It doesn't follow a strict schema like structured data, but it still contains elements like labels or keys that make the data identifiable and searchable.
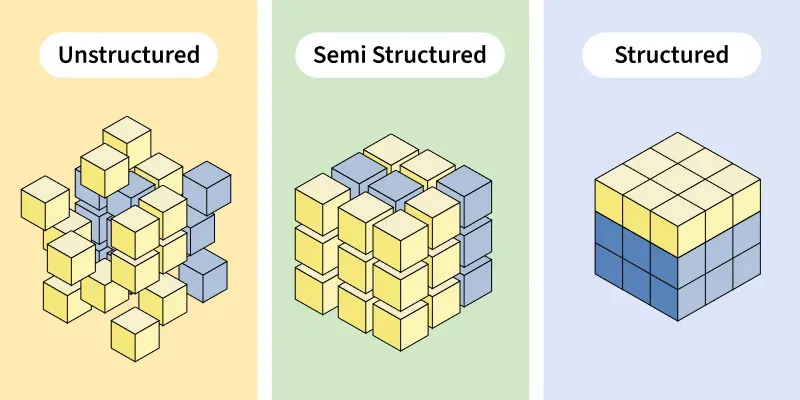 Unstructured vs Semi Structured vs Structured Data
Unstructured vs Semi Structured vs Structured DataCharacteristics of Semi-Structured Data
- Flexible Schema: The structure can vary from one entry to another. For example, one JSON object may have five fields while another has only three.
- Human-Readable Format: Many types like XML or JSON are easy for humans and machines to understand.
- Scalable: Easily handled by modern NoSQL databases, making it great for Big Data environments.
- Metadata-Rich: Tags and attributes provide context that helps with sorting and analysis.
Importance of Semi-Structured Data
As data becomes more complex and varied, semi-structured formats offer a balance between flexibility and manageability. They allow organizations to store and process different types of information in one place, making it easier to handle diverse data formats. Additionally, semi-structured data enables quick adaptation to new data sources without the need to redesign existing databases. This flexibility supports more efficient data analysis and integration, especially when combining structured and unstructured data, making it a valuable asset in modern data-driven environments.
Examples of Semi-Structured Data:
- JSON (JavaScript Object Notation)
- XML (eXtensible Markup Language)
- CSV files with inconsistent rows
- Emails (with structured headers and unstructured body text)
- Sensor data from IoT devices
- HTML web pages
Semi-structured data have different structure because of heterogeneity of the sources. Sometimes they do not contain any structure at all. This makes it difficult to tag and index. So while extract information from them is tough job. Here are possible solutions -
- Graph based models (e.g OEM) can be used to index semi-structured data
- Data modelling technique in OEM allows the data to be stored in graph based model. The data in graph based model is easier to search and index.
- XML allows data to be arranged in hierarchical order which enables the data to be indexed and searched
- Use of various data mining tools
Semi-Structured Data Management
Unlike structured data, semi-structured data is best managed using NoSQL databases or document stores. Popular technologies include:
- MongoDB: A document-based NoSQL database that works well with JSON-like formats.
- Cassandra: Handles wide-column data with semi-structured schema design.
- Elasticsearch: Can index and search through semi-structured log files and documents.
- Cloud Storage (e.g. AWS S3, Azure Blob): Used to store large volumes of semi-structured data like logs, emails, and telemetry data.
Applications
Semi-structured data is used across various industries:
- E-commerce: Product catalogs stored in JSON format, allowing flexibility in item attributes.
- Healthcare: Patient forms and reports stored in XML with variable fields.
- IoT and Smart Devices: Sensor data captured in key-value formats.
- Web Development: HTML and JSON used to render dynamic content on websites.
- Social Media Platforms: User activity and messages logged in semi-structured logs.
Challenges
Despite its flexibility, semi-structured data comes with a few challenges:
- Complex Querying: Not as straightforward as SQL queries on structured data.
- Data Cleaning: Irregular structure may lead to inconsistency and harder integration.
- Tool Compatibility: Not all analytics tools support semi-structured formats out of the box.
To read Differences between Structured, Semi-structured and Unstructured data refer the following article - Difference between Structured, Semi-structured and Unstructured data
Similar Reads
What is Structured Data? Structured data send to data that is organized and design in a specific way to make it easily readable and understand by both humans and machines. This is typically achieved through the use of a well-defined schema or data model, which provides a structure for the data.For example, in a customer dat
3 min read
What is Unstructured Data? Unstructured data refers to information that does not have a predefined format or structure. It is messy, unorganized and hard to sort. Unlike structured data, which is organized into rows and columns (like an Excel sheet), unstructured data comes in many different forms such as text documents, imag
5 min read
What is Database? A database is an organized collection of data stored electronically. It allows users and applications to easily access, update, and manipulate information. This data contains text, numbers, images, videos and more. Databases are managed using specialized software known as a Database Management Syste
13 min read
Large objects(LOBs) for Semi Structured and Unstructured Data Large objects (LOBs) are a type of data type used to store semi-structured and unstructured data in a database. LOBs are typically used for storing data that is too large to fit into a traditional data type, such as text documents, images, videos, and audio files. LOBs are particularly useful for st
5 min read
What is XML Data Model in DBMS? The database management system market is filled with many choices, and XML is a strong contender due to the elegant syntax model it uses to organize and structure data. The text would give you information on the main parts of the Data Model for XML, thus, you would be able to understand the essentia
6 min read
What is Data Dictionary? In a database management system (DBMS), a data dictionary can be defined as a component that stores a collection of names, definitions, and attributes for data elements used in the database. The database stores metadata, that is, information about the database. These data elements are then used as p
7 min read