Estimating Limits from Graphs
Last Updated :
12 Aug, 2024
The concept of limits has been around for thousands of years. Earlier mathematicians in ancient civilizations used limits to approximate the area of a circle. However the formal concept was not around till the 19th century. This concept is essential to calculus and serves as a building block for analyzing derivatives, continuity, and differentiability. Intuitively, limits give us an idea about the values function approaches at a particular value of x. Using this idea, limits can also be estimated to a certain extent just by looking at the graph. Let's look at these ideas in detail.
Limit
The limit of a function at a number x = a can be thought of as the value function starts to take while reaching towards x = a. The point x = a can be approached from either of the sides, the left-hand side or the right-hand side. For example, let's consider a function f(x), then the limit of the function at x = a is denoted as,
\lim_{x \to a} f(x)
The left-hand limit is denoted as,
\lim_{x \to a^{-}} f(x)
Similarly, the right-hand limit is denoted as,
\lim_{x \to a^{+}} f(x)
- If f(x) gets closer and closer to a specific value L as x approaches a chosen value c from the right, then it is said that the limit of f(x) as x approaches c from the right is L.
- If f(x) gets closer and closer to a specific value L as x approaches a chosen value c from the left, then it is said that the limit of f(x) as x approaches c from the left is L.
- If the limit of f(x) as x approaches c is the same from both the right and the left, then it is said the limit of f(x) as x approaches c is L.
If f(x) never approaches a specific finite value as x approaches c, then we say that the limit does not exist. If f(x) has different right and left limits, then the two-sided limit (\lim_{x→c}f(x) ) does not exist.
Limits to any function can be calculated through two approaches:
- Algebraic Method
- Graphical Method
Algebraic methods involve manipulating the function such that its limit can be calculated easily. The graphical method simply involves making a graph of the function, and then the limit can be estimated just by looking at the graph.
Estimating Limits from Graphs
Consider the function f(x),
f(x) = 3x + 4
This is an equation of a line. Let's see what the value of the limit of this function at x = 1 is. The figure below shows the graph for this function,

Notice that as we approach from both the left-hand side and right-hand side of x = 1, the function moves toward a single value. This value is called the limit of the function.
Unbounded Limits
Sometimes there are certain kinds of functions that move towards infinity. In such cases, the value of the limit goes up to infinite. For example, for function f(x) given below,
f(x) = |\frac{1}{x}|
The limit for this function at x = 0,
\lim_{x \to 0} \frac{1}{x} = \infty

Notice in the figure that the limit at x = 0 is unbounded and is going up to infinity. Such limits are called unbounded limits.
One-Sided Limits
Sometimes functions are not continuous, which means they tell us two different limits while approaching from two different sides. For example, the greatest integer function is inherently discontinuous, and at these discontinuities, we observe two different values.
f(x) =[x]

At x = 1, there are two values when approached from two different sides. In such cases, mostly we are asked to tell the value from one side. These are called one-sided limits.
Limits and Graphical Behavior
Limits can tell a lot about a function's behavior at some particular point. Then how should one use it? In cases where it is known that the function is discontinuous, it becomes hard to analyze the graph of the function solely using derivatives. In such cases, limits can be used to find the values of the function at the points of discontinuities. For example, let's say we have a function f(x),
f(x)= \begin{cases} x^2 + 4,& \text{if } x\geq 1\\ 0, & \text{otherwise} \end{cases}
It is obvious from the function definition that this function is discontinuous, so derivatives are not useful at such places. Graph shapes for individual pieces are already known. Let's calculate the value of the function at discontinuity x = 1.
Left-hand Limit at x =1,
\lim_{x \to 1^{-}}f(x) = 0
Right-hand Limit at x =1,
\lim_{x \to 1^{+}}f(x)
⇒\lim_{x \to 1^{+}}x^2 + 4
⇒ 5
So, the values of both limits are different. Now we can plot the function on a graph.

Solved Questions on Estimating Limits from Graphs
Question 1: Find the \lim_{x \to 1} x^2
Answer:
Graph of x2 is an upward parabola which is centered at origin. The figure below shows the graph of the given function.

Notice that the function starts moving towards taking a value of 1 as one moves towards the value of x = 1.
Thus, \lim_{x \to 1} x^2 =1
Question 2: Find the \lim_{x \to 0} log(x)
Answer:
Graph of log(x) is a saturating function. The figure below shows the graph of the given function.

Notice that the function starts moving towards taking a value of -∞ as one moves towards the value of x = 0. This is an example of unbounded limit mentioned above.
Thus, \lim_{x \to 0} log(x) =-\infty
Question 3: Find the limit of the function at x = 1.

Solution:
In the graph, the white dot at x = 1 indicates that the function is not defined at x = 1. That means, there should be no value of the function at x =1.
Limit allows us to calculate the values the function was approaching had it been defined at x =1.
So, in this case from graph it can be seen that the function is approaching value of 5.
\lim_{x \to 1} f(x) = 5
Question 4: Find the value of the limit of the function f(x) = \frac{1}{x} at x = 0.
Solution:
The figure shows the graph for the given function
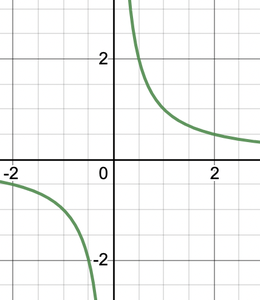
The figure makes it clear that there are two limits depending on from which side we are approaching the function.
Left Hand Side Limit:
While approaching zero from the negative side of the origin takes the function to negative infinity.
\lim_{x \to 0^{-}}f(x) = -\infty
Right Hand Side Limit:
While approaching zero from the positive side of the origin takes the function to positive infinity.
\lim_{x \to 0^{+}}f(x) = \infty
Question 5: Find the \lim_{x \to 1} x^2
Answer:
Graph of x2 is an upward parabola which is centered at origin. The figure below shows the graph of the given function.

Notice that the function starts moving towards taking a value of 1 as one moves towards the value of x = 1.
Thus, \lim_{x \to 1} x^2 =1
Question 5: Find out the limit at x = 0 for the given function,

Answer:
In the figure, the given function is not continuous at origin. That means there will be two different values of the limit - one from left-hand side and another from right-hand side.
Left- Hand Limit for the function
\lim_{x \to 0^{-}} f(x) = 5
Right - Hand Limit for the function,
\lim_{x \to 0^{+}} f(x) = 0
Practice Problems on Limits
1: Find the value of the limit of the function f(x) = \lim_{x \to 2} (4x+ 3)
2: Find the value of the limit of the function f(x) = \lim_{x \to -1} (x^3 + 4x^2+2x + 3)
3: Find the value of the limit of the function f(x) = \lim_{x \to 0} \frac{\sin(x)}{x}
4: Find the value of the limit of the function f(x) = \lim_{x \to 1} \frac{\cos(x)}{x}
5: Find the value of the limit of the function f(x) = \lim_{x \to \infty} \frac{5x^2 - 3x + 1}{4x^2 + 8}
6: Find the value of the limit of the function f(x) = \lim_{x \to 2} \frac{x^3-4}{x^2-4}
7: For the function p(x) shown in the graph as x approaches infinity, determine \lim_{x \to \infty} p(x).
8: Given the graph of q(x) what is \lim_{x \to -\infty} q(x)?
9: Estimate \lim_{x \to 4^+} r(x) from the graph of r(x) where x approaches 4 from the right.
10: From the graph of s(x) determine \lim_{x \to 5^-} s(x) where x approaches 5 from the left.
Related Articles:
Summary
The concept of limits is fundamental in calculus and mathematical analysis, serving as the foundation for defining continuity, derivatives, and integrals. Limits describe the behavior of a function as its argument approaches a particular value. Formally, the limit of a function f(x) as x approaches c is the value that f(x) gets closer to as x gets arbitrarily close to c. This can be expressed as \lim_{x \to c} f(x) = L, where L is the limit. Understanding limits allows us to deal with situations involving infinite processes and instantaneous rates of change, which are essential for modeling and solving real-world problems. Limits also help in analyzing the behavior of functions at points of discontinuity and in establishing the precise definition of continuity. Overall, the concept of limits is a crucial stepping stone in the journey from algebra to the more advanced topics in calculus.
Similar Reads
CBSE Class 11 Maths Notes CBSE Class 11 Maths Revision Notes have been designed in the most basic and detailed format possible, covering nearly all domains such as differential calculus, arithmetic, trigonometry, and coordinate geometry. We know how hard it gets when you shift to an altogether new grade where subjects are no
15+ min read
Chapter 1: Sets
Representation of a SetSets are defined as collections of well-defined data. In Math, a Set is a tool that helps to classify and collect data belonging to the same category. Even though the elements used in sets are all different from each other, they are all similar as they belong to one group. For instance, a set of dif
8 min read
Types Of SetsIn mathematics, a set is defined as a well-defined collection of distinct elements that share a common property. These elements— like numbers, letters, or even other sets are listed in curly brackets "{ }" and represented by capital letters. For example, a set can include days of the week. The diffe
13 min read
Universal SetsUniversal Set is a set that has all the elements associated with a given set, without any repetition. Suppose we have two sets P = {1, 3, 5} and Q = {2, 4, 6} then the universal set of P and Q is U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}. We generally use U to denote universal sets. Universal Set is a type of set that
6 min read
Venn DiagramVenn diagrams are visual tools used to show relationships between different sets. They use overlapping circles to represent how sets intersect, share elements, or stay separate. These diagrams help categorize items, making it easier to understand similarities and differences. In mathematics, Venn di
14 min read
Operations on SetsSets are fundamental in mathematics and are collections of distinct objects, considered as a whole. In this article, we will explore the basic operations you can perform on sets, such as union, intersection, difference, and complement. These operations help us understand how sets interact with each
15+ min read
Union of SetsUnion of two sets means finding a set containing all the values in both sets. It is denoted using the symbol '∪' and is read as the union. Example 1:If A = {1, 3. 5. 7} and B = {1, 2, 3} then A∪B is read as A union B and its value is,A∪B = {1, 2, 3, 5, 7}Example 2:If A = {1, 3. 5.7} and B = {2, 4} t
12 min read
Chapter 2: Relations & Functions
Cartesian Product of SetsThe term 'product' mathematically refers to the result obtained when two or more values are multiplied together. For example, 45 is the product of 9 and 5.To understand the Cartesian product of sets, one must first be familiar with basic set operations such as union and intersection, which are appli
7 min read
Relations and FunctionsIn mathematics, we often deal with sets of numbers or objects and the ways they are connected. Two important concepts that help us describe these connections are relations and functions.A relation is simply a connection between two sets of objects. Think of it as a rule that pairs elements from one
3 min read
Domain and Range of RelationsThe domain is the set of all possible input values (the "x" values), and the range is the set of all possible output values (the "y" values) in a relation.For any two non-empty sets A and B, we define the relation R as the subset of the Cartesian product of A × B where each member of set A is relate
8 min read
Piecewise FunctionPiecewise Function is a function that behaves differently for different types of input. As we know a function is a mathematical object which associates each input with exactly one output. For example: If a function takes on any input and gives the output as 3. It can be represented mathematically as
11 min read
Range of a FunctionFunctions in math can be thought of as vending machines. Given the money in the form of input, they give some cans or cookies in return. Similarly, functions take some input numbers and give us some output. It can be said that, in real life, Everything can be formulated and solved with the help of f
7 min read
Chapter 3: Trigonometric Functions
Chapter 4: Principle of Mathematical Induction
Chapter 5: Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
Complex NumbersComplex numbers are an essential concept in mathematics, extending the idea of numbers to include solutions for equations that don't have real solutions. Complex numbers have applications in many scientific research areas, signal processing, electromagnetism, fluid dynamics, quantum mechanics, and v
12 min read
Algebra of Real FunctionsThe algebra of real functions refers to the study and application of algebraic operations on functions that map real numbers to real numbers. A function can be thought of as a rule or set of rules which map an input to an output knows as its image. It is represented as x ⇢ Function ⇢ y. A real funct
5 min read
Algebraic Operations on Complex NumbersA complex number is a number that includes both a real and an imaginary part. It is written in the form:z = a + biWhere:a is the real part,b is the imaginary part,i is the imaginary unit, satisfying i2 = −1.Algebraic operations on complex numbers follow specific rules based on their real and imagina
7 min read
Polar Representation of Complex NumbersComplex numbers, which take the form z = x + yi, can also be represented in a way that highlights their geometric properties. This alternative representation is known as the polar form. The polar representation of a complex number expresses it in terms of its magnitude (modulus) and direction (argum
9 min read
Absolute Value of a Complex NumberThe absolute value (also called the modulus) of a complex number z = a + bi is its distance from the origin in the complex plane. The absolute value tells you how far a number is from zero, regardless of its direction (positive or negative).It is denoted as ∣z∣ and is given by the formula:|z| = \sqr
7 min read
Conjugate of Complex NumbersIn the world of mathematics, complex numbers are one of the most important discoveries by mathematicians as they help us solve many real-life problems in various fields such as the study of electromagnetic waves, engineering, and physics.The Conjugate of a Complex Number is also a complex number obt
6 min read
Imaginary NumbersImaginary numbers are numbers as the name suggests are the number that is not real numbers. All the numbers real and imaginary come under the categories of complex numbers. Imaginary numbers are very useful in solving quadratic equations and other equations whose solutions can not easily be found us
9 min read
Chapter 6: Linear Inequalities
Compound InequalitiesCompound Inequalities are the combination of two or more inequalities. These inequalities are combined using two conditions that are AND, and OR. These conditions have specific meanings and they are solved differently. The inequities in compound inequalities are individually solved using normal rule
10 min read
Algebraic Solutions of Linear Inequalities in One VariableA linear inequality is a mathematical expression involving an inequality symbol (<, >, ≤, or ≥) and a linear expression. Unlike linear equations, which give a specific solution, linear inequalities define a range of possible solutions.Example: 2x+3>5 In this case, the inequality indicates t
8 min read
Graphical Solution of Linear Inequalities in Two VariablesWe know how to formulate equations of different degree, and it is used a lot in real life, but the question arises, is it always possible to convert a situation into an equation? Sometimes we get statements like, the number of Covid cases per day in Delhi has reached more than 10,000. This phrase “L
8 min read
Solving Linear Inequalities Word ProblemsWe are well versed with equations in multiple variables. Linear Equations represent a point in a single dimension, a line in a two-dimensional, and a plane in a three-dimensional world. Solutions to linear inequalities represent a region of the Cartesian plane. It becomes essential for us to know ho
10 min read
Chapter 7: Permutations and Combinations
Fundamental Principle of CountingThe fundamental principle of counting is a basic concept used to determine the total number of possible outcomes in a situation where there are multiple independent events. It allows us to count a large number of possibilities without needing to list each one individually.For example, consider guess
11 min read
PermutationIn Mathematics, Permutation is defined as a mathematical concept that determines the number of possible arrangements for a specific set of elements. therefore, it plays a big role in computer science, cryptography, and operations research. For example, take a set {1, 2, 3}:All Permutations taking al
15+ min read
CombinationsCombination is a way of choosing items from a set, (unlike permutations) when the order of selection doesn't matter. In smaller cases, it's possible to count the number of combinations. Combination refers to the mixture of n things taken k at a time without repetition.Example: For set S = {a, b, c},
8 min read
Chapter 8: Binomial Theorem
Chapter 9: Sequences and Series
Sequences and SeriesA sequence is an ordered list of numbers following a specific rule. Each number in a sequence is called a "term." The order in which terms are arranged is crucial, as each term has a specific position, often denoted as an​, where n indicates the position in the sequence.For example:2, 5, 8, 11, 14,
10 min read
General and Middle Terms - Binomial Theorem - Class 11 MathsBinomial theorem or expansion describes the algebraic expansion of powers of a binomial. According to this theorem, it is possible to expand the polynomial "(a + b)n" into a sum involving terms of the form "axzyc", the exponents z and c are non-negative integers where z + c = n, and the coefficient
7 min read
Arithmetic SeriesAn arithmetic series is the sum of the terms of an arithmetic sequence, where an arithmetic sequence is a sequence of numbers in which the difference between consecutive terms is constant. Or we can say that an arithmetic progression can be defined as a sequence of numbers in which for every pair of
5 min read
Arithmetic SequenceAn arithmetic sequence or progression is defined as a sequence of numbers in which the difference between one term and the next term remains constant.For example: the given below sequence has a common difference of 1.1 2 3 4 5 . . . n ⇑ ⇑ ⇑ ⇑ ⇑ . . . 1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th . . . nth TermsThe Arithmetic
8 min read
Geometric Progression or GPGeometric Progression (GP) is a sequence of numbers where each term after the first is found by multiplying the previous term by a constant called the common ratio.For Example, the sequence given below forms a GP with a common ratio of 2 1 2 4 8 16 . . . n⇑ ⇑ ⇑ ⇑ ⇑ . . . 1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th . . . nt
12 min read
Geometric SeriesIn a Geometric Series, every next term is the multiplication of its Previous term by a certain constant, and depending upon the value of the constant, the Series may increase or decrease.Geometric Sequence is given as: a, ar, ar2, ar3, ar4,..... {Infinite Sequence}a, ar, ar2, ar3, ar4, ....... arn {
3 min read
Arithmetic Progression and Geometric ProgressionArithmetic Progression and Geometric Progression: The word "sequence" in English means a collection of some numbers or objects in such a way that it has a first member, a second member, and so on. Sequences can be of anything, for example. - January, February, .... is the sequence of months in a yea
10 min read
Special Series in Maths - Sequences and Series | Class 11 MathsSpecial Series: A series can be defined as the sum of all the numbers of the given sequence. The sequences are finite as well as infinite. In the same way, the series can also be finite or infinite. For example, consider a sequence as 1, 3, 5, 7, … Then the series of these terms will be 1 + 3 + 5 +
10 min read