Have you ever wondered how a simple click on your mouse or a tap on your screen can instantly connect you to a world of information, entertainment, and communication? The internet is one of the most transformative inventions of our time, yet its inner workings remain a mystery to many. How does data travel across the globe in milliseconds? What makes it possible for billions of devices to communicate seamlessly? And what exactly happens behind the scenes when you stream a video, send an email, or browse a website?
In this blog, we’ll demystify the internet and break down its complex mechanisms into simple, easy-to-understand concepts. So, this guide will take you on a journey through the fascinating infrastructure that powers the internet. From data packets and IP addresses to undersea cables and wireless networks, we’ll explore the technology that keeps the world connected. Now, before going to the how its work let's understand what is Internet?
What is Internet?
The internet is a global network of interconnected computers and devices that communicate with each other to share information, resources, and services. Think of it as a massive web of connections that allows people and machines to exchange data instantly, no matter where they are in the world. From sending emails and browsing websites to streaming videos and playing online games, the internet powers nearly every aspect of modern life.
The Internet connects over 4.5 billion users and 1.8 billion websites through standard protocols like TCP/IP. Information is divided into packets that travel through routers and switches, typically taking 20 to 200 milliseconds for a round trip. Each device on the Internet has a unique Internet Protocol (IP) address, with IPv4 supporting just over 4.3 billion addresses. To address this limitation, IPv6 was introduced, providing a vast address space for future devices.
Brief History of Internet
After knowing what is Internet let's explore and get to know the some history of Internet and some facts.
The internet began in the 1960s as ARPANET, a U.S. Department of Defense project to create a communication network that could withstand a nuclear attack. In 1969, the first message was sent between two computers, marking the birth of networked communication. The 1970s saw the development of TCP/IP, the foundational protocols for data transmission, and the first email was sent in 1971. By the 1980s, the internet expanded beyond military and academic use, with the introduction of the Domain Name System (DNS) in 1984, making it easier to navigate.
The 1990s brought the World Wide Web, invented by Tim Berners-Lee, and the first web browser, Mosaic, which made the internet accessible to the public. The rise of e-commerce and search engines like Google transformed how people used the internet. The 2000s introduced social media Facebook, Twitter (X) and mobile internet with the iPhone, while the 2010s saw the growth of cloud computing and the Internet of Things (IoT). Today, the internet continues to evolve with Web3, AI, and quantum computing, shaping the future of global connectivity and innovation.
Interesting Facts about Internet
- In 1969 the first message was sent over ARPANET between two computers at UCLA and Stanford. The message was supposed to be "LOGIN," but the system crashed after "LO."
- In 1971 the first email was sent by Ray Tomlinson, who also introduced the "@" symbol to separate the user’s name from the computer’s name.
- In 1989 Tim Berners-Lee, a British scientist, invented the WWW while working at CERN. He created the first web browser, web server, and HTML (Hypertext Markup Language).
- In the year 1998 Google was founded, revolutionizing how people search for information online.
Now, we have gain lots of knowladge about the Internet so lets jump into the woking of the internet.
How Does the Internet Work
This section will discuss the details of the Internet, including its components, infrastructure, and functionality. Explore the article to learn how the Internet works.
What Are The Components of the Internet?
Generally, two main components uphold the functionality of the Internet, they are:
- Packets
- Protocols
So what are Packets and Protocols?
In networking, the data that is being transmitted through the internet is sent via small segments/chunks which are later translated into bits, and the packets get routed to their endpoint (destination) through different networking devices i.e. routers or switches.
Later, once the packet arrives at the receiver’s end, that small chunks of data get reassembled to utilize or check the data that he/she requested. That’s why they are used to push ease in networking and large data can be easily sent by sending small units and this whole process of sending/receiving small bits is known as Packet Switching.
An Example to Understand the Complete Concept:
Let’s say a user wants to load an image from the internet so the moment the user clicks over the image, the whole image will not open in one go. A small amount of data will start going from the server and will reach the endpoint (user) and the moment all data reaches the user’s system, the image will open on the user’s end.
Those small packets are being sent via wires, radio waves, etc. of the internet and once they complete their fetching, the user will be able to view the whole image. Theoretically, a packet may consist of 1000-1500 bytes depending upon the structure and connection.
What is the Basic Infrastructure of the Internet?
On the other end, do you know what a challenging task could be? Connecting two computers with the help of any communication method. To solve the connection issue, protocols were introduced. It is a standardized method of performing certain tasks and data formatting so that two or more devices can communicate with each other.
Let's narrow it down for better clarity:
Besides this, there are several other protocols for testing, routing, and encryption, and for streaming games/videos, rather than using TCP, we use UDP (User Datagram Protocol).
The bottom line is, no matter what kind of connection you’re providing to which device, it can interpret and understand these protocols, that’s just because they’ll be connected over the Internet.
How Does the Internet Work with Diagrams?
From opening a web browser to visiting a website, it all happens with specific methods that we're going to check in these 5 easy steps.
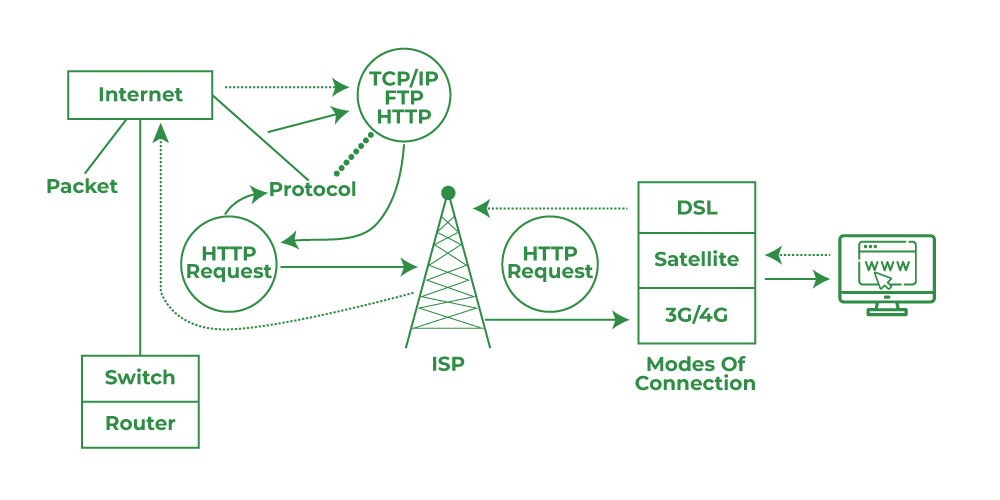 Internet Working Metrics
Internet Working Metrics- Firstly, you'll be required to connect your system or PC with any router or modem to establish a connection. This connection is the base of the internet connection.
- When you open the browser and start typing something like "www.google.com", your system will push a query command to your ISP (Internet Service Provider) that is connected with other servers that store and process data.
- Now, the web browser will start indexing the URL that you've entered and will fetch the details in numeric format (in their language to identify the address (unique) that you're trying to reach.
- Next, now your browser will start sending the HTTP request where you're trying to reach and send a copy of the website on the user's system. Note: The server will send data in the form of small packets (from the website to the browser)
- Once all the data (of small packets) is received at the user's end (PC/Laptop), the browser will start arranging all those small packets and later will form a collective file (here, the browser will gather all the small packets and rearrange them just like a puzzle) and then you'll be able to see the contents of that website.
Note: The action happens so quickly that we don't even notice what's going behind. Only, when the connection is poor, you do face difficulty in reaching or loading any website or its content.
What are the Modes of Connecting Through the Internet?
There are certain ways of getting connected to the Internet and going online. So, for that, you need an ISP (Internet Service Provider), the type of ISP you’ll be choosing will depend upon the availability in your area and what kind of services they’re offering to their customers. So, here we are listing some universal modes of the internet:
- DSL: This technology (Digital Subscriber Line) uses a Broadband connection which has been in trend for the past few years. Your ISP will connect your premises with the help of telephone wire even though you own a telephone.
- Dial-Up: People used to connect their system with the help of a dial-up connection, and it is one of the slowest types of Internet connection. This is used to enable internet connectivity with the help of a telephone connection and the user must have multiple connections then only they can use a Dial-up connection.
- Cable TV Connection: It is being used to connect your system to the Internet, and for that, you, the ISP will connect it via cable TV wire. It also uses Broadband technology and you don’t need to have a Cable connection for that. Cable is considered as most accessible and faster than dial-up and DSL that we have for connection.
- Satellite: It also uses broadband technology but without interacting with any cable connection. Hence, it connects wirelessly with the help of a satellite and this enables its availability anywhere in the world. Thus, being fancy and accessible it comes with a few drawbacks:
a- There can be network disturbance if the weather is unstable because it connects via satellite.
b- The connectivity is not stable and they are considered slower as compared to DSL or cable connection. - 3G/4G/5G: This is the new age technology in the entire world. It connects wirelessly via different ISPs and is widely used in cell phones. But they aren’t considered as stable as DSL or cable and most importantly they come with a DATA LIMITATION cap for each month.
What are Internet Connection Protocols & Why is it Important for the Internet?
The protocols decide how the technology is going to work in what governing ways and what quantity of data will be shared. They all are defined by protocols and as per standard, both the parties (sender/receiver) have to follow the same rule to communicate. However, these protocols are categorized into 3 major units:
- TCP/IP: It is a variety of internet protocols (TCP/IP) for communicating between a sender and a receiver. TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) / IP (Internet Protocol) ensures that all users who are connected to the internet have their own unique identity known as IP Address. However, how data will flow into what segments (packets) is being decided by TCP. It divides the whole message into small packets and reassembles them before it reaches the receiver.
- FTP: It is used for communicating from one point to another (computer) over LAN (Local Area Network) or WAN (Wide Area Network). File Transfer Protocol or FTP acts like a host and establishing connections between computers and transferring files between them are seamless whereas one connection is used for data connection and the other for the control connection.
- HTTP: The base of the Internet starts from HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) and is being used to communicate all over (World Wide Web) WWW. The concept of HTTP is to provide data over the Internet (image, video, text, etc.) and the moment a user opens their web browser, they’re connecting to the Internet and establishing an HTTP connection. The foundation of HTTP began in the ’90s by Tim Berners-Lee which runs on top of the TCP/IP network.
What are the Physical Infrastructures of the Internet Acted As Pillars?
As we’ve discussed above, the Internet is built with different architectures and that’s what makes it feasible for the general population. Besides this, some of the most important types include the following:
- Switches: Switches help for connecting devices in a single network and use small packet switching to send and receive data packets over the Internet. Besides this, they have multiple ports by which a system can be connected. So, when a packet arrives at any port, it starts cross-checking the specifications and forwards the same to its destination. It also supports broadcast and unicast communication.
- Router: They operate at the layer 3 OSI (Open Systems Interconnection Model) model that is created for sending, receiving, and forwarding small data packets within the connected system over the same network. In this architecture, once the router receives the data packets, it inspects the destined address, then consults its routing and transfers the same packet to its desired location.
How do Websites and Several Applications use the Internet?
Let us understand in a simplified way, considering this article that you’re reading right now. How you’re accessing it? The answer is pretty simple, as we discussed above, this article is being sent via cable or radio waves to your system in the form of small data packets from our web server right through the router and switches.
Now, right after this, once your system receives those small packets, the system will pass the same to your web browser, and at last, your web browser (chrome, edge, etc.) will reassemble all those small packets in a singular unit so that you can now view the display for what you’ve requested from the server i.e. this article.
However, there are other specifications too which involved in this process, they are:
- DNS Query: They act as a directory in the web browser. When you’re looking for any specific domain, let’s say www.geeksforgeeks.org So here, your browser doesn’t know this address, and for that, it will start looking out for validation and a request will be sent to the server. Once the identity is confirmed from the database, you’ll get to see the results on your system.
- Handshaking (TCP & TLS): When two systems connect via a router, the process of determining protocols, speed, compression, and error correction during that particular session is simply called handshaking between networking devices. In this, establishing a connection with that IP is what we call TCP handshaking whereas, it is also mandated to keep your system safe so that no attackers can read those data packets and for that, encryption is being created which is known as TLS handshake.
- HTTP (Request & Response): When you request any page from the browser, take an example of www.geeksforgeeks.org here, so when you send a request to read the article “ How does the Internet work?” then the server pushes the content to the form of CSS, HTML, and JavaScript and same will get distributed in small data packets. The moment your system receives those packets, your browser will start interpreting those packets, and the whole article will appear on your screen. (It might sound typical, but won’t take more than 3 seconds)
The bottom line is there are several technologies and architectures involved in making a stable and working internet connection right from the beginning. In case, you would like to read in-depth knowledge of these technologies, refer to these links:
Also Read
 How Does the Internet Work?
How Does the Internet Work?
Similar Reads
How Google Search Works!! The Google Search: It happens billions of times a day in the blink of an eye and we can have anything before us our minds can think of! Let's explore the art and science that makes it possible. Crawling & Indexing: The journey of a query starts before we ever type a search, with crawling and ind
2 min read
Internetworking Terms and Concepts The term Internetworking means interconnection i.e. interconnecting two or more computers. Inter means between and networking means the exchange of information or data among multiple connected devices. Internetworking means connecting two or more computer networks using devices like routers, gateway
3 min read
Web3.0: The Next Era of the Internet Web3.0, commonly known as Web3, is the next era of the Internet. It aims to address the limitations of the previous versions of the Web. From Web 1.0 to Web 2.0, we have been consuming information in a way that we have very little control over. However, Web3.0 claims that it will provide information
9 min read
Access Networks An access network is a type of network which physically connects an end system to the immediate router (also known as the “edge routerâ€) on a path from the end system to any other distant end system. Examples of access networks are ISP, home networks, enterprise networks, ADSL, mobile network, FTTH
5 min read
How Web 3.0 is Going to Impact the Digital World The internet: a familiar term that encompasses a whole universe in itself. Calling it probably the greatest human invention since sliced bread wouldn’t be wrong. This global network of billions of interconnected computers and other such devices is single-handedly responsible for impacting the everyd
7 min read
Network Layer Services The network layer is a part of the communication process in computer networks. Its main job is to move data packets between different networks. It helps route these packets from the sender to the receiver across multiple paths and networks. Network-to-network connections enable the Internet to funct
6 min read