In this article we will try to understand each and every aspect which may help us to understand about Staging in Git. To keep a track of modifications or changes in the file we have to bring that changes to our staging area which we bring by using Staging. Below command and this process of adding these changes or modifications in an area to keep a track of it are called staging. While Hunk means a piece of changes. For example, we have written 4 lines of text in a file and modified 4 lines of text in that file that is known as a hunk which you can consider as a piece of change.
Following command we may use to add all the modified data while working on git:
git add .
Staging Changes
Here we will edit our file a.txt and after using the git status command we can see it is showing something in the green part that means that the file is staged but it is not committed and the part which is coming in red is there are some changes made in the file which are not being staged for example we may write hello in the file and then used "git add ." command to put it in the staging area but after that if we write "bhailogs" in the file and then if we are not adding that change in the staging area by using the git add command then we will see that in the red color which means that there are some changes which need to be tracked or staged. Now we will use various methods to add changes in a file to the staging area. If we want to stage all changes we will use the git add -A command or git add. where represents the current directory.

Unstage a File
Now if you want a file to be unstaged that is we don't want that file to be in the staging area so what we can do is we can use the command git reset file_path to unstage a file. Now here we can see that we have added all the files in the staging area after applying the git status command we can see that all the files are in the staging area so now I want that b.txt should not be in the staging area so to remove b.txt from the staging area we have used the command git reset file_path but here we are in the path only so we don't need to mention the entire path in file path because b.txt exists in our current directory so we will write git reset file_name to remove b.txt from the staging area.

Add changes by hunk
Here we have used the git add -p command and here we can see that there are no changes to be staged after that, we have edited the file a.txt. After editing
the file we again used the command git add -p command which will open an interactive prompt that will ask the user whether we want to
Stage this hunk along with various parameters.
| Stages of Hunk | Action Performed |
|---|
| y | Stage this hunk for the next commit |
| n | do not stage this hunk for the next commit |
| q | quit; do not stage this hunk or any of the commits |
| a | stage this hunk and all later hunks in the file |
| d | do not stage this hunk or any of the later hunks in the file |
| e | manually edit the current hunk |
| ? | print hunk help |
which makes it easy to see changes that you want to stage or not.
 Showing interactive prompt by using git add -p
Showing interactive prompt by using git add -p Here I am entering y to add this hunk in the staging area
Here I am entering y to add this hunk in the staging areaInteractive add
git add -i is the command which provides us an interactive interface along with various commands in that interface. So now let's deep dive into this interactive add what is it and how its various commands provided in the interface works.
 Showing interface provided by git add -i command
Showing interface provided by git add -i commandHere we can see the top half of the command output gives us the current state of the index broken up into staged and unstaged columns.
- a.txt has 1 line added and 0 lines removed. It is currently staged as the current status reports nothing in the unstaged column.
- b.txt has 0 lines added and 0 lines removed and has been staged. There are no further changes since it has been staged as indicated by the "nothing" line under the unstaged column.
The bottom half shows what you can do. Either enter a number (1-8) or a letter (s,u,r,a,p,d,q,h).
status shows output identical to the top part of the output above.
 Using status command
Using status commandNow to understand the working of the update command what we have done is have made some changes to a.txt and in staging whenever we modify something in your file or any folder we have to add those changes in the staging area. But we have not added those changes to the staging area. So here we will use the update command to add this file to the staging area. As you can see here on using the git status command we can see that we have modified a.txt but we have not added those changes into the staging area.
 Using git status command to see the status of a.txt
Using git status command to see the status of a.txtNow let's see the update command
 Using update command
Using update commandAfter using the update command now if we see the status of our project using git status so we can see the file a.txt has been added into the staging area.
 Using the git status command to verify whether the changes are staged or not using the update command
Using the git status command to verify whether the changes are staged or not using the update commandrevert basically reverts back information to the head. So when you get into the interactive mode using it add -I command and press 3 over there you get in the revert command so what happens now is it shows you files and for which file you want the revert to revert information back to head you can type that index number and then press enter. So what will happen it will mention an asterisk on that index position. and if you press enter after that it puts the respective file in the untracked files.
 Using revert command
Using revert commandSo you can also check now

with the git status command that the file b.txt is now in the untracked files.
 Using git status command to verify that is b.txt is in the untracked files
Using git status command to verify that is b.txt is in the untracked filesadd untracked it allows you to add untracked files in the staging area.
 Using add untracked command
Using add untracked commandNow we can see that b.txt is added into the staging area.
 Using git status to see b.txt is in the staging area
Using git status to see b.txt is in the staging areapatch it allows for one path to be selected out of output similar to status for further analysis
But here there are no changes to be staged therefore here it will show us no changes.
 using patch command
using patch commanddiff displays what will be committed.
 using diff command
using diff commandquit exits the command
 using quit command
using quit commandhelp presents further help on using commands.
 using help command
using help commandStaged Changes : To display the hunks that are staged for commit
 Using git diff --cached
Using git diff --cachedStage a single file: Now if you want to stage a single file what you do is type in the command git add file_name it's that easy and you will see that the respective file is being added. Now what I have done is I have put my b.txt in the untracked files using the command git reset file_name here my file_name is b.txt and then I have used the command git add file_name to bring my b.txt in the staging area.
 Using git add to stage a file
Using git add to stage a filestage deleted files: To remove a file from git permanently use the -f flag in the command git rm -f file_name.
 Using git rm -f file_name to remove the file permanently
Using git rm -f file_name to remove the file permanentlyTo delete the file from git without removing it from disk, use the --cached flag
So to understand this what I have done is created a file r.txt then added it into the staging area and then removed it using the --cached flag from git so what happened is it was removed from the staging area but did not get deleted from the disk and is put by git into the untracked files so now if I want that file r.txt to be added what I will do is use git add r.txt to add that file again into the staging area.
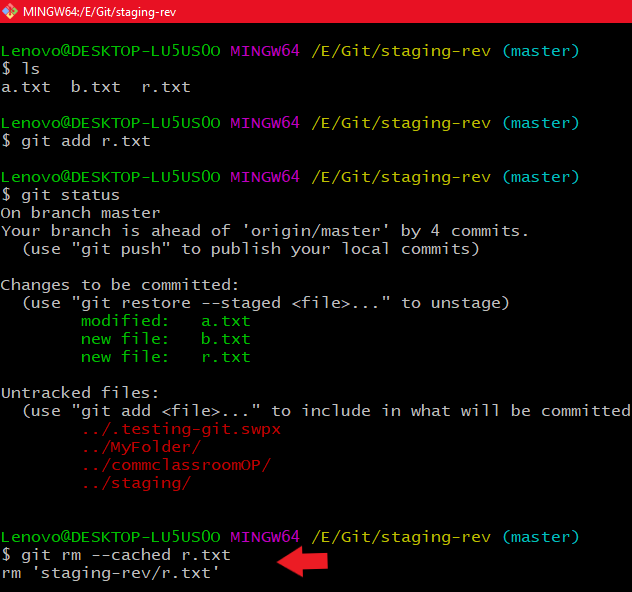 Using git rm --cached file_name
Using git rm --cached file_name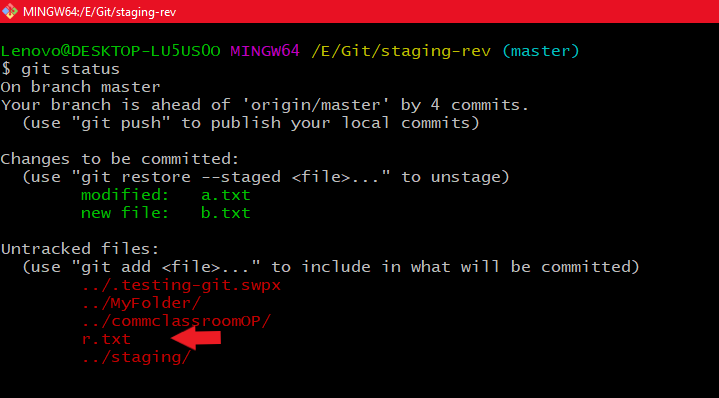 Using git status command to see whether r.txt is in untracked files or not
Using git status command to see whether r.txt is in untracked files or not Using git add command to add r.txt file to the staging area
Using git add command to add r.txt file to the staging area
Similar Reads
Frontend Developer Interview Questions and Answers Frontend development is an important part of web applications, and it is used to build dynamic and user-friendly web applications with an interactive user interface (UI). Many companies are hiring skilled Frontend developers with expertise in HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and modern frameworks and librarie
15+ min read
Git Tutorial Git is an essential tool for developers, enabling them to manage and track project changes. Whether you're working on a solo project or collaborating with a team, Git keeps everything organized and under control. This Git Tutorial, from beginner to advanced, will give you a complete understanding of
12 min read
Git Cheat Sheet Git Cheat Sheet is a comprehensive quick guide for learning Git concepts, from very basic to advanced levels. By this Git Cheat Sheet, our aim is to provide a handy reference tool for both beginners and experienced developers/DevOps engineers. This Git Cheat Sheet not only makes it easier for newcom
10 min read
Git Rebase Git Rebase is a command that moves or combines a sequence of commits to a new base commit. It helps you place your changes on top of another commit, resulting in a cleaner, linear history, especially useful when working with feature branches. Unlike git merge, which creates a merge commit to combine
10 min read
Version Control Systems Version Control Systems (VCS) are essential tools used in software development and collaborative projects to track and manage changes to code, documents, and other files. Whether you're working alone or as part of a team, version control helps ensure that your work is safe, organized, and easy to co
7 min read
Git Bash Git bash is a command-line tool that is used as Git CLI emulation for Microsoft Windows. It provides a terminal-like interface and enables users to run Git commands and interact with a repository, as well as offering Unix command line features. Essentially, Git Bash brings the powerful functionaliti
9 min read
How to Create a New Branch in Git? Git is a powerful and widely used version control system that helps developers manage code changes across projects efficiently. One of the fundamental features of Git is branching, which allows developers to diverge from the main line of development and work on different tasks or features independen
4 min read
50+ Essential Git Commands for Beginners and Developers Git is a powerful version control system that helps developers track changes, collaborate seamlessly, and manage codebases efficiently. Whether you're working on a solo project or collaborating with a team, Git ensures your work is safe, versioned, and organized. So we’ll explore 50+ essential Git c
7 min read
How to Set Git Username and Password in GitBash? Setting up your Git username and password is an essential step when working with Git repositories. It helps you confirm your identity when sending (pushing) changes or getting (pulling) updates from a remote repository. In this guide, we will show you how to easily set your Git username and password
3 min read
How To Get Changes From Master Into a Branch in Git? In Git, branches are essential for organizing and managing development work. Whether you are working on a feature, a bug fix, or any other task, you often work in a separate branch so that the changes don’t directly affect the master or main branch (the primary production branch).There are two main
3 min read