Predicting missing links in a graph
Link prediction, also known as graph completion, is a common problem when dealing with graphs. More precisely, from a partially observed graph—that is a graph for which only a portion of the existing edges are known—we want to predict whether or not an edge exists between any given node pairs, as seen in Figure 6.1. Formally, let  be a graph where
be a graph where  is its set of nodes and
is its set of nodes and  is its set of edges. The set of edges
is its set of edges. The set of edges  are known as observed links, while the set of edges
are known as observed links, while the set of edges  are known as unknown links. The goal of the link prediction problem is to exploit the information of
are known as unknown links. The goal of the link prediction problem is to exploit the information of  and
and  to estimate
to estimate  . The partially observed graph can be seen here:
. The partially observed graph can be seen here:
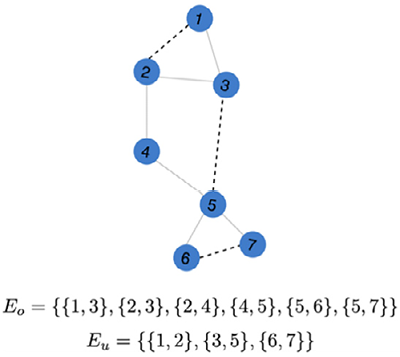
Figure 6.1: Partially observed graph with observed link  (solid lines) and unknown link
(solid lines) and unknown link  (dashed lines)
(dashed lines)
The link prediction problem is widely used in different domains, such as a recommender system, in order to propose friendships in social networks or items to purchase on e-commerce websites. It...