Introduction to Bioinformatics
- 1. 1
- 2. Prepared by: Asad Khan B-01 6th Semester BS Botany 2
- 3. 1. Introduction to bioinformatics. 2. Why bioinformatics is necessary? 3. Goals of bioinformatics 4. Field of bioinformatics 5. Where bioinformatics help? 6. Applications of bioinformatics 7. Software and tools of bioinformatics 8. References 3
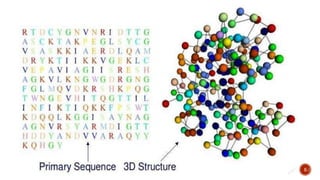
- 4. Bioinformatics is the application of Information technology to store, organize and analyze the vast amount of biological data. The stored data is available in the form of sequences and structures of proteins and nucleic acids (the information carrier). The biological information of nucleic acids is available as sequences while the data of proteins is available as sequences and structures Sequences are represented in single dimension where as the structure contains the three dimensional data of sequences. 4
- 5. 5
- 6. Bioinformatics is a field in which biology, mathematics, statistics, CS and IT are merged into a single discipline to process biological data. Complex machines are used to read in biological data at a much faster rate than before. The term “Bioinformatics” was invented by Paulien Hogeweg and Ben Hesper in 1970 6
- 7. 7
- 8. The need for bioinformatics has arisen from the recent explosion of publicly available genomic information, such as resulting from the Human Genome Project. Gain a better understanding of gene analysis, taxonomy, & evolution. To work efficiently on the rational drug designs and reduce the time taken for the development of drug manually. 8
- 9. To uncover the wealth of Biological information hidden in the mass of sequence, structure, literature and biological data. It is being used now and in the foreseeable future in the areas of molecular medicine. It has environmental benefits in identifying waste and clean up bacteria. In agriculture, it can be used to produce high yield, low maintenance crops. 9
- 10. Molecular Medicine Gene Therapy Drug Development Microbial genome applications Crop Improvement Forensic Analysis of Microbes Biotechnology Evolutionary Studies Bio-Weapon Creation 10
- 11. In Experimental Molecular Biology In Genetics and Genomics In generating Biological Data Analysis of gene and protein expression Comparison of genomic data In Simulation & Modeling of DNA, RNA & Protein 11
- 12. 1. Prediction of Protein Structure:- It is easy to determine the primary structure of proteins in the form of amino acids which are present on the DNA molecule but it is difficult to determine the secondary, tertiary or quaternary structures of proteins. Tools of bioinformatics can be used to determine the complex protein structures. 12
- 13. 2. Genome Annotation:- In genome annotation, genomes are marked to know the regulatory sequences and protein coding. It is a very important part of the human genome project as it determines the regulatory sequences. 13
- 14. 3. Comparative Genomics:- Comparative genomics is the branch of bioinformatics which determines the genomic structure and function relation between different biological species. For this purpose, intergenomic maps are constructed which enable the scientists to trace the processes of evolution that occur in genomes of different species. 14
- 15. 4. Health and Drug discovery:- The tools of bioinformatics are also helpful in drug discovery, diagnosis and disease management. Complete sequencing of human genes has enabled the scientists to make medicines and drugs which can target more than 500 genes. 15
- 16. 5. Preventative medicine; Gene identification by sequence inspection and prediction of splice sites allows mutations to be corrected easily. This is much used in the analysis of mutations that cause cancer. 16
- 17. 6. Gene therapy; mutations are easily detected and quantified through next-generation sequencing technology in a heterogeneous sample thus a cost effective precision medicine, “right drug at right dose to the right patient at the right time”can be administered. 17
- 18. Waste cleanup Microbial genome applications Antibiotic resistance Alternative energy sources Crop improvement and development of resistant varieties Forensic analysis Bio-weapon creation Insect resistance Sequence analysis Literature analysis 18
- 19. Blast Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. It is an algorithm for comparing biological sequences information, such as amino acid sequence of different proteins or the nucleotides of DNA sequences. BLAST is used to identify library sequences that resembles the query sequences. 19
- 20. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bioinformatics https://www.slideshare.net/moab005/basics-of-bioinformatics https://www.slideshare.net/nadeemakhter7374/bioinformatics-simple https://www.slideshare.net/hopejuli/application-of-bioinformatics-in-different- fields-of-sciences 20
- 21. THE END 21
- 22. THANKS 22