Database-management-system-dbms-ppt.pptx
- 2. Content What is Database Management System? Brief History Why Use a DBMS? Purpose of DBMS Data models Architecture of DBMS levels or layers of DBMS architecture Components of DBMS Advantage of DBMS Disadvantage of DBMS DBMS Languages References
- 3. What is Database Management System? A Database Management System (DBMS), or simply a Database System (DBS) consist of : A collection of interrelated and persistent data (usually referred to as the database (DB)). A set of application programs used to access, update and manage that data (which form the data management system (MS)).
- 4. Brief History Early 1960s: first general purpose database by Charles Bachman from GE. Used the network data model. Late 1960s: IBM developed Information Management System (IMS). Used the hierarchical data model. Led to SABRE, the airline reservation system developed by AA and IBM. Still in use today. 1970: Edgar Code of IBM developed the relational data model. Led to several DBMS based on relational model, as well as important theoretical results. Code wins Turing award. 1980s: relational model dominant. SQL standard. Late 1980s, 1990s: DBMS vendors extend systems, allowing more complex data types (images, text).
- 5. Why Use a DBMS? Data independence and efficient access. Reduced application development time. Data integrity and security. Uniform data administration. Concurrent access, recovery from crashes.
- 6. Purpose of DBMS 1. Data redundancy and inconsistency Same information may be duplicated in several places. All copies may not be updated properly. 2. Difficulty in new program to carry out each new task 3. Data isolation — Data in different formats. Difficult to write new application programs. files and formats
- 7. Purpose of DBMS … Security problems Every user of the system should be able to access only the data they are permitted to see. E.g. payroll people only handle employee records, and cannot see customer accounts; tellers only access account data and cannot see payroll data. Difficult to enforce this with application programs. Integrity problems Data may be required to satisfy constraints. E.g. no account balance below $25.00. Again, difficult to enforce or to change constraints with the file-processing approach.
- 8. Data models Hierarchical Model The hierarchical data model organizes data in a tree structure. There is a hierarchy of parent and child data segments. This structure implies that a record can have repeating information, generally in the child data segments. Hierarchical DBMSs were popular from the late 1960s, with the introduction of IBM's Information Management System (IMS) DBMS, through the 1970s.
- 9. Network Model The popularity of the network data model coincided with the popularity of the hierarchical data model. Some data were more naturally modeled with more than one parent per child. So, the network model permitted the modeling of many-to- many relationships in data. In 1971, the Conference on Data Systems Languages (CODASYL) formally defined the network model.
- 10. Relational Model (RDBMS - relational database management system) A database based on the relational model developed by E.F. Code. A relational database allows the definition of data structures, storage and retrieval operations and integrity constraints. In such a database the data and relations between them are organized in tables. A table is a collection of records and each record in a table contains the same fields.
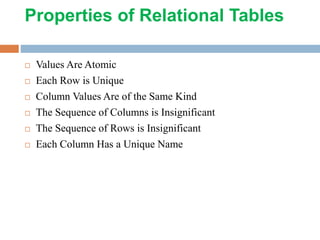
- 11. Properties of Relational Tables Values Are Atomic Each Row is Unique Column Values Are of the Same Kind The Sequence of Columns is Insignificant The Sequence of Rows is Insignificant Each Column Has a Unique Name
- 12. Object-Oriented Model Object DBMSs add database functionality to object programming languages. They bring much more than persistent storage of programming language objects. A major benefit of this approach is the unification of the application and database development into a seamless data model and language environment.
- 13. Semi structured Model In semi structured data model, the information that is normally associated with a schema is contained within the data, which is sometimes called ``self-describing''. In such database there is no clear separation between the data and the schema, and the degree to which it is structured depends on the application.
- 14. Architecture of DBMS An early proposal for a standard terminology and general architecture database a system was produced in 1971 by the DBTG (Data Base Task Group) appointed by the Conference on data Systems and Languages. The DBTG recognized the need for a two level approach with a system view called the schema and user view called subschema. The American National Standard Institute terminology and architecture in 1975.ANSI-SPARC recognized the need for a three level approach with a system catalog. There are following three levels or layers of DBMS architecture: 1. External Level 2. Conceptual Level 3. Internal Level
- 16. levels or layers of DBMS architecture External Level: - External Level is described by a schema i.e. it consists of definition of logical records and relationship in the external view. Conceptual Level: - Conceptual Level represents the entire database. Conceptual schema describes the records and relationship included in the Conceptual view. . Internal Level: - Internal level indicates hoe the data will be stored and described the data structures and access method to be used by the database.
- 17. Components of DBMS 1. Hardware: Can range from a PC to a network of computers. 2. Software: DBMS, operating system, network software (if necessary) and also the application programs. 3. Data: Used by the organization and a description of this data called the schema. 4. People: Includes database designers, DBAs, application programmers, and end-users. 5. Procedure: Instructions and rules that should be applied to the design and use of the database and DBMS.
- 18. Advantage of DBMS Controlling Redundancy Sharing of Data Data Consistency Integration of Data Integration Constraints Data Security Report Writers
- 19. Advantage of DBMS… Control Over Concurrency Backup and Recovery Procedures Data Independence
- 20. Disadvantage of DBMS Cost of Hardware and Software Cost of Data Conversion Cost of Staff Training Appointing Technical Staff Database Damage
- 21. DBMS Languages Data Definition Language-DDL Data Definition Language (DDL) statements are used to define the database structure or schema. Some examples: CREATE - to create objects in the database ALTER - alters the structure of the database DROP - delete objects from the database TRUNCATE - remove all records from a table, including all spaces allocated for the records are removed COMMENT - add comments to the data dictionary RENAME - rename an object
- 22. Data Manipulation Language (DML) Data Manipulation Language (DML) statements are used for managing data within schema objects. Some examples: SELECT - Retrieve data from the a database INSERT - Insert data into a table UPDATE - Updates existing data within a table DELETE - deletes all records from a table, the space for the records remain MERGE - UPSERT operation (insert or update) CALL - Call a PL/SQL or Java subprogram EXPLAIN PLAN - explain access path to data LOCK TABLE - control concurrency