Workshop unit test
- 1. Unit Test THE WAY OF THE FORCE Francesco Garavaglia 01/2016
- 2. Why Unit Test Terminology / definition TDD Test in practice AGENDA 2
- 3. 3 Why Why 3
- 4. Why should we TEST? Why should we test at all? REMEMBER Testing is just one step in QA 4
- 5. “I don’t have time to write tests because I am too busy debugging.” 5
- 6. Why have unit tests? Why have unit tests? Find bugs early / fast feedback Increase QA Why not to have unit tests Increases development time? CostOfWritingUnitTests < Sum(BugFixing) 6
- 7. Unit Test You will Do, Powerful you will be
- 9. The Concept of Unit Testing A unit test is code written by a developer that tests as small a piece of functionality (the unit) as possible. One function may have multiple unit tests according to the usage and outputs of the function. Tests ensure The code meets expectations and specifications: Does what it says it should do. The code continues to meet expectations over time: Avoiding regression. 9
- 10. 10 Unit testing is a method by which individual units of source code are tested to determine if they are fit for use. One can view a unit as the smallest testable part of an application. Unit tests are created by programmers or occasionally by white box testers during the development process. Unit?
- 11. A Silver Bullet Unit Test is not
- 13. Test Driven Design It’s NOT testing, but using tests to DRIVE the design As a side-effect, you got unit tests! With good level of coverage! 13TDD: Test Driven Design
- 14. 14 RED GREEN REFACTOR Write a failing test. With empty class/method. Fill in the class/method implementation. Make the tests pass. Make code better.
- 15. Unit Testing Tools Production Code Unit Test Code Test Runner 15
- 16. Types of Software Testing UnitTesting (do the parts perform correctly alone?) IntegrationTesting (do the parts perform correctly together?) User Acceptance Testing (does the system meet the end user’s expectations?) 16
- 17. Unit Testing vs. Integration Testing Busines s Entity Data Layer Data Access Layer User Interfa ce Unit Testing tests one layer Integration Testing tests across layers. 17
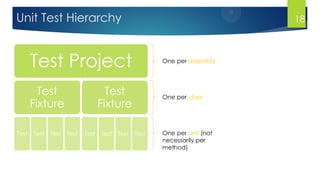
- 18. Unit Test Hierarchy Test Project Test Fixture Test Test Test Test Test Fixture Test Test Test Test One per assembly One per class One per unit (not necessarily per method) 18
- 20. What does a unit test look like? Using NUnit.Framework; [TestFixture] public class CarTests { [Test] public voidTest_Car_Paint () { // Arrange Color paint = Color.Red; Car car = new Car(); // Act car.paint(Color.Red); // Assert Assert.AreEqual(car.Color, paint); } … } 20
- 21. Structure of A Unit Test Setup Prepare an input Call a method Check an output Tear down 21
- 22. Test Assertions Assertions are the ‘checks’ that you may perform to determine if a test passes or fails. For instance: Assert.IsTrue() Assert.IsInstance() Assert.AreEqual() Generally speaking, you want ONE assertion per test. 22
- 23. Unit Testing with Mocks Busines s Entity Data Layer Data Access Layer Unit Testing tests one layer A Mock allows a dependency to be imitated so the Unit test can be isolated. 23
- 24. Executing Tests Manually: 1. Compile Test project (to .dll or .exe) 2. Open in Test runner. 3. Select and execute tests. Automatically: 1. Build server compiles and runs tests as part of nightly build operation. 2. Any test failures = entire build fails. 24
- 25. The right way you know now
- 27. Unit Test Best Practices 1. Consistent 2. Atomic 3. Single Responsibility 4. Self-descriptive 5. No conditional logic or loops 6. No exception handling 7. Informative Assertion messages 8. No test logic in production code 9. Separation per business module 10. Separation per type 27
- 28. Consistent Multiple runs of the test should consistently return true or consistently return false, provided no changes were made on code Code that can cause problems: Dim currentDate as Date = Now() Dim value as Integer = New Random().Next 28
- 29. Atomic Only two possible results: PASS or FAIL No partially successful tests. Isolation of tests: Different execution order must yield same results. Test B should not depend on outcome of Test A Use Mocks instead. 29
- 30. Single Responsibility One test should be responsible for one scenario only. Test behavior, not methods: One method, multiple behaviors Multiple tests One behavior, multiple methods One test 30
- 31. Single Responsibility Sub TestMethod() Assert.IsTrue(behavior1) Assert.IsTrue(behavior2) Assert.IsTrue(behavior3) End Sub Sub TestMethodCheckBehavior1() Assert.IsTrue(behavior1) End Sub Sub TestMethodCheckBehavior2() Assert.IsTrue(behavior2) End Sub Sub TestMethodCheckBehavior3() Assert.IsTrue(behavior3) End Sub 31
- 32. Self Descriptive Unit test must be easy to read and understand Variable Names Method Names Class Names No conditional logic No loops Name tests to represent PASS conditions: Public Sub CanMakeReservation() Public Sub TotalBillEqualsSumOfMenuItemPrices() Self descriptive 32
- 33. No conditional logic or loops Test should have no uncertainty: All inputs should be known Method behavior should be predictable Expected output should be strictly defined Split in to two tests rather than using “If” or “Case” Tests should not contain “While”, “Do While” or “For” loops. If test logic has to be repeated, it probably means the test is too complicated. Call method multiple times rather than looping inside of method. 33
- 34. No conditional logic or loops Sub TestBeforeOrAfter() If before Then Assert.IsTrue(behavior1) ElseIf after Then Assert.IsTrue(behavior2) Else Assert.IsTrue(behavior3) End If End Sub Sub TestBefore() Dim before as Boolean = true Assert.IsTrue(behavior1) End Sub Sub TestAfter() Dim after as Boolean = true Assert.IsTrue(behavior2) End Sub Sub TestNow() Dim before as Boolean = false Dim after as Boolean = false Assert.IsTrue(behavior3) End Sub 34
- 35. No Exception Handling Indicate expected exception with attribute. Catch only the expected type of exception. Fail test if expected exception is not caught. Let other exceptions go uncaught. 35
- 36. No Exception Handling <ExpectedException(“MyException”)> _ Sub TestException() myMethod(parameter) Assert.Fail(“MyException expected.”) End Sub 36
- 37. Informative Assertion Messages By reading the assertion message, one should know why the test failed and what to do. Include business logic information in the assertion message (such as input values, etc.) Good assertion messages: Improve documentation of the code, Inform developers about the problem if the test fails. 37
- 38. No test logic in Production Code Separate Unit tests and Production code in separate projects. Do not create Methods or Properties used only by unit tests. Use Dependency Injection or Mocks to isolate Production code. 38
- 39. Separation per Business Module Create separate test project for every layer or assembly Decrease execution time of test suites by splitting in to smaller suites Suite 1 - All Factories Suite II - All Controllers Smaller Suites can be executed more frequently 39
- 40. Separation per Type Align Test Fixtures with type definitions. Reminder: Unit tests are separate from integration tests! Different purpose Different frequency Different time of execution Different action in case of failure 40
- 41. Use the tests



















![What does a unit test look like?
Using NUnit.Framework;
[TestFixture]
public class CarTests
{
[Test]
public voidTest_Car_Paint ()
{
// Arrange
Color paint = Color.Red;
Car car = new Car();
// Act
car.paint(Color.Red);
// Assert
Assert.AreEqual(car.Color, paint);
}
…
}
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/workshop-unittest-160115224044/85/Workshop-unit-test-20-320.jpg)





















