Speed control of DC motor using pulse width modulation technique
- 1. Mini Project SPEED CONTROL OF D.C MOTOR USING PULSE WIDTH MODULATION
- 2. GUIDED BY: Mrs Mariam jabali laskar PRESENTED BY : SHOAIB NAFI ( IMANUL HAQUE MAZARBHUIYA( 31360087
- 3. ABSTRACT In this circuit, the DC motor is operated by a 555 integrated circuit. The IC 555 in this circuit is being operated in Astable mode. In this mode, the circuit can be used as a pulse width modulator with a few small adjustments to the circuit. The frequency of operation of the circuit is provided by the passive parameters of resistances and capacitances attached to it. The resistance between pin-7 and pin- 8, the resistance between pin-6 and pin-7 and the capacitance between pin-2 and the ground govern the frequency of operation and duty cycle of the IC 555 in Astable mode. The duty cycle is governed by the resistor which is in between pin-6 and pin-7 of the IC 555 timer. So, by taking advantage of the circuits working, we can change the 555 Astable multivibrator into a pulse width modulator by using a variable resistor instead of a constant resistor in between pin-6 and pin-7.
- 4. One of the best things about this circuit is that we can make it work as an astable multivibrator with little hardware and by little cost which can save both the cost involved in making it as well as the space on the printed circuit board is saved. if we want a sophisticated pulse width modulator which works more accurately and which can have more adjusting capabilities, then it is better to use a microcontroller based pulse width modulator than the one which we are using now. However, the circuit or the application for which we are using a pulse width modulator is not so sensitive and hence does not demand so much of accuracy. In such a case, the circuit which we are using with a bare IC 555 is better as it saves our monetary as well as space resources in building the circuit. The duty cycle of the circuit can be changed by changing the resistance between pin-7 and pin-6. If we increase the duty cycle, the speed of the motor increases and if we decrease the duty cycle, the speed of the motor decreases.
- 6. 1.1 GOAL “To explain PULSE WIDTH MODULATION technique in brief.” Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Basics There are many forms of modulation used for communicating information. When a high frequency signal has amplitude varied in response to a lower frequency signal we have AM (amplitude modulation). When the signal frequency is varied in response to the modulating signal we have FM (frequency modulation. These signals are used for radio modulation because the high frequency carrier signal is needs for efficient radiation of the signal. When communication by pulses was introduced, the amplitude, frequency and pulse width become possible modulation options. In many power electronic converters where the output voltage can be one of two values the only option is modulation of average conduction time. Fig. 1.1 sine wave modulated pulses
- 7. 1. Linear Modulation The simplest modulation to interpret is where the average ON time of the pulses varies proportionally with the modulating signal. The advantage of linear processing for this application lies in the ease of de-modulation. The modulating signal can be recovered from the PWM by low pass filtering. For a single low frequency sine wave as modulating signal modulating the width of a fixed frequency (fs) pulse train the spectra is as shown in Fig 1.2. Clearly a low pass filter can extract the modulating component fm. Fig. 1.2 Spectra of PWM
- 8. 2. Sawtooth PWM The simplest analog form of generating fixed frequency PWM is by comparison with a linear slope waveform such as a saw tooth. As seen in Fig 1.2 the output signal goes high when the sine wave is higher than the saw tooth. This is implemented using a comparator whose output voltage goes to logic HIGH when ne input is greater than the other. Other signals with straight edges can be used for modulation a rising ramp carrier will generate PWM with Trailing Edge Modulation. Fig. 1.3 Sine Sawtooth PWM
- 9. It is easier to have an integrator with a reset to generate the ramp in Fig1.4 but the modulation is inferior to double edge modulation. Fig. 1.4 Trailing Edge Modulation
- 10. 3. Regular Sampled PWM The scheme illustrated above generates a switching edge at the instant of crossing of the sine wave and the triangle. This is an easy scheme to implement using analog electronics but suffers the imprecision and drift of all analog computation as well as having difficulties of generating multiple edges when the signal has even a small added noise. Many modulators are now implemented digitally but there is difficulty is computing the precise intercept of the modulating wave and the carrier. Regular sampled PWM makes the width of the pulse proportional to the value of the modulating signal at the beginning of the carrier period. In Fig 1.5 the intercept of the sample values with the triangle determine the edges of the Pulses. For a saw tooth wave of frequency fs the samples are at 2fs. Fig. 1.5 Regular Sampled PWM
- 11. There are many ways to generate a Pulse Width Modulated signal other than fixed frequency sine sawtooth. For three phase systems the modulation of a Voltage Source Inverter can generate a PWM signal for each phase leg by comparison of the desired output voltage waveform for each phase with the same sawtooth. One alternative which is easier to implement in a computer and gives a larger modulation depth is using space vector modulation. 4. Modulation Depth Fig. 1.6 Saturated Pulse Width Modulation
- 12. For a single phase inverter modulated by a sine-sawtooth comparison, if we compare a sine wave of magnitude from -2 to +2 with a triangle from -1 to +1 the linear relation between the input signal and the average output signal will be lost. Once the sine wave reaches the peak of the transgle the pulses will be of maximum width and the modulation will then saturate. The Modulation depth is the ratio of the current signal to the case when saturation is just starting. Thus sine wave of peak 1.2 compared with a triangle with peak 2.0 will have a modulation depth of m=0.6.
- 13. 2. THEORY
- 14. 2.1 COMPONENTS USED IN MINI PROJECT “SPEED CONTROL OF D.C. MOTOR USING PWM METHOD” •BATTERY •CAPACITOR •VARIABLE REGULATOR • IC 555 TIMER •RESISTOR •MOTOR •AMPLIFIER TRANSISTOR
- 16. .DC Motor is a Machine which converts Electrical energy into Mechanical energy. .It takes Electrical energy as input and produces Mechanical rotations of the MOTOR shaft. .DC Motors are widely used in many industrial applications and in day to day life.
- 17. ADVANTAGES There various advantages are: PWM technique enables greater efficiency of DC Motor. PWM technique improves speed control and reduces power loss. Internal Motor resistance can be easily overcome. The pulses reach full supply voltage which in turn produces more Torque. DISADVANTAGES Increased Complexity. Speed obtained is less than the specified speed due to losses. Speed remains limited.
- 18. INTRODUCTION TO IC 555 TIMER Introduced by Signetics in 1972, most popular is NE555 by STM electronics and Fairchild Semiconductor. • The 555 timer IC is an integrated circuit (chip) used in a variety of timer, pulse generation, and oscillator applications. • The 555 is used to provide time delays, as an oscillator, and as a flip- flop element. • It gets its name from the three 5k ohm resistors which give the two comparators reference voltage. • Depending on the manufacturer, the standard 555 package includes 25 transistors, 2 diodes and 15 resistors on a silicon chip installed in an 8-PIN DIP (Dual in-line) package. • It is available in low power CMOS type ICM7555 package and 556 Dual Timer (14 pin) with two timer in one IC and 558 which is Quad timer.
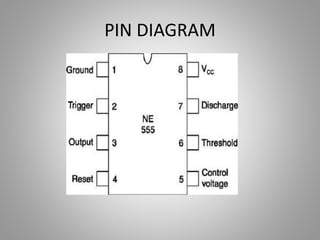
- 19. PIN DESCRIPTION PIN 1- Ground, The ground pin connects the555 timer to the negative (0v) supply rail. PIN 2-Trigger, when < 1/3 Vcc (active low)this makes the output high (+Vcc). It monitors the discharging of the timingcapacitor in an astable circuit. PIN 3-Output, The output pin can drive any TTL circuit and is capable of sourcing or sinking up to 200mA of current at an output voltage equal to approximately Vcc - 1.5V so small speakers, LEDs or motors can be connected directly to the output. PIN 4-Reset, when less than about 0.7V (active low) this makes the output low (0V), overriding other inputs. When not required it should be connected to +Vcc.
- 20. PIN 5-Control Voltage, this can be used to adjust the threshold voltage which is set internally to be 2/3 Vcc. Usually this function isnot required and the control input is connected to 0V with a 10nF capacitor to eliminate electrical noise. PIN 6-Threshold, when > 2/3 Vcc (active high)this makes the output low (0V)*. It monitors the charging of the timing capacitor in astable and monostable circuits. PIN 7-Discharge, The discharge pin is connected directly to the Collector of an internal NPN transistor which is used to "discharge" the timing capacitor to ground when the output at pin 3 switches "LOW".PIN 8- Supply +Vcc, This is the power supply pin and for general purpose TTL 555 timers is between 4.5V and 15V (18V Absolute Maximum).
- 21. PIN DIAGRAM
- 22. 3.CIRCUIT DESIGN .1 “Circuit design of speed control of D.C motor”
- 23. • 4.2 GOAL • “To explain working of the PWM circuit.” •4.3 BASIC BLOCK DIAGRAM As shown in block diagram there are mainly three blocks: Astable Multivibrator, Monostable Multivibrator and Driving Circuit. Fig. 4.1 Block Diagram
- 24. The Basic Blocks are explained below: • Astable Multivibrator: This block produce square pulses of same frequency according to time constant RC. These pulses are fed to next block as triggering pulses. • Monostable Multivibrator: This block produces square pulses of variable frequencies. The frequency of output pulse can be varied by changing the value of resistor shown in figure. These pulses are fed to the driving circuit. Driving Circuit: This block provides power required to drive the motor. As the frequency of output pulses of Monostable multivibrator changes, the average voltage supplied to motor changes. Hence, the speed of motor changes
- 25. 5. CONCLUSION
- 26. •5.1 GOAL “To conclude the work carried out.” •5.2 CONCLUSION •From the project work, following points can be concluded. •It fulfils all the requirements for its application. •The motor responds to the average value of the pulses and not to the individual pulses as the chopper works at high frequency. •Changing the duty-cycle of the pulse by changing the speed of regulator changes the average voltage level. •It is possible to improve overall performance of the motor speed.
- 27. THANK YOU