XMLDB Building Blocks And Best Practices - Oracle Open World 2008 - Marco Gralike
- 1. ORACLE XMLDB Building Blocks and Best Practices Marco Gralike – AMIS – OOW 2008
- 2. Who Am I Started as DBA with Oracle 7 on Windows NT 3.1 (1994) Experienced with Oracle 7.x / 8.x / 9.x / 10.x and 11.1 Started with Oracle XMLDB in 2003 (Oracle 10.1.3) Oracle 11g Beta tester for Oracle XMLDB Dedicated XMLDB Blog (blog.gralike.com) Active Oracle OTN XMLDB Forum Member Oracle ACE Award for XMLDB Community Contributions
- 3. Disclaimer Pay attention to: “ Choice” “ Design” The following are “ Rules of Numb ” Every environment has its own unique criteria and needs… “ Testing” “ Performance” “ Maintainability” “ Extendibility”
- 4. Overview THE PROBLEM WITH XML… WORST PRACTICES ? A small Tom Kyte Intermezzo to some issues DESIGN XML SCHEMATA STORAGE STRUCTURES CLOB Storage XMLIndex Partitioning Object Relational Storage Binary XML Storage
- 5. THE PROBLEM WITH XML…
- 6. Let’s presume it is Relational
- 8. Query Optimizer - Access Paths
- 9. Structured Data Unstructured (XML) Data
- 10. How to Containerize a Tree? Keeping it intact? To much empty space…! Access Optimization..? Shredding it? Rebuilding and shredding off the tree structure…? There is no solution for this…yet…
- 11. Impedance Mismatch Different data models. E.g. XPath models an XML document as a tree, while most general purpose programming languages have no native data types for a tree. Different programming paradigms. XSLT is a functional language, while Java is object-oriented , and Perl is a procedural one. Source: Wikipedia SXML
- 12. Issues in General NO PROBLEM Data Shipping / Transport XML via XML UI’s that “Understand”, are based on XML PROBLEM Accessing Data in XML structures CPU Intensive Memory Intensive ORA-04030, XML Fragments, DOM Transformation: XML Relational Risk : Data / Information Loss
- 13. So the issues you will encounter with XML The nature of XML: It is (most of the time) not Structured It can not be stored in a Universal XML “Container” It can not be accessed via a standard Access Path Method that “understands” the free format XML structure all the time… It is all about free format OK and Not OK Standards: W3C, Oasis, etc Performance problem induced by its Nature… Nature is not structured…(as is Human Nature)
- 14. WORST PRACTICES ? ( A small Tom Kyte Intermezzo)
- 15. No Data Optimization and its Results…
- 16. Relational Fundamentals What goes IN, must come OUT (IN=OUT) Regarding Data Integrity, Meaning and Context Why do we DESIGN in the First Place? ACID: Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability Edgar F Codd’s 12 Rules defining a “Relational Database” Database Normalization (3NF) Nullology Imperfections of the (Procedural / Query) Language Maintainability , Performance , Usability Decades of Innovation, Methods and Standards
- 17. Storing XML in Oracle XML Database File Storage XML Database Native XML Enabled Oracle XMLDB A World within a World More then one Option Complies to Standards Still License Free Core part of (OXJR)DBMS The (Relational) foundation is there and can be used for solving XML imperfections
- 18. Mr. Thomas Kyte A Notorious Presentation from 2006 “ Worst Practices For Developers and DBAs Alike”
- 19. Probably You Do Not Need to Actually Design Anything
- 20. Quickly Answer: How many tables do you really need? FOUR at most! OBJECT *object_id name owner created … ATTRIBUTES *attribute_id attribute_name attribute_type … OBJ_ATTR_VALUES *object_id *attribute_id attribute_name attribute_type … LINKS *object_id1 *object_id2 …
- 21. Quickly Answer: How many tables do you really need? But of course ONE is best! And you are industry standard as well! Create table Object ( object_id number primary key, data xmltype );
- 22. Mr. Tom Kyte Has a Point Though… Logical Design? Physical Design?
- 23. Hidden Design Opportunities Here is your Design ! Create table Object ( data xmltype );
- 24. CREATE TABLE "MARCO".“OBJECT" OF "SYS"."XMLTYPE" XMLSCHEMA " http://www.myserver.com/myapp/1.0/xsd/object.xsd " ELEMENT “ROOT" ID 4733 PCTFREE 10 PCTUSED 40 INITRANS 1 MAXTRANS 255 NOCOMPRESS LOGGING STORAGE(INITIAL 65536 NEXT 1048576 MINEXTENTS 1 MAXEXTENTS 2147483645 PCTINCREASE 0 FREELISTS 1 FREELIST GROUPS 1 BUFFER_POOL DEFAULT) TABLESPACE "USERS“ VARRAY "XMLEXTRA"."NAMESPACES" STORE AS BASICFILE LOB "NAMESPACES660_L" (ENABLE STORAGE IN ROW CHUNK 8192 PCTVERSION 10 CACHE STORAGE(INITIAL 65536 NEXT 1048576 MINEXTENTS 1 MAXEXTENTS 2147483645 PCTINCREASE 0 FREELISTS 1 FREELIST GROUPS 1 BUFFER_POOL DEFAULT)) VARRAY "XMLEXTRA"."EXTRADATA" STORE AS BASICFILE LOB "EXTRADATA659_L" (ENABLE STORAGE IN ROW CHUNK 8192 PCTVERSION 10 CACHE STORAGE(INITIAL 65536 NEXT 1048576 MINEXTENTS 1 MAXEXTENTS 2147483645 PCTINCREASE 0 FREELISTS 1 FREELIST GROUPS 1 BUFFER_POOL DEFAULT)) “ Hidden” Oracle Design Features XML Schema: your container for Logical and Physical Design Physical Design
- 25. XML SCHEMATA
- 26. What should you take into account? Logical Design XML Instance / Document XML Schema ( XDB Annotations ), XML Evolution, Validation Physical Design Oracle Database / Storage Design based on XML Logical Design Binary Storage (Encrypted, Compressed, Validation, Evolution?) Indexes ( BTree , IOT, XMLIndex , Function Based, Text) Is your XML data CONTENT or DOCUMENT driven? Access Paths - The Optimizer – Performance?
- 27. Logical XML Schema Design Data Unstructured, Semi-structured, Structured Structured Russian Doll All elements and attributes are declared locally . Minimum reuse Salami Slice All elements and attributes are declared globally . Maximum reuse Venetian Blind Reuse of complete content models is easy. It encourages the use of named Complex Types Source: xfront.com (http://www.xfront.com/globalversuslocal.html)
- 28. Controle over Schemata Maintained via the Repository Storage, Evolution, Security Storage can be a Black Box (without schemata) CLOB Binary XML (ALLOW NONSCHEMA) Using Namespaces (Recursiveness!) Overhead (due to parsing) XDB Annotations influence: Storage, Behavior, Name
- 29. XDB Annotations Levels root simpletype, complextype xmlns:xdb="http://xmlns.oracle.com/xdb" xdb:storeVarrayAsTable xdb:defaultTable xdb:maintainDom xdb:maintainOrder xdb:SQLInline New: Oracle V.11.1.0.7.0 - Partitioning xdb:tableprops
- 30. XDB Annotations Nested Tables
- 31. Mixing Logical and Physical Design
- 32. Generate or Manual Creation Generate via DBMS_XMLSCHEMA XML Schema Based XDB Annotations ! JDeveloper or XMLSpy Manual Creation DBMS_METADATA.GET_DDL EVENT setting alter session set events='31098 trace name context forever'; /oracle/diag/rdbms/xmldb/XMLDB/trace Use Oracle 11g generation to apply in 10gR2 (IOT <> BTREE)
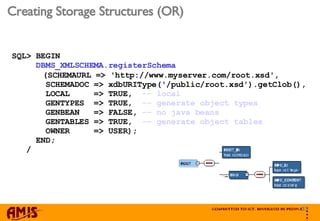
- 33. Creating Storage Structures (OR) SQL> BEGIN DBMS_XMLSCHEMA.registerSchema (SCHEMAURL => 'http://www.myserver.com/root.xsd', SCHEMADOC => xdbURIType('/public/root.xsd').getClob(), LOCAL => TRUE, -- local GENTYPES => TRUE, -- generate object types GENBEAN => FALSE, -- no java beans GENTABLES => TRUE, -- generate object tables OWNER => USER); END; /
- 34. Result - Object Relational Storage SQL> select * from tab; TNAME TABTYPE ------------------------------ ------- INFO_TABLE TABLE ROOT_TABLE TABLE SQL> select dbms_metadata.get_ddl('TABLE','ROOT_TABLE') from dual; DBMS_METADATA.GET_DDL('TABLE','ROOT_TABLE') ------------------------------------------------------ CREATE TABLE "MARCO"."ROOT_TABLE" OF "SYS"."XMLTYPE" XMLSCHEMA "http://www.myserver.com/root.xsd" ELEMENT "ROOT" PCTFREE 10 PCTUSED 40 INITRANS 1 MAXTRANS 255 NOCOMPRESS LOGGING STORAGE(INITIAL 65536 NEXT 1048576 MINEXTENTS 1 MAXEXTENTS 2147483645 PCTINCREASE 0 FREELISTS 1 FREELIST GROUPS 1 BUFFER_POOL DEFAULT) TABLESPACE "USERS" VARRAY "XMLEXTRA"."NAMESPACES" STORE AS BASICFILE LOB "NAMESPACES780_L" ... VARRAY "XMLDATA"."INFO"."SYS_XDBPD$" STORE AS BASICFILE LOB "SYS_XDBP..." DISALLOW NONSCHEMA ...
- 35. Creating Storage Structures (Binary) SQL> BEGIN DBMS_XMLSCHEMA.registerSchema (SCHEMAURL => 'http://www.myserver.com/root.xsd', SCHEMADOC => xdbURIType('/public/root.xsd').getClob(), LOCAL => TRUE, -- local GENTYPES => FALSE, -- generate object types GENBEAN => FALSE, -- no java beans GENTABLES => TRUE, -- generate object tables OPTIONS => DBMS_XMLSCHEMA.REGISTER_BINARYXML , OWNER => USER); END; /
- 36. Result - Binary XML Storage SQL> select * from tab; TNAME TABTYPE ------------------------------ ------- ROOT_TABLE TABLE SQL> select dbms_metadata.get_ddl('TABLE','ROOT_TABLE') from dual; DBMS_METADATA.GET_DDL('TABLE','ROOT_TABLE') ------------------------------------------------ CREATE TABLE "MARCO"."ROOT_TABLE" OF "SYS"."XMLTYPE" XMLTYPE STORE AS BASICFILE BINARY XML ( TABLESPACE "USERS" ENABLE STORAGE IN ROW CHUNK 8192 PCTVERSION 10 NOCACHE LOGGING STORAGE(INITIAL 65536 NEXT 1048576 MINEXTENTS 1 MAXEXTENTS 2147483645 PCTINCREASE 0 FREELISTS 1 FREELIST GROUPS 1 BUFFER_POOL DEFAULT)) XMLSCHEMA "http://www.myserver.com/root.xsd" ELEMENT "ROOT" DISALLOW NONSCHEMA ... TABLESPACE "USERS"
- 37. Functions XMLisValid() isSchemaValid() isSchemaValidated() XMLisWelformed()…? Binary XML Storage Option *) XMLSCHEMA *) ALLOW ANYSCHEMA (DIS)ALLOW NONSCHEMA XML Validation Mutually Exclusive Procedures setSchemaValidated() schemaValidate()
- 38. Syntax Example SQL> create table "XML_XSD01" of XMLTYPE 2 XMLTYPE STORE AS BASICFILE BINARY XML 3 XMLSCHEMA "http://www.myserver.com/root.xsd" 4 ELEMENT "ROOT" 5 DISALLOW NONSCHEMA ; Table created. SQL> create table "XML_XSD01_B6396229" of XMLTYPE 2 XMLTYPE STORE AS BASICFILE BINARY XML 3 XMLSCHEMA "http://www.myserver.com/root.xsd" 4 ELEMENT "ROOT" 5 ALLOW ANYSCHEMA ; Table created. B.6396229
- 40. CLOB, Object Relational, Binary XML XMLType (Tables) XMLType Views XMLDB Data Storage (Object) Relational Objects Relational Tables Relational World XMLDB World Binary XML Structured Mixed complex[y] BINARY XSD [y/n] XMLIndex Content complex[n] OR XSD [y] BTree, IOT Hybrid Content complex[n] Mixed XSD [y] BTree, IOT Unstructured Document na CLOB XSD [n] XMLIndex
- 41. Some XML Storage Issues (*) 11g - XML Schema - “preserve space” - - + BTree / IOT + + + Function / Text + + - XMLIndex + - ++ Memory Management ++ + - Throughput + - ++ XPath Performance + - ++ DML - (*) + - (*) Whitespace ++ - + Schema Based Binary XML CLOB O.R.
- 42. XMLIndex to the Rescue Logical Index designed for the XMLDB domain “ Revival” of CLOB Storage (select) Use Path Subsetting Full Blown XMLIndex can be BIG Token Tables (XDB.X$......) Query Rewrite on Tokens Fuzzy Searches, // Can be maintained Manually Doesn’t support all XPath expressions Path Table XMLIndex XML Information
- 43. XMLINDEX index PATH INDEX (PATHID, RID) BTREE ORDER INDEX (RID, ORDER_KEY) BTREE VALUE INDEX (SUBSTRB("VALUE",1,1599)) FUNCTION BASED locator : pointer to XML fragments PATH_TABLE RID RowID locator RAW value varchar2 (4000) pathID RAW order key RAW
- 44. XMLIndex Examples SQL> CREATE INDEX XMLIX_INFO on INFO_TABLE (object_value) 2 INDEXTYPE IS XDB.XMLIndex ; SQL> CREATE INDEX XMLIX_ROOT on ROOT_TABLE (object_value) 2 INDEXTYPE IS XDB.XMLIndex 3 PARAMETERS ('PATHS ( INCLUDE (/ROOT/ID 4 /ROOT/INFO/INFO_ID 5 ) 6 NAMESPACE MAPPING (xmlns=" http://www.myserver.com/root.xsd ")) 7 PATH TABLE XMLBIN_PATH_TABLE 8 PATH ID INDEX XMLBIN_PATHID_IX 9 ORDER KEY INDEX XMLBIN_ORDERKEY_IX');
- 45. Object Relational Storage Partioning Equi Partitioning List Partitioning See OTN Forum Hybrid CLOB, Binary XML, and OR Storage See 11gR1 Online Manual
- 46. XML Equi Partitioning by Reference
- 47. Equi Partitioning of Table PART_DEMO EMP_PROJ_P11 reference_id EMPLOYEES_PROJ_TAB “ employees”.”employee” EMP_PROJ_P12 PROJ_DETAILS_TAB
- 48. Equi Partitioning XML SQL> CREATE TABLE PART_DEMO OF SYS.XMLTYPE 2 XMLSCHEMA "EmpProjectInfo.xsd" ELEMENT "EmployeeProjectInfo" 3 NESTED TABLE xmldata."EMPLOYEES"."EMPLOYEE" STORE AS EMPLOYEES_PROJ_TAB 4 (nested table PROJECT_DETAILS STORE AS PROJ_DETAILS_TAB ) 5 partition by range( xmldata."EMPLOYEE_REFERENCE_ID") 6 ( partition P11 values less than (50) 7 NESTED TABLE xmldata."EMPLOYEES"."EMPLOYEE" STORE AS EMP_PROJ_P11 (STORAGE 8 nested table PROJECT_DETAILS STORE AS PROJ_DETAILS_P11 ) 9 , partition P21 values less than (MAXVALUE) 10 NESTED TABLE xmldata."EMPLOYEES"."EMPLOYEE" STORE AS EMP_PROJ_P21 (STORAGE 11 nested table PROJECT_DETAILS STORE AS PROJ_DETAILS_P21 ) 12 ); B.6364855
- 49. Binary XML Storage Post Parse XML Representation Secure Files Compression Encryption Encoding XML Schemata
- 50. XML Binary Examples SQL> CREATE TABLE "ROOT_TABLE" OF "SYS"."XMLTYPE" 2 XMLTYPE STORE AS SECUREFILE BINARY XML 3 XMLSCHEMA "http://www.myserver.com/root.xsd" ELEMENT "ROOT" 4 DISALLOW NONSCHEMA 5 COMPRESS 6 ; SQL> alter table "ROOT_TABLE" 2 modify lob (XMLDATA) 3 (COMPRESS HIGH); -- ALTER TABLE "ROOT" MODIFY LOG (XMLDATA) -- COMPRESS | NOCOMPRESS | COMPRESS MEDIUM | COMPRESS HIGH B.6364855
- 52. RECAP
- 53. Recap… XML is NOT relational… There are a lot of design decisions to make… There is more control then you would wish for… Design with future demands in mind ! There is no universal solution for XML data, yet… … but it is being improved by Oracle constantly… But what ever you do… … you will have to go the “Full Monty”
- 54. Oracle Open World 2008 - XMLDB Sessions
- 55. References XMLDB Developers Guide The XMLDB Forum http:// forums.oracle.com/forums/forum.jspa?forumID =34 XML DB FAQ Thread http:// forums.oracle.com/forums/thread.jspa?threadID =410714 Blog http:// technology.amis.nl/blog http:// blog.gralike.com Asktom at http://asktom.oracle.com (“Files” section)







































![CLOB, Object Relational, Binary XML XMLType (Tables) XMLType Views XMLDB Data Storage (Object) Relational Objects Relational Tables Relational World XMLDB World Binary XML Structured Mixed complex[y] BINARY XSD [y/n] XMLIndex Content complex[n] OR XSD [y] BTree, IOT Hybrid Content complex[n] Mixed XSD [y] BTree, IOT Unstructured Document na CLOB XSD [n] XMLIndex](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/marco-gralike-amis-xmldb-building-blocks-and-best-practices-oow-2k8-1223212753060316-9/85/XMLDB-Building-Blocks-And-Best-Practices-Oracle-Open-World-2008-Marco-Gralike-40-320.jpg)















![Questions? [email_address] http://www.amis.nl](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/marco-gralike-amis-xmldb-building-blocks-and-best-practices-oow-2k8-1223212753060316-9/85/XMLDB-Building-Blocks-And-Best-Practices-Oracle-Open-World-2008-Marco-Gralike-56-320.jpg)