Elliptic Curve Cryptography for those who are afraid of maths
- 1. Elliptic Curve Cryptography for those who are afraid of math(s) Martijn Grooten, Virus Bulletin @martijn_grooten BSides San Francisco, 29 February 2016
- 3. Disclaimer: This talk will be useless.
- 4. Disclaimer: This talk will be useless. I am not a cryptographer.
- 5. Disclaimer: This talk will be useless. I am not a cryptographer. Some things are wrong.
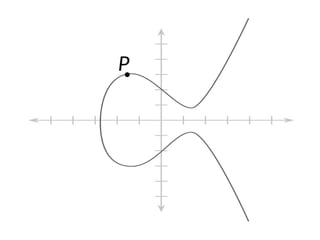
- 6. Elliptic curves y2 = x3 + a·x + b
- 7. Elliptic curves y2 = x3 + a·x + b …and a prime number p.
- 8. Elliptic curves y2 = x3 + a·x + b …and a prime number p. choice!
- 10. points
- 11. points≈numbers
- 12. P Q
- 13. P Q
- 14. P Q
- 15. P Q P+Q
- 17. P
- 18. P
- 19. P
- 20. P P+P
- 21. P 2·P
- 23. P 2·P
- 24. P 2·P
- 25. P 2·P 2·P+P
- 26. P 2·P 3·P
- 27. P 2·P 3·P 4·P
- 30. So:
- 31. So: We can “add” points to each other.
- 32. So: We can “add” points to each other. We can “multiply” points by an integer.
- 33. So: We can “add” points to each other. We can “multiply” points by an integer. P + Q = Q + P 3·P + P = 2·P + 2·P = 4·P 5·(7·P) = 7·(5·P) etc.
- 34. So: We can “add” points to each other. We can “multiply” points by an integer. P + Q = Q + P 3·P + P = 2·P + 2·P = 4·P 5·(7·P) = 7·(5·P) etc. The points on a curve form an Abelian Group (very exciting!).
- 35. From P to 100·P in eight steps
- 36. From P to 100·P in eight steps To go from a point P to 100·P:
- 37. From P to 100·P in eight steps To go from a point P to 100·P: P → 2·P 2·P → 3·P 3·P → 6·P 6·P → 12·P 12·P → 24·P 24·P → 25·P 25·P → 50·P 50·P → 100·P
- 38. “Division” is very slow
- 39. “Division” is very slow Given points P and Q, where Q=n·P, the best way to find the number n is to try P, 2·P, 3·P, etc. That is very slow.
- 40. “Division” is very slow Given points P and Q, where Q=n·P, the best way to find the number n is to try P, 2·P, 3·P, etc. That is very slow. The Discrete Logarithm Problem for elliptic curves.
- 41. ECDH (Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman)
- 42. ECDH (Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman) The challenge: Alice and Bob want to “agree” on a secret key over a public channel.
- 43. ECDH (Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman) The challenge: Alice and Bob want to “agree” on a secret key over a public channel. For example: Alice is a web browser, Bob a web server and they want to exchange a key to encrypt a TLS session.
- 44. ECDH (Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman)
- 45. Alice and Bob have agreed (publicly!) on an elliptic curve and a point P on the curve. ECDH (Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman)
- 46. Alice and Bob have agreed (publicly!) on an elliptic curve and a point P on the curve. Alice chooses secret large random number a. ECDH (Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman)
- 47. Alice and Bob have agreed (publicly!) on an elliptic curve and a point P on the curve. Alice chooses secret large random number a. Bob chooses secret large random number b. ECDH (Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman)
- 48. ECDH (Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman)
- 49. Alice computes a·P (a times the point P) and shares the answer with Bob. ECDH (Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman)
- 50. Alice computes a·P (a times the point P) and shares the answer with Bob. Bob computes b·P and shares this too. ECDH (Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman)
- 51. Alice computes a·P (a times the point P) and shares the answer with Bob. Bob computes b·P and shares this too. Alice computes a·(b·P) (a times the point Bob gave her). ECDH (Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman)
- 52. Alice computes a·P (a times the point P) and shares the answer with Bob. Bob computes b·P and shares this too. Alice computes a·(b·P) (a times the point Bob gave her). Bob computes b·(a·P). ECDH (Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman)
- 53. Alice computes a·P (a times the point P) and shares the answer with Bob. Bob computes b·P and shares this too. Alice computes a·(b·P) (a times the point Bob gave her). Bob computes b·(a·P). Secret key: a·(b·P) = b·(a·P) ECDH (Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman)
- 54. Homework: find ECDH in Wireshark
- 56. Random number generators True randomness
- 57. Random number generators True randomness
- 58. Random number generators True randomness
- 59. Random number generators True randomness output
- 60. Random number generators True randomness output
- 61. Random number generators using ECC Discrete Logarithm Problem: n → n·P gives “random” points/numbers.
- 62. Random number generators using ECC Discrete Logarithm Problem: n → n·P gives “random” points/numbers. n0
- 63. Random number generators using ECC Discrete Logarithm Problem: n → n·P gives “random” points/numbers. n0 n1 n0·P
- 64. Random number generators using ECC Discrete Logarithm Problem: n → n·P gives “random” points/numbers. n0 n1 n2 n0·P n1·P
- 65. Random number generators using ECC Discrete Logarithm Problem: n → n·P gives “random” points/numbers. n0 n1 n2 n0·P n1·P n2·P
- 66. Random number generators using ECC Discrete Logarithm Problem: n → n·P gives “random” points/numbers. n0 n1 n2 n0·P n1·P n2·P n1 n2
- 67. Random number generators using ECC Discrete Logarithm Problem: n → n·P gives “random” points/numbers. n0 n1 n2 n0·P n1·P n2·P n1 n2 n1·P
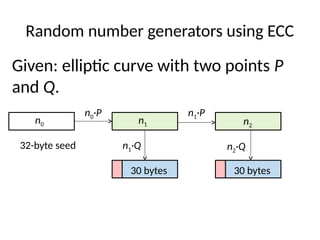
- 68. Random number generators using ECC Given: elliptic curve with two points P and Q.
- 69. Random number generators using ECC n0 Given: elliptic curve with two points P and Q. 32-byte seed
- 70. Random number generators using ECC n0 n1 Given: elliptic curve with two points P and Q. n0·P 32-byte seed
- 71. Random number generators using ECC n0 n1 Given: elliptic curve with two points P and Q. n0·P n1·Q32-byte seed 30 bytes
- 72. Random number generators using ECC n0 n1 n2 Given: elliptic curve with two points P and Q. n0·P n1·P n1·Q32-byte seed 30 bytes
- 73. Random number generators using ECC n0 n1 n2 Given: elliptic curve with two points P and Q. n0·P n1·P n1·Q n2·Q32-byte seed 30 bytes 30 bytes
- 74. Random number generators using ECC n0 n1 n2 Given: elliptic curve with two points P and Q. n0·P n1·P n2·P n1·Q n2·Q32-byte seed 30 bytes 30 bytes
- 75. Random number generators using ECC n0 n1 n2 Given: elliptic curve with two points P and Q. n0·P n1·P n2·P n1·Q n2·Q32-byte seed 30 bytes 30 bytes Note: ideas from this slide and the next are borrowed from Bernstein, Heninger and Lange (NCSC ‘14).
- 76. Random number generators using ECC Fact: P=d·Q for some (large) number d.
- 77. Random number generators using ECC n0 n1 n2 Fact: P=d·Q for some (large) number d. n0·P n1·P n2·P n1·Q n2·Q32-byte seed 30 bytes 30 bytes
- 78. Random number generators using ECC n0 n1 n2 Fact: P=d·Q for some (large) number d. n0·P n1·P n2·P n1·Q n2·Q32-byte seed 30 bytes 30 bytes 216 possibilities
- 79. Random number generators using ECC n0 n1 n2 Fact: P=d·Q for some (large) number d. n0·P n1·P n2·P n1·Q n2·Q32-byte seed 30 bytes 30 bytes 216 possibilities r1
- 80. Random number generators using ECC n0 n1 n2 Fact: P=d·Q for some (large) number d. n0·P n1·P n2·P n1·Q n2·Q32-byte seed 30 bytes 30 bytes 216 possibilities r1 d·r1
- 81. Random number generators using ECC n0 n1 n2 Fact: P=d·Q for some (large) number d. n0·P n1·P n2·P n1·Q n2·Q32-byte seed 30 bytes 30 bytes 216 possibilities r1 d·r1 n2 = n1·P = n1(d·Q)
- 82. Random number generators using ECC n0 n1 n2 Fact: P=d·Q for some (large) number d. n0·P n1·P n2·P n1·Q n2·Q32-byte seed 30 bytes 30 bytes 216 possibilities r1 d·r1 n2 = n1·P = n1(d·Q) = d·(n1·Q)
- 83. Random number generators using ECC n0 n1 n2 Fact: P=d·Q for some (large) number d. n0·P n1·P n2·P n1·Q n2·Q32-byte seed 30 bytes 30 bytes 216 possibilities r1 d·r1 n2 = n1·P = n1(d·Q) = d·(n1·Q) = d·r1
- 84. So who, if anyone, knows d?
- 85. So who, if anyone, knows d?
- 86. So who, if anyone, knows d? “Dual_EC_DRBG”
- 87. So who, if anyone, knows d? “Dual_EC_DRBG” NB: this RNG is bad for many other reasons!
- 88. What happened at Juniper?
- 89. What happened at Juniper? Juniper used Dual_EC_DRBG (in ScreenOS) but with different P, Q.
- 90. What happened at Juniper? Juniper used Dual_EC_DRBG (in ScreenOS) but with different P, Q. In theory that is OK, but…
- 91. What happened at Juniper? Juniper used Dual_EC_DRBG (in ScreenOS) but with different P, Q. In practice… Oops. In theory that is OK, but…
- 92. Anything else up their sleeve?
- 93. Anything else up their sleeve? The widely used curves (P-256 etc.) use “unexplained” constants. We can't exclude that they weren't chosen to create a backdoor.
- 94. Anything else up their sleeve? The widely used curves (P-256 etc.) use “unexplained” constants. We can't exclude that they weren't chosen to create a backdoor. There probably isn't such a backdoor, but we should aim for “nothing up my sleeve” constants (e.g. Curve25519).
- 95. Suggested reading "A Riddle Wrapped in an Enigma" by Neal Koblitz and Alfred J. Menezes http://eprint.iacr.org/2015/1018.pdf
- 96. ECC: a good idea? Elliptic curve cryptography is a good idea because we can do with much smaller keys.
- 97. ECC: a good idea? Elliptic curve cryptography is a good idea because we can do with much smaller keys. 256-bit ECC ≈ 3072-bit RSA.
- 98. ECC: a good idea? Elliptic curve cryptography is a good idea because we can do with much smaller keys. 256-bit ECC ≈ 3072-bit RSA. Elliptic curve crypto uses complicated maths. That is its biggest weakness.
- 99. Thank you! @martijn_grooten [email protected] www.virusbulletin.com PS “How Broken Is Our Crypto Really?” 3 March, 8:00am, room 2005 @ RSA.
- 100. Thank you! @martijn_grooten [email protected] www.virusbulletin.com PS “How Broken Is Our Crypto Really?” 3 March, 8:00am, room 2005 @ RSA.