Java 7 & 8 - A&BP CC
- 1. 1 Java 7 & 8 Yannick De Turck Ken Coenen
- 2. 2 Java 7 & 8 18h15 – Java 7 (Ken) 18h45 – Q&A 19h – Java 8 (Yannick) 19h30 – Q&A 19h45 – Exercises 20h30 – Solutions 21h - Finish
- 3. 3 Java 7 (July 28th 2011) String in switch-statement Automatic resource management Diamond syntax Better Exception handling with multi-catch Literal enhancements New IO API Fork Join Framework JVM enhancements
- 4. 4 Java 7: String in switch-statement
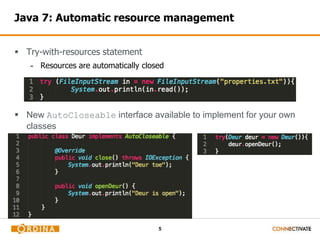
- 5. 5 Java 7: Automatic resource management Try-with-resources statement - Resources are automatically closed New AutoCloseable interface available to implement for your own classes
- 6. 6 Java 7: Automatic resource management
- 7. 7 Java 7: Diamond syntax Type Inference for Generic Instance Creation No longer required to repeat the type when instantiation
- 8. 8 Java 7: Better Exception handling with multi-catch No longer one Exception per catch limit
- 9. 9 Java 7: Better Exception handling with multi-catch Precise rethrowing
- 10. 10 Java 7: Literal enhancements Prefix binary literals with 0b or 0B Use underscores in your number literals to increase readability
- 11. 11 Java 7: New IO API A whole new package: java.nio Non-blocking IO Buffer oriented instead of Stream oriented New classes to improve working with files - Files - Path - FileSystem - WatchService - FileVisitor - ...
- 12. 12 Java 7: New IO API
- 13. 13 Java 7: New IO API
- 14. 14 Java 7: New IO API
- 15. 15 Java 7: Fork Join Framework Parallel programming - Divide a process into smaller tasks via recursion which are handled by a processor - Combine the processed pieces into one result - Divide & conquer
- 16. 16 Java 7: Fork Join Framework Extend RecursiveAction or RecursiveTasks if (my portion of the work is small enough) { do the work directly } else { split my work into two pieces invoke the two pieces and wait for the results } Practical example: ForkBlur.java
- 17. 17 Java 7: JVM enhancements Support for dynamically typed languages - Introduction of invokedynamic A new bytecode instruction on the JVM for method invocation http://niklasschlimm.blogspot.be/2012/02/java-7-complete-invokedynamic- example.html - Performance improvements for other languages living in the JVM such as Ruby, Groovy, … Garbage-First Collector (or G1 collector) - Will eventually replace the Concurrent Mark-Sweep Collector (CMS) - Advantages: works with regions, more predictable
- 18. 18 Java 8 (March 18th 2014) Lambda Expressions Extension Methods Functional Interfaces Method and Constructor References Streams and Bulk Data Operations for Collections Removal of PermGen New Date & Time API New Default API for Base 64 Encoding Improvements for Annotations General Performance Improvements
- 19. 19 Java 8: Lambda Expressions Allows writing code in a functional style Passing behaviour to a method Prior to Java 8: Anonymous Inner Class Java 8: Lambda Expressions Gets rid of boiler plate code More readable and clear code Type of param may be specified but isn’t obligated (params) -> expression () -> System.out.println(“Hello world!”); myButton.addActionListener () -> { doThis(); doThat(); }((e) -> println(“Clicked!));
- 20. 20 Java 8: Lambda Expressions
- 21. 21 Java 8: Extension Methods Add non-abstract method implementations to interfaces using the ‘default’ keyword But what happens if default methods collide when using multiple interfaces?
- 22. 22 Java 8: Extension Methods Override method and pick the right implementation
- 23. 23 Java 8: Functional Interfaces @FunctionalInterface An interface with exactly one abstract method Lambda expression is applicable as implementation Build-in Functional Interfaces (java.util.function) - Predicate<T>: boolean test(T t); - Function<T>: R apply(T t); - Supplier<T>: T get(); - Consumer<T>: void accept(T t); - Comparator<T>: int compare(T o1, T o2);
- 24. 24 Java 8: Functional Interfaces
- 25. 25 Java 8: Method and Constructor References Pass references of methods or constructors using the :: keyword Useful in combination with the Predicate class Bit shorter compared to lambdas ContainingClass::staticMethodName ContainingObject::instanceMethodName ContainingType::methodName ClassName::new String::valueOf s::toString String::toString String::new
- 26. 26 Java 8: Method and Constructor References
- 27. 27 Java 8: Method and Constructor References
- 28. 28 Java 8: Streams and Bulk Data Operations for Collections java.util.Stream A sequence of elements on which one or more operations can be performed Intermediate vs terminal operation - Intermediate: returns the stream itself in order to be able to chain operations - Terminal: returns a result of a certain type Streams are created on a source such as a java.util.Collection Can be executed sequential or parallel Parallel utilises Fork-Join - Watch out with long-running tasks! Blocks threads in the pool
- 29. 29 Java 8: Streams and Bulk Data Operations for Collections
- 30. 30 Java 8: Streams and Bulk Data Operations for Collections Maps - Don’t support streams :-( - … But they now support various new and useful methods for executing common tasks! V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K,? super V> action) V computeIfPresent(K key, BiFunction<? super K,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction) V computeIfAbsent(K key, Function<? super K,? extends V> mappingFunction) V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) ...
- 31. 31 Java 8: Streams and Bulk Data Operations for Collections
- 32. 32 Java 8: Streams and Bulk Data Operations for Collections Optional<T> - May or may not contain a non-null value - Avoid working with null (no NPEs!)
- 33. 33 Java 8: Removal of PermGen PermGen memory space completely removed - PermSize and MaxPermSize JVM arguments are ignored and a warning gets displayed Gets replaced by Metaspace - XX:MaxMetaspaceSize flag, default is unlimited - System memory is the limit instead of the fixed size at startup of PermGen - Metaspace will dynamically resize depending on demand at runtime Note that this does not magically fixes your memory leaks!
- 34. 34 Java 8: New Date & Time API Inspired by Joda Time - Human time vs computer time (aka millis since epoch) Offers a solution to the sometimes cumbersome way of calculating dates and time Interesting new classes: - Clock - ZoneId - LocalDate (date without timezone) - LocalTime (time without timezone) - LocalDateTime (datetime without timezone) - DateTimeFormatter - …
- 35. 35 Java 8: New Date & Time API
- 36. 36 Java 8: New Default API for Base64 Encoding More extensive API than the 1.6+ Base64 API (sun.misc.BASE64Encoder) 3 encoders and decoders - Basic (For regular encoding) - URL (Encoded String needs to be used in file or url) - MIME (MIME friendly encoding)
- 37. 37 Java 8: New Default API for Base64 Encoding
- 38. 38 Java 8: Improvements for Annotations Annotations in Java 8 are repeatable @Repeatable
- 39. 39 Java 8: Improvements for Annotations
- 40. 40 Java 8: General Performance Improvements Performs a bit faster compared to Java 7 Great performance improvement when making use of parallelism Example with Arrays.sort
- 41. 41 Sources https://github.com/yannickdeturck/workshop-java-7-8 (or shorter url: http://tinyurl.com/lzy56ng) Java 8 Cheatsheet: http://www.java8.org
- 42. 42 Questions ?
Editor's Notes
- #2: Welkom, onszelf voorstellen, ABP, structuur avond, volgende workshops, kleine inleiding waarom deze workshop interessant zou moeten zijn -> self assessment, enterprise omgeving Java 7
- #5: String in switch is faster than if … equals else … (Java compiler generates generally more efficient bytecode). Uses the String.equals method.
- #6: The try-with-resources statement is a try statement that declares one or more resources. A resource is as an object that must be closed after the program is finished with it. The try-with-resources statement ensures that each resource is closed at the end of the statement. Any object that implements java.lang.AutoCloseable, which includes all objects which implement java.io.Closeable, can be used as a resource. The resource is closed automatically in a finally block that’s added at compile time (http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/articles/java/trywithresources-401775.html)
- #7: Eg. The classes InputStream and OutputStream, in Java SE 7 and later, implements the interface java.lang.AutoCloseable. The resource is closed automatically in a finally block that’s added at compile time (http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/articles/java/trywithresources-401775.html)
- #8: You can replace the type arguments required to invoke the constructor of a generic class with an empty set of type parameters (<>) as long as the compiler can infer the type arguments from the context (so no-go for anonymous inner classes!). Note that omitting the diamond operator doesn’t have the same effect. You’ll get an unchecked conversion warning, because the instantiation refers to the raw type instead of the generic class.
- #9: Pipeline is used to group Exceptions that should be handled the same way. This feature can reduce code duplication and lessen the temptation to catch an overly broad exception.
- #10: Note that NoSuchFieldException extends ReflectiveOperationException. The compiler is smart enough to determine that only NoSuchFieldException can be thrown so it’s not mandatory to add the ReflectiveOperationException to the method signature. Advantage can be that if you have multiple implementations of a ReflectiveOperationException, you do not need to list them all in the catch declaration. This again saves time.
- #11: Integral types (byte, short, int, and long) can also be expressed using the binary number system. Any number of underscore characters (_) can appear anywhere between digits in a numerical literal. This can improve the readability of your code.
- #12: Lots of interesting stuff in there, be sure to have a look at that package! A zip file system provider is also available in JDK 7 (check out http://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/technotes/guides/io/fsp/zipfilesystemprovider.html for more information). Stream: Element not cached, can’t move back and forth without first buffering Buffer: Data is read into a buffer to be processed later, can move back and forth. More flexible during processing but the buffer might not contain all data necessary to process it. Blocking: read(), write() -> Thread blocked until data is read of fully written Non-blocking: Thread gets what’s available (possibly nothing) or thread writes but doesn’t wait until it’s fully written. -> Single thread can manage multiple inputs and outputs Files: Static methods that operate on files, directories, or other types of files. FileSystem: Provides an interface to a file system and is the factory (getInstance()) for objects to access files and other objects in the file system. Path: Offers more functionalities than File, File now has a toPath()-method. Similar methods compared to File but methods now throw Exceptions (example: delete()) More properties available for consulting (DOS and POSIX), returns null if it isn’t supported on the system.
- #14: Listens to events that take place in the directory that’s being watched. watchKey.take(): Retrieves and removes next watch key, waiting if none are yet present. Returns: the next watch key watchKey.reset(): Resets this watch key. If this watch key has been cancelled or this watch key is already in the ready state then invoking this method has no effect. Otherwise if there are pending events for the object then this watch key is immediately re-queued to the watch service. If there are no pending events then the watch key is put into the ready state and will remain in that state until an event is detected or the watch key is cancelled. Returns: true if the watch key is valid and has been reset, and false if the watch key could not be reset because it is no longer valid
- #15: Crawls through a directory, skips, svn-folders and prints out the directories and files found.
- #16: A divide and conquer algorithm works by recursively breaking down a problem into two or more sub-problems of the same (or related) type, until these become simple enough to be solved directly. Tasks are divided into smaller parts to be processed, results are combined into one
- #17: ForBlur.java is an example of a picture being blurred by going through it’s pixels
- #18: The heap is partitioned into a set of equal-sized heap regions, each a contiguous range of virtual memory. G1 performs a concurrent global marking phase to determine the liveness of objects throughout the heap. After the mark phase completes, G1 knows which regions are mostly empty. It collects in these regions first, which usually yields a large amount of free space. This is why this method of garbage collection is called Garbage-First. G1 compacts sufficiently to completely avoid the use of fine-grained free lists for allocation, and instead relies on regions. Also, G1 offers more predictable garbage collection pauses than the CMS collector, and allows users to specify desired pause targets.
- #19: Hot topic op Devoxx. Java releases komen sneller en sneller uit dus belangrijk om bij te blijven
- #20: Functionali programming: Immutable data. State is handled via parameter passing, avoids side effects. Split up the problem in a chain of functions that need to be executed where each function takes input and returns a result. Think about what transformations need to happen. Recursion is used more often. Functions are first class citizens. Data flow. OOP: Mutable. State changes. Write the exact steps in detail to solve a particular problem. Control flow. Note that when using brackets in a lambda expression ‘;’s are mandatory at the end of the line!! Java compiler compiles lambda expressions and convert them into private methods of the class.
- #21: Note how the type of param can be left out and parentheses aren’t necessary if there’s only one param.
- #22: Specify implementations in your interface! This also allows existing interfaces to be extended with new functionalities without breaking backwards compatibility. Not limited to only one default method.
- #24: A warning is given by your IDE when more than one method is specified inside a FunctionalInterface. Trying to compile the project will also fail. When omitting the @FunctionalInterface annotation, the project will compile and a lambda expression can be used to implement calculate(int a). Some of the functional interfaces might be familiar if you’ve used Guava such as Predicate. Supplier: provides objects
- #25: Anonymous inner class vs lambda. Notice how you are actually passing a function as a parameter. Assigning the lambda to a variable is usually skipped.
- #26: :: syntax was introduced in Java 8 to reference methods
- #27: These method references are possible since they accept a param of F and have a result of T. forEach accepts a Consumer<T> where T is the type of an element of the Collection.
- #28: Picking the right constructor method is context dependent, in this case since BookFactory defines a method with 2 params, the second constructor of Book is used.
- #29: Why stream? Not a data structure that stores elements, it conveys elements from a source Does not modify its source (functional in nature), instead it produces a new stream Laziness-seeking, opportunity for optimalisation (example: find first 3 strings with even number of characters, doesn’t need to traverse through all elements) Collections have an finite size where as streams do not Each element of a stream is only visited once thus a new stream must be generated to revisit the same elements
- #31: putIfAbsent: If the specified key doesn’t have a value (null) assign the specified value to it. Returns null if the value was assigned, otherwise return the value. (note: already existed in ConcurrentMap in Java <8, now available to all Maps) forEach: execute the consumer for each element computeIfPresent: If the value for the specified key is present and non-null, attempts to compute a new mapping given the key and its current mapped value computeIfAbsent: If the specified key is not already associated with a value (or is mapped to null), attempts to compute its value using the given mapping function and enters it into this map unless null getOrDefault: Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, or defaultValue if this map contains no mapping for the key
- #35: Human time: separate fields for years, months, days, hours, minutes, seconds, and, in line with the current fashion, nanoseconds. Machine time: number of milliseconds since epoch, which you may obtain, for example, via System.currentTimeMillis() call. This does not replace the existing Data API, it simply offers a better solution for doing calculations with dates.
- #37: sun.misc.BASE64Encoder wasn’t even documented…
- #38: Basic vs Url: Url-friendly encoding Notice output no longer than 76 chars and ends with carriage return followed by a line feed
- #39: Note that the container annotation is still used but this time the Java compiler is responsible for wrapping the repeating annotations into a container annotation.
- #40: Note that the container annotation is still used but this time the Java compiler is responsible for wrapping the repeating annotations into a container annotation.