Lecture Notes- Network Services - Copy.pptx
- 1. © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential Presentation_ID 1 Network Protocols and Services Tutor: Dr. Muhammad Ali Kazmi
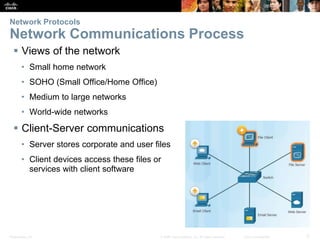
- 2. Presentation_ID 2 © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential Network Protocols Network Communications Process Views of the network • Small home network • SOHO (Small Office/Home Office) • Medium to large networks • World-wide networks Client-Server communications • Server stores corporate and user files • Client devices access these files or services with client software
- 3. Presentation_ID 3 © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential Network Protocols Communications Protocols TCP/IP Protocol Suite • Application Layer • Transport Layer • Internet Layer • Network Access Layer
- 4. Presentation_ID 4 © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential Network Protocols Communications Protocols (Cont.) OSI Model (Open Systems Interconnection model) Message Delivery • Unicast – one-to-one • Multicast – one-to-many • Broadcast – one-to-all
- 5. Presentation_ID 5 © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential Network Protocols Communications Protocols (Cont.) Three important addresses • Protocol address • Network host address • Physical address
- 6. © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential Presentation_ID 6 Ethernet and Internet Protocol (IP)
- 7. Presentation_ID 7 © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential Ethernet and Internet Protocol (IP) Ethernet Operates at Layer 1 and 2 • Defined by the IEEE 802.2 and 802.3 standards Ethernet responsibilities • Data encapsulation • Media access control • Put bits on the medium Ethernet Frame • Two key identifiers o Destination MAC address o Source MAC address • Uses hexadecimal IEEE: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
- 8. Presentation_ID 8 © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential Ethernet and Internet Protocol (IP) IPv4 Characteristics • Connectionless • Unreliable • Media Independent
- 9. Presentation_ID 9 © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential Ethernet and Internet Protocol (IP) Types of IPv4 Addresses Classes – A, B, C, D, and E Public • Can be used on the Internet Private • Used within an organization • 10.0.0.0 /8 • 172.16.0.0 /12 • 192.168.0.0 /16
- 10. Presentation_ID 10 © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential Ethernet and Internet Protocol (IP) The Default Gateway Required IP information to communicate on a TCP/IP network • IP address • Subnet mask Default gateway IP address • Required to send data to a remote network • Address is the Layer 3 device, such as a router connected to the same network IP addressing information • Configured manually • Obtained automatically using DHCP
- 11. © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential Presentation_ID 11 Connectivity Verification
- 12. Presentation_ID 12 © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential Connectivity Verification ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) Used to provide feedback and troubleshoot network problems Message types • Host confirmation – echo request and echo reply with the ping utility • Destination or service unreachable codes o 0 – net unreachable o 1 – host unreachable o 2 – protocol unreachable o 3 – port unreachable
- 13. Presentation_ID 13 © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential Connectivity Verification Ping and Traceroute Utilities Ping • Test the local stack o ping 127.0.0.1 • Test connectivity on the LAN • Test remote connectivity Traceroute – Test the path a packet takes (Windows:Tracert) Tracert
- 14. © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential Presentation_ID 14 Address Resolution Protocol
- 15. Presentation_ID 15 © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential Address Resolution Protocol MAC and IP Two addresses assigned to an Ethernet device • MAC address (Layer 2 physical address) • IP address (Layer 3 logical address) A device must have both addresses to communicate with another TCP/IP-based device • Uses the source and destination MAC address • Uses the source and destination IP address
- 16. Presentation_ID 16 © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential Address Resolution Protocol MAC and IP (Cont.) When communicating with a device on a remote network, the destination MAC address is the MAC address of the Layer 3 device interface on the same network as the device originating the packet.
- 17. Presentation_ID 17 © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential Address Resolution Protocol ARP Protocol used to discover and obtain the destination MAC address Used to resolve IPv4 addresses to MAC addresses IPv4 and MAC address mappings kept in an ARP table
- 18. Presentation_ID 18 © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential Address Resolution Protocol ARP Issues ARP Broadcasts – could impact large networks ARP Spoofing (ARP poisoning) – security risk
- 19. © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential Presentation_ID 19 The Transport Layer
- 20. Presentation_ID 20 © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential The Transport Layer Transport Layer Characteristics Tracks individual conversations Moves data between applications on network devices Segments data Identifies applications using a port number Two key protocols • TCP • UDP
- 21. Presentation_ID 21 © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential The Transport Layer Transport Layer Characteristics (Cont.) TCP • Used for majority of the major TCP/IP protocols • Requires more overhead (bytes in the header) • Reliable (3-way handshake) UDP • Used for voice and video • Fast, fast, fast • Does not resend dropped packets
- 22. Presentation_ID 22 © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential The Transport Layer Transport Layer Operation Destination port numbers • Uses well-known port numbers Source port numbers • Uses dynamic port numbers
- 23. © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential Presentation_ID 23 Network Services
- 24. Presentation_ID 24 © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential Network Services DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) • Provides IP addressing information such as IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, DNS server IP address, and domain name • Messages o Discover o Offer o Request o Ack(nowledge)
- 25. Presentation_ID 25 © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential Network Services DNS Dynamic Name System (DNS) • Manages and provides domain names and associated IP addresses • Hierarchy of servers • 90% of malicious software used to attack networks uses DNS to carry out attack campaigns
- 26. Presentation_ID 26 © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential Network Services HTTP Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) • Port 80 • Governs the way a web server and client interact • TCP-based • Has specific server responses
- 27. © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential Presentation_ID 27 Summary
- 28. Presentation_ID 28 © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential A protocol is a set of communication rules defined for a specific purpose. The TCP/IP protocol suite is the most widely used set of protocols in the world. The TCP/IP protocol stack has four layers. Starting from the top the layers are Application, Transport, Internet, and Network Access. The OSI reference model has seven layers. Starting from the top the layers are Application, Presentation, Session, Transport, Network, Data Link, and Physical. Ethernet operates at Layer 2 of the OSI model and requires the use of a source and destination MAC address for communicating on a network. ARP is used to discover the MAC address associated with a specific IP address. IP operates at Layer 3 of the OSI model and requires the use of a source and destination IP address for communicating on a network. ICMP is used for testing connectivity. The ping and traceroute commands are common ICMP utilities. Summary