Flow of control ppt
- 1. - Made by SHRABANTI PROGRAMING IN
- 2. Every C++ program must have at least one function called main(). When we run a C++ program, the first statement executed will be at the beginning of main() and the last statement at the end of main(). Therefore, the main() is also known as driver function as it drives the program. The Von-Neumann architecture of computers supports only sequential processing. The normal flow of execution of statements in a high-level language program is also in the sequential order, that is, each statement is executed in its order of occurrence in the program. Some problems often require That the normal flow of control be altered depending on the requirements. C++ supports a number of control structures to perform the processing. FLOW OF CONTROL INTRODUCTION
- 3. CONTROL STRUCTURES Control Structures Loop or Iteration if-else Sequence Selection switch while , for do-while
- 4. These are the instructions given to the computer to perform some action and form the smallest executable unit within a C++ program. A semicolon (;) terminates a statement. SIMPLE STATEMENT : It is a single statement. COMPOUND STATEMENT : It is a group of statements separated from each other by a semicolon(;). This group of statements is also called a block of code enclosed within a pair of curly braces { }. The significance of the block is that the group of statements enclosed within the curly braces is treated as a single unit. STATEMENTS
- 5. The statements written within a sequential structure are called selection or conditional statements because we select the execution of a particular statement after checking some condition. If the condition is proved then a particular action would be performed and if the condition is false, some other action would be performed. The conditional statements are as follows: if-statement if-else statement nested if switch CONDITIONAL STATEMENTS (SELECTION)
- 6. It tests a condition. The statements associated with if is (are) executed only when the condition is true, otherwise the statements is (are) not executed at all. The syntax of if statement is as shown below: If-statement if(expression) { statement; } where if is the keyword, expression is a booleon expression within a set of parenthesis and statement can be a simple or compound statement.
- 7. //to print whether a student is passed depending upon the marks #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> void main () { clrscr (); int x , y ; cout << “Enter the two integers” ; cin >> x >> y ; if ( x > y ) cout << x ; getch (); }
- 8. It tests a condition. Statement 1 is executed when the condition is true otherwise Statement 2 is executed. The syntax of if-else statement is: If-else statement if(expression) { statement; } else { statement; } where if is the keyword, expression is the booleon expression, else is the keyword and statement can be simple or compound statement.
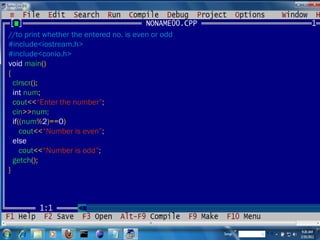
- 9. //to print whether the entered no. is even or odd #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> void main () { clrscr (); int num ; cout << “Enter the number” ; cin >> num; if (( num % 2 )== 0 ) cout << “Number is even” ; else cout << “Number is odd” ; getch (); }
- 10. One or more if statements embedded within the if statement are called nested ifs. The following if-else statement is a nested if statement nested to level two: Nested if
- 11. //to print whether the entered no. is positive, negative or equal to zero #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> void main () { clrscr (); int num ; cout << “Enter the number” ; cin >> num ; if ( num == 0 ) cout << “Number is equal to zero” ; else { if ( num > 0 ) cout << “Number is positive” ; else cout << “Number is negative” ; } getch (); }
- 12. In if-else-if ladder the different conditions are evaluated from the start and when a condition is evaluated as true, the following statements are executed and the rest of statements are skipped. When all the n conditions become false, then the final else having the default-statement will be executed. The if-else-if ladder
- 13. This statement is used when we have to select one option out of many alternatives. It is a multi branch statement that makes the control to jump to one of the several statements based on the value of an integer variable or an expression. The general Form of the switch is: switch switch(expression) { case constant 1: statement sequence 1; break; case constant 2: statement sequence 2; break; case constant 3: statement sequence 3; break; . . . case constant n-1: statement sequence n-1; break; default: statement sequence; }
- 15. //to print the corresponding day of the week #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> void main () { clrscr (); int a,b,c ; char op ; cout << “Enter the two operands and the operator(+ - * /)” ; cin >> a >> b >> op ; switch ( op ) { case ‘+’ : cout << “The sum is” << c = a + b ; break ; case ‘-’ : cout << “\nThe difference is” << c = a - b ; break ; case ‘*’ : cout << “\nThe product is” << c = a * b ; break ; case ‘/’ : cout << “\nThe div is” << c = a / b ; break ; default : cout << “\nWrong operator entered” ; } getch (); }
- 16. Repetitive Execution means a set of statements are executed again and again till the condition remains true and if the condition is false, the statement next to those set of statements would be executed. There are3 types of statements to implement repetative execution (Iteration/Looping). while statement (Entry controlled loop-Pretest) do while statement (Exit controlled loop-Post test) for statement (counter controlled loop or deterministic loop) REPETITIVE EXECUTION
- 17. It may not be executed even once if the condition is false initially. It is executed till the condition remains true and the control comes out of the loop when the condition becomes false. There must be some loop terminating condition inside the body of the loop to avoid infinite looping. The syntax of while statement is as follows: while loop while(expression) { statement; } where, while is the keyword, expression is the booleon expression which evaluates either to true or false & statement can be simple or compound statement.
- 18. //to find the sum of the digits of a number #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> void main () { clrscr (); int n , rem , sum = 0 ; cout << “Enter the numbers “ ; cin >> n ; while ( n != 0 ) { rem = n % 10 ; sum += rem ; n /= 10 ; } cout << “The sum of the digits of the number is “ << sum ; getch (); }
- 19. This loop is executed at least once. It is executed till the condition remains true and the control comes out of the loop when condition becomes false. There must Be some loop terminating condition inside the body of the loop to avoidinfinite Looping. The syntax of do-while loop is as follows: do-while loop do { statement; } while(expression); where, while is the keyword, expression is the booleon expression which evaluates either to true or false & statement can be simple or compound statement.
- 20. //to print first n natural numbers and their sum #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> void main () { clrscr (); int n , i = 1 ,sum =0 ; cout << “Enter the value of n: ” ; cin >> n ; cout << “\nFirst “ << n << “ natural numbers are:\n\n” ; do { cout << i << ‘ ‘ ; sum += I ; i ++; } while ( i <= n ); cout << “\n\nSum = “ << sum ; getch (); }
- 21. The loop controlled variable is assigned some value. The condition is checked. If the condition is true, then the body of for loop is executed. Then, the arithmetic expression is evaluated. After the evaluation the condition is checked again and if it is true, then again the body of for loop is executed and then the arithmetic expression is checked again. The for loop is executed again and again till the condition remains true. The general syntax of the for loop is: for loop for(initial assignment;condition;arithmetic expression) { body of for loop }
- 23. //to print first n natural numbers and their sum #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> void main () { clrscr (); int n , sum =0 ; cout << “Enter the value of n: ” ; cin >> n ; cout << “\nFirst “ << n << “ natural numbers are:\n\n” ; for ( i = 1 ; i <= n ;++ i ) { cout << i << ‘ ‘ ; sum += i ; } cout << “\n\nSum = “ << sum ; getch (); }
- 24. Nesting of loops means one or more loops within a loop. In this case inner loop must terminate before the outer loop. Nested loop //to print number pattern #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> void main () { clrscr (); int i , j ; for ( i = 1 ; i <= 20 ;++ i ) { for ( j = 1 ; j <= 20 - i ;++ j ) cout << ‘ ‘ ; for ( j = 1 ; j <= i ;++ j ) cout << “* “ ; } cout << endl ; getch (); }
- 25. * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Output screen
- 26. JUMP STATEMENTS break statement : The break statements enable a program to skip over part of the code. A break statement terminates the smallest enclosing while, do while, for or switch statement. Execution resumes at the statement immediately following the body of the terminated statement. continue : continue is another jump statement like the break statement but the continue statement is somewhat different from break. Instead of forcing termination, it forces the next iteration of the loop to take place, skipping any code in between. exit function : It is a pre-defined function defined in header file process.h and stdlib.h. This function is used to terminate the execution of the program.
- 27. Use of break and continue statement
- 28. A goto statement can transfer the program control anywhere in the program. The target destination of a goto statement is marked by a label. Both of these i.e target label and goto must appear in the same function. goto statement (unconditional branching) Syntax for goto: goto label;
- 29. END