Medium term load demand forecast of Kano zone using neural network algorithms
- 1. TELKOMNIKA Telecommunication, Computing, Electronics and Control Vol. 18, No. 4, August 2020, pp. 2112~2117 ISSN: 1693-6930, accredited First Grade by Kemenristekdikti, Decree No: 21/E/KPT/2018 DOI: 10.12928/TELKOMNIKA.v18i4.14032 2112 Journal homepage: http://journal.uad.ac.id/index.php/TELKOMNIKA Medium term load demand forecast of Kano zone using neural network algorithms Huzaimu Lawal Imam1 , Muhammad Sani Gaya2 , G. S. M. Galadanci3 1,3 Department of Physics, Bayero University Kano, Nigeria 2 Department of Electrical Engineering, Kano University of Science and Technology, Nigeria Article Info ABSTRACT Article history: Received Sep 3, 2019 Revised Mar 1, 2020 Accepted Mar 23, 2020 Electricity load forecasting refers to projection of future load requirements of an area or region or country through appropriate use of historical load data. One of several challenges faced by the Nigerian power distribution sectors is the overloaded power distribution network which leads to poor voltage distribution and frequent power outages. Accurate load demand forecasting is a key in addressing this challenge. This paper presents a comparison of generalized regression neural network (GRNN), feed-forward neural network (FFNN) and radial basis function neural network for medium term load demand estimation. Experimental data from Kano electricity distribution company (KEDCO) were used in validating the models. The simulation results indicated that the neural network models yielded promising results having achieved a mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) of less than 10% in all the considered scenarios. The generalization capability of FFNN is slightly better than that of RBFNN and GRNN model. The models could serve as a valuable and promising tool for the forecasting of the load demand. Keywords: Capability Layer Load Neural network Weight This is an open access article under the CC BY-SA license. Corresponding Author: Muhammad Sani Gaya, Department of Electrical Engineering, Kano University of Science and Technology, 02 Gaya Road, Wudil City, 713211, Nigeria. Email: [email protected] 1. INTRODUCTION Electricity load forecasting is an essential part of power system energy management. Load forecast refers to estimating the future load through the use of historic available load data. It is a key in the planning, operation and dispatch of electrical energy. Appropriate load prediction provides electricity companies or governments with timely and adequate information to operate the system economically and reliably. Load forecast is critical and necessary because the availability of electricity is one of the most important factors for industrial development especially in a developing country like Nigeria. Some of the main issues with the Nigerian power sector include high operating cost, high energy losses and high suppressed demand throughout the country. The distribution sector is tasked with the need to ensure adequate network coverage and provision of quality power supply to the public in addition to sufficient marketing and customer service delivery. To reduce the high technical losses and improve the quality of voltage distribution at the electricity distribution sector there is vehement need of constant network upgrade or overhauling which may not be achieved without accurate load demand forecast. Accurate load forecast greatly influences the planning process undertaken in operation centres of energy providers that relate to the actual electricity generation, distribution, system maintenance as well as
- 2. TELKOMNIKA Telecommun Comput El Control Medium term load demand forecast of Kano zone using network algorithm (Huzaimu Lawal Imam) 2113 electricity pricing among others. Over the years, many researches were conducted on the Nigerian power sector and its related challenges. Nevertheless, most of these researches centre on general problems of power generation or transmission or distribution or combine and the researches on load demand focuses on the Nigerian wide electricity demand [1, 2] or demand of a town or city [3] or may be short term forecast [2, 4]. Several models related to this work were developed such as grey model [5], support vector regression [6], but the main issues with the support vector machine are the choice of the kernel function parameters, extensive memory requirement and difficulty of interpretation, multi-model artificial neural networks [7], fast-learning recurrent neural network [8]; stability is the major drawback of recurrent neural network. Deep learning neural networks [9], large amount of data requirement and determination of suitable topology are main demerits of deep learning method. Neuro-fuzzy model or fuzzy-neural network [10, 11] utilizes the mapping techniques of neural network to obtain the Fuzzy parameters, nevertheless, when the number of input is large, the number of rules becomes large which increases computational burden, thus in turn affecting the generalization capability of the model. Fuzzy logic model [12], the main inconveniences with Fuzzy logic methods are difficulty in rules formation, membership function selection and inadaptability. This paper focuses on estimating the medium-term load demand of Kano zone using neural network algorithms. Neural network has gained wide acceptability over the last few decades, especially in the field of system identification, modelling and control applications [13]. It presents a better alternative in approximating a complex nonlinear system and capable to handle well uncertainty [14, 15]. Generalized regression neural network (GRNN), radial basis function neural network (RBFNN) and feed-forward network (FFNN) are class of neural network that are mostly used in mapping a complex nonlinear system. GRNN has a great advantage of faster training and converging to a global solution [16]. In GRNN, the output is predicted using weighted average of the outputs of training data. Radial basis function network structure is a multi-layer feed-forward network. It enhances accuracy and reduces the training time complexity. Feed-forward networks are easier to build, quite stable and have unidirectional flow of information. The available performance measures such MAPE, mean square error (MSE), root mean square error (RMSE) were used in evaluating the forecasting and generalization abilities of the proposed models. The paper is organized as follows: section 2 describes research methodology, section 3 presents the simulation results and section 4 is the conclusion. 2. RESEARCH METHOD This section describes the approaches used to build the neural network models. Since neural networks are classified based on their structure (how the neurons are organized in a systematic manner from input layer to the output layer) as feedforward and recurrent neural network, this paper considered the two classes of the network. The typical methods deployed in developing the neural network models are as follows: 2.1. Generalized regression neural network (GRNN) GRNN is quite capable to deal with noise, converge to global solution and do not traps in the local minima. The utilization of Gaussian functions by GRNN has immensely aided in achieving high prediction accuracy. The main principle of GRNN is expressed as: 𝑌( 𝑥) = Σ 𝑘=1 𝑁 𝑦 𝑘 𝑒 − 𝑑 𝑘 2𝜎2 Σ 𝑘=1 𝑁 𝑒 − 𝑑 𝑘 2𝜎2 (1) where 𝑌( 𝑥) depicts the estimation value of input 𝑥, 𝑦 𝑘 represents the activation function, 𝑒 − 𝑑 𝑘 2𝜎2 is the Gaussian function and 𝑑 𝑘 is the squared Euclidean distance. The structure of GRNN is illustrated in Figure 1. From the Figure 1, it can be seen that the GRNN is composed of four layers. The input layer which responsible for feeding the next layer, the pattern layer that computes the Euclidean distance and activation function, the summation layer and the output layer are responsible for normalizing the output vector. The training procedure of GRNN is entirely different from other neural networks. The GRNN finishes the training once each input-output vector pair from the training dataset is fed into the input layer. The number of neurons in the pattern layer is mostly equal to the number of patterns in the training dataset. 2.2. Radial basis function neural network (RBFNN) Radial basis function neural network has proven to be universal approximator that utilizes radial basis function as activation function. The Figure 2 depicts the structure of the radial basis function neural network [17]. From the Figure 2, it can be seen that the network consists of input layer, hidden layer
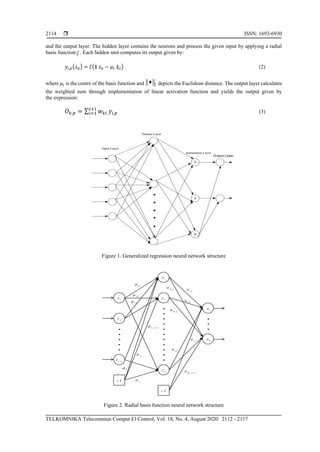
- 3. ISSN: 1693-6930 TELKOMNIKA Telecommun Comput El Control, Vol. 18, No. 4, August 2020: 2112 - 2117 2114 and the output layer. The hidden layer contains the neurons and process the given input by applying a radial basis function . Each hidden unit computes its output given by: 𝑦𝑖,𝑝(𝑧 𝑝) = 𝜉(∥ 𝑧 𝑝 − 𝜇𝑖 ∥2) (2) where 𝜇𝑖 is the centre of the basis function and 2• depicts the Euclidean distance. The output layer calculates the weighted sum through implementation of linear activation function and yields the output given by the expression: 𝑂 𝑘,𝑝 = ∑ 𝑤 𝑘𝑖 𝐼+1 𝑖=1 𝑦𝑖,𝑝 (3) Input Layer Pattern Layer Summation Layer Output Layer S S D • • • • • Figure 1. Generalized regression neural network structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 z 2 z 1I z + 1+ 1 1 2 1 1I 1 2 I 1 y 2 y I y 1− 2 , 1I + 1 1 w1K w 1 2 w 2K w 1 I w 1, 1I w + , 1K I w + 1 o K o . . . Figure 2. Radial basis function neural network structure
- 4. TELKOMNIKA Telecommun Comput El Control Medium term load demand forecast of Kano zone using network algorithm (Huzaimu Lawal Imam) 2115 2.3. Feed-forward neural network (FFNN) Neural networks adapt to the environmental changes. The adaptability enhances their performance, even if there are large variations and uncertainties [18]. Neural networks comprise of nodes and links. The nodes receive the incoming signals, process them and yield an output. The links indicate the direction of the information flow which can be in only one direction or bidirectional [18]. The classification of the neural networks are based on their architecture as feed-forward or recurrent neural network [14, 19]. Feed-forward neural network as shown in Figure 3 is the most commonly used for modelling and control because of its stable nature and simplicity [20, 21]. This paper utilizes feed-forward neural network for the forecasting. Details regarding choice of feed-forward neural network could be found in [13, 18, 22-24]. Input Layer Hidden Layer Output Layer Figure 3. Feedforward neural network architecture 2.4. Model building The historic data set from KEDCO was pre-processed and randomly divided into training data set and testing data set. Each of the models was developed using training data containing 80% of the whole data set while the generalization capabilities of the developed models were evaluated using the test data set which contained 20% of the data set. The remaining part of this section below shows how models were realized. 2.4.1. Generalized regression neural network model The structure of the GRNN is selected as depicted in Figure 1. The pattern layer (second layer) has radbas neurons and biases. The weights of pattern layer are set to 𝑃1 . The bias is set to column vector of 0.8328/spread. The summation layer (third layer) has purelin neurons. High value of spread enhances the network generalization capability, minimizes forecasting error and the results of the network becomes smoother. The spread is chosen to be 1.0. 2.4.2. RBFNN model The structure of the RBFNN was chosen exactly the same as that of the GRNN with the only difference that the third layer of the RBFNN is also composed of biases. Since there is no established systematic approach of selecting the structure. It was choosen through trial and error method and realized structure is similar to that shown in Figure 2. 2.4.3. FFNN model The architecture of FFNN is similar to that illustrated in Figure 3. Choice of appropriate network parameters are key for effective learning and better performance. The hidden layer is made up of ten (10) neurons. The tag-sig and purelin were used as the transfer functions for the hidden and output layer respectively. 3. RESULTS AND ANALYSIS Through simulation the performance capabilities and accuracies of different models could be tested. The one-month prediction performances of the models during training and testing phase were illustrated in Figures 4 and 5 respectively. The accuracy of the models were evaluated using commonly performance measures and the results are presented in the Table 1.
- 5. ISSN: 1693-6930 TELKOMNIKA Telecommun Comput El Control, Vol. 18, No. 4, August 2020: 2112 - 2117 2116 Figure 4. Models prediction performances for one- month training phase Figure 5. Models prediction performance for one-month testing phase Table 1. One-month models performance Model Training Phase Testing Phase MSE RMSE MAPE (%) MSE RMSE MAPE (%) FFNN 0.0041 0.0642 0.0016 0.0531 0.0729 0.0017 RBFNN 0.0041 0.0642 8.5954E-15 531.9490 23.064 0.0404 GRNN 0.0389 0.1971 0.0055 1.8499 1.3601 0.0307 Similarly, the Figure 6 and Figure 7 illustrated the models prediction performances for the two months during the training and testing phase respectively. The accuracy of the models was evaluated and the results are illustrated in the Table 2. It is apparent that during the training phase depicted in Figure 4, the predictions of the models were able to follow exactly the trajectory of the observed data and the agreement tally with the evaluated results illustrated in the Table 1 and the predictions are highly accurate [25] having achieved the MAPE of less than 10% [25] by each model. During the testing phase as shown in Figure. 5, also the predictions of the models are quite accurate having achieved the MAPE of less than 10%. For the two months, the predictions of the models during training phase is quite promising as shown in Figure 6 and each of the model was able to achieved the MAPE of less than 10% as presented in the Table 2 indicating highly accurate prediction. During the testing phase as illustrated in Figure 7, the models demonstrated their capabilities of tracking well the path of the observed data and the achieved MAPEs are quite attractive. Figure 6. Models prediction performances for two-month training phase Figure 7. Models prediction performances for two-month testing phase Table 2. Two-month models’ performance Model Training Phase Testing Phase MSE RMSE MAPE (%) MSE RMSE MAPE (%) FFNN 0.0045 0.0668 0.0005 0.01 0.0873 0.00051 RBFNN 7.101E-06 0.0027 2.444E-05 109.11 10.4455 0.0254 GRNN 0.0003 0.0185 7.152E-05 15.22 3.9011 0.0150 4. CONCLUSION The paper has presented the neural network algorithms for medium term load forecasting of Kano zone. During the training phase in both the two scenarios the obtained results demonstrated that the models are quite effective and reliable in forecasting the load. Although, the models were able to achieved the MAPE of
- 6. TELKOMNIKA Telecommun Comput El Control Medium term load demand forecast of Kano zone using network algorithm (Huzaimu Lawal Imam) 2117 less than 10% during the testing phases, the performances of the FFNN is slightly better than the RBFNN and GRNN model. The prediction performances of the models are quite promising and reliable. The models could serve as the useful and efficient tools for the load forecasting of the zone. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The authors wish to thank KEDCO, Kano University of Science and Technology, Wudil and Bayero University Kano for their support. REFERENCES [1] A. A. Mati, et al., “Electricity Demand Forecasting in Nigeria using Time Series Model,” The Pacific Journal of Science and Technology, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 479-485, January 2009. [2] M. Buhari, S. S. Adamu, “Short-Term Load Forecasting Using Artificial Neural Network,” Proceedings of the International Multi-conference of Engineers and Computer Scientists, 2012. [3] A. E. James, et al., “Artificial Neural Network for Energy Demand Forecast,” International Journal of Electrical and Electronic Science, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 8-13, 2018. [4] H. L. Imam, et al., “Short Term Load Forecast of Kano zone using Artificial Intelligent Techniques,” Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 562-568, 2019. [5] X. Che, “Application of Improved Grey Model in Medium and Long Term Load Forecasting,” IOP Conf. Series: Earth and Environmental Science, vol. 128, pp. 1-5, 2018. [6] A. Zare-Noghabi, et al., “Medium-Term Load Forecasting Using Support Vector Regression, Feature Selection, and Symbiotic Organism Search Optimization,” Conference: 2019 IEEE PES General Meeting, 2019. [7] R. M. Nezzar, et al., “Mid-Long-Term Load Forecasting using Multi-Model Artificial Neural Networks,” International Journal on Electrical Engineering and Information, vol.8, no. 2, pp. 389-401, 2016. [8] G.M. Khan, et al., “Electrical Load Forecasting using Fast Learning Recurrent Neural Networks,” Proceedings of International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 1-6, 2013. [9] D. L. Marino, K. Amarasinghe and M. Manic, "Building energy load forecasting using Deep Neural Networks," IECON 2016-42nd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, pp. 7046-7051, 2016. [10] O. E. Dragomir, F. Dragomir, et al., "Medium term load forecasting using ANFIS predictor," 18th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation, pp. 551-556, 2010. [11] A. Jarndal, "Load forecasting for power system planning using a genetic-fuzzy-neural networks approach," 2013 7th IEEE GCC Conference and Exhibition (GCC), pp. 44-48, 2013. [12] N. Ammar, et al., “Analysis Load Forecasting of Power System Using Fuzzy Logic and Artificial Neural Network,” Journal of Telecommunication, Electronic and Computer Engineering, vol. 9, no. 3, pp. 181-192, 2017. [13] M. S. Gaya, et al., “Estimation of Turbidity in Water Treatment Plant using Hammerstein-Wiener and Neural Network Technique,” Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 666-672, 2017. [14] M. S. Gaya, et al., “Feed-Forward Neural Network Approximation Applied to Activated Sludge System,” CCIS, vol. 402, pp. 587–598, 2013. [15] N. S. A. Yasmin, et al., “Estimation of pH and MLSS using Neural Network,” TELKOMNIKA Telecommunication, Computing, Electronics and Control, vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 912-918, 2017. [16] A. J. Al-Mahasneh, et al., “Review of Applications of Generalized Regression Neural Networks in Identification and Control of Dynamic Systems,” Neural and Evolutionary Computing, 2018. [17] A. P. Engelbrecht, “Computational intelligence: An introduction,” Second Edition. Chichester, West Sussex England: John Wiley & Sons, 2007. [18] M. S. Gaya, “Neuro-Fuzzy Modelling and Neural Network Internal Model Control of an Activated Sludge System,” Ph. D. Thesis. Skudai, Dept. of Control and Mechatronics, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 2014. [19] Z. Yusuf, et al., “Neural Network Model Development with Soft Computing Techniques for Membrane Filtration Process,” International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, vol. 8, no. 4, pp. 2614-2623, 2018. [20] M. S. Gaya, et al., “ANFIS Modelling of Carbon Removal in Domestic Wastewater Treatment Plant,” Applied Mechanics and Material, vol. 372, pp. 597-601, 2013 [21] M. S. Gaya, et al., Comparison of Control Strategies Applied to Nonlinear Quarterly Car Passive Suspension System. International Review of Automatic Control, vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 203-208, 2015. [22] S. Sumatjhi, S. Paneerselvam, “Computational Intelligence Paradigms: Theory and Applications using MATLAB,” CRC Press, London, 2010. [23] T. Masters, “Practical Neural Network Recipes in C++,” Academic Press, New York, 1993. [24] A. Jain, et al., “Artificial Neural Network: A tutorial, IEEE-Computer Magazine,” Computer, vol. 29, no. 3, pp. 31-44, March 1996. [25] Lawrence K. D, Klimberg R. K, Lawrence S. M, “Fundamental of Forecasting using Excel,” New York: Industrial Press Inc., 2009.

![TELKOMNIKA Telecommun Comput El Control
Medium term load demand forecast of Kano zone using network algorithm (Huzaimu Lawal Imam)
2113
electricity pricing among others. Over the years, many researches were conducted on the Nigerian power sector
and its related challenges. Nevertheless, most of these researches centre on general problems of power generation
or transmission or distribution or combine and the researches on load demand focuses on the Nigerian wide
electricity demand [1, 2] or demand of a town or city [3] or may be short term forecast [2, 4].
Several models related to this work were developed such as grey model [5], support vector
regression [6], but the main issues with the support vector machine are the choice of the kernel function
parameters, extensive memory requirement and difficulty of interpretation, multi-model artificial neural
networks [7], fast-learning recurrent neural network [8]; stability is the major drawback of recurrent neural
network. Deep learning neural networks [9], large amount of data requirement and determination of suitable
topology are main demerits of deep learning method. Neuro-fuzzy model or fuzzy-neural network [10, 11]
utilizes the mapping techniques of neural network to obtain the Fuzzy parameters, nevertheless,
when the number of input is large, the number of rules becomes large which increases computational burden,
thus in turn affecting the generalization capability of the model. Fuzzy logic model [12], the main
inconveniences with Fuzzy logic methods are difficulty in rules formation, membership function selection
and inadaptability. This paper focuses on estimating the medium-term load demand of Kano zone using neural
network algorithms.
Neural network has gained wide acceptability over the last few decades, especially in the field
of system identification, modelling and control applications [13]. It presents a better alternative in
approximating a complex nonlinear system and capable to handle well uncertainty [14, 15]. Generalized
regression neural network (GRNN), radial basis function neural network (RBFNN) and feed-forward network
(FFNN) are class of neural network that are mostly used in mapping a complex nonlinear system. GRNN has
a great advantage of faster training and converging to a global solution [16]. In GRNN, the output is predicted
using weighted average of the outputs of training data. Radial basis function network structure is a multi-layer
feed-forward network. It enhances accuracy and reduces the training time complexity. Feed-forward networks
are easier to build, quite stable and have unidirectional flow of information. The available performance
measures such MAPE, mean square error (MSE), root mean square error (RMSE) were used in evaluating
the forecasting and generalization abilities of the proposed models. The paper is organized as follows: section
2 describes research methodology, section 3 presents the simulation results and section 4 is the conclusion.
2. RESEARCH METHOD
This section describes the approaches used to build the neural network models. Since neural networks
are classified based on their structure (how the neurons are organized in a systematic manner from input layer
to the output layer) as feedforward and recurrent neural network, this paper considered the two classes of
the network. The typical methods deployed in developing the neural network models are as follows:
2.1. Generalized regression neural network (GRNN)
GRNN is quite capable to deal with noise, converge to global solution and do not traps in the local
minima. The utilization of Gaussian functions by GRNN has immensely aided in achieving high prediction
accuracy. The main principle of GRNN is expressed as:
𝑌( 𝑥) =
Σ 𝑘=1
𝑁
𝑦 𝑘 𝑒
−
𝑑 𝑘
2𝜎2
Σ 𝑘=1
𝑁
𝑒
−
𝑑 𝑘
2𝜎2
(1)
where 𝑌( 𝑥) depicts the estimation value of input 𝑥, 𝑦 𝑘 represents the activation function, 𝑒
−
𝑑 𝑘
2𝜎2
is the Gaussian function and 𝑑 𝑘 is the squared Euclidean distance. The structure of GRNN is illustrated in
Figure 1. From the Figure 1, it can be seen that the GRNN is composed of four layers. The input layer which
responsible for feeding the next layer, the pattern layer that computes the Euclidean distance and activation
function, the summation layer and the output layer are responsible for normalizing the output vector.
The training procedure of GRNN is entirely different from other neural networks. The GRNN finishes
the training once each input-output vector pair from the training dataset is fed into the input layer. The number
of neurons in the pattern layer is mostly equal to the number of patterns in the training dataset.
2.2. Radial basis function neural network (RBFNN)
Radial basis function neural network has proven to be universal approximator that utilizes radial
basis function as activation function. The Figure 2 depicts the structure of the radial basis function neural
network [17]. From the Figure 2, it can be seen that the network consists of input layer, hidden layer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5214032-200724021239/85/Medium-term-load-demand-forecast-of-Kano-zone-using-neural-network-algorithms-2-320.jpg)
![TELKOMNIKA Telecommun Comput El Control
Medium term load demand forecast of Kano zone using network algorithm (Huzaimu Lawal Imam)
2115
2.3. Feed-forward neural network (FFNN)
Neural networks adapt to the environmental changes. The adaptability enhances their performance,
even if there are large variations and uncertainties [18]. Neural networks comprise of nodes and links.
The nodes receive the incoming signals, process them and yield an output. The links indicate the direction
of the information flow which can be in only one direction or bidirectional [18]. The classification of the neural
networks are based on their architecture as feed-forward or recurrent neural network [14, 19]. Feed-forward
neural network as shown in Figure 3 is the most commonly used for modelling and control because of its stable
nature and simplicity [20, 21]. This paper utilizes feed-forward neural network for the forecasting. Details
regarding choice of feed-forward neural network could be found in [13, 18, 22-24].
Input Layer
Hidden Layer
Output Layer
Figure 3. Feedforward neural network architecture
2.4. Model building
The historic data set from KEDCO was pre-processed and randomly divided into training data set
and testing data set. Each of the models was developed using training data containing 80% of the whole data
set while the generalization capabilities of the developed models were evaluated using the test data set which
contained 20% of the data set. The remaining part of this section below shows how models were realized.
2.4.1. Generalized regression neural network model
The structure of the GRNN is selected as depicted in Figure 1. The pattern layer (second layer) has
radbas neurons and biases. The weights of pattern layer are set to 𝑃1
. The bias is set to column vector
of 0.8328/spread. The summation layer (third layer) has purelin neurons. High value of spread enhances
the network generalization capability, minimizes forecasting error and the results of the network becomes
smoother. The spread is chosen to be 1.0.
2.4.2. RBFNN model
The structure of the RBFNN was chosen exactly the same as that of the GRNN with the only
difference that the third layer of the RBFNN is also composed of biases. Since there is no established systematic
approach of selecting the structure. It was choosen through trial and error method and realized structure is
similar to that shown in Figure 2.
2.4.3. FFNN model
The architecture of FFNN is similar to that illustrated in Figure 3. Choice of appropriate network
parameters are key for effective learning and better performance. The hidden layer is made up of ten (10) neurons.
The tag-sig and purelin were used as the transfer functions for the hidden and output layer respectively.
3. RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
Through simulation the performance capabilities and accuracies of different models could be tested.
The one-month prediction performances of the models during training and testing phase were illustrated in
Figures 4 and 5 respectively. The accuracy of the models were evaluated using commonly performance
measures and the results are presented in the Table 1.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5214032-200724021239/85/Medium-term-load-demand-forecast-of-Kano-zone-using-neural-network-algorithms-4-320.jpg)
![ ISSN: 1693-6930
TELKOMNIKA Telecommun Comput El Control, Vol. 18, No. 4, August 2020: 2112 - 2117
2116
Figure 4. Models prediction performances for
one- month training phase
Figure 5. Models prediction performance for
one-month testing phase
Table 1. One-month models performance
Model Training Phase Testing Phase
MSE RMSE MAPE (%) MSE RMSE MAPE (%)
FFNN 0.0041 0.0642 0.0016 0.0531 0.0729 0.0017
RBFNN 0.0041 0.0642 8.5954E-15 531.9490 23.064 0.0404
GRNN 0.0389 0.1971 0.0055 1.8499 1.3601 0.0307
Similarly, the Figure 6 and Figure 7 illustrated the models prediction performances for the two months
during the training and testing phase respectively. The accuracy of the models was evaluated and the results
are illustrated in the Table 2. It is apparent that during the training phase depicted in Figure 4, the predictions
of the models were able to follow exactly the trajectory of the observed data and the agreement tally with
the evaluated results illustrated in the Table 1 and the predictions are highly accurate [25] having achieved
the MAPE of less than 10% [25] by each model. During the testing phase as shown in Figure. 5, also
the predictions of the models are quite accurate having achieved the MAPE of less than 10%. For the two
months, the predictions of the models during training phase is quite promising as shown in Figure 6 and each
of the model was able to achieved the MAPE of less than 10% as presented in the Table 2 indicating highly
accurate prediction. During the testing phase as illustrated in Figure 7, the models demonstrated their
capabilities of tracking well the path of the observed data and the achieved MAPEs are quite attractive.
Figure 6. Models prediction performances for
two-month training phase
Figure 7. Models prediction performances for
two-month testing phase
Table 2. Two-month models’ performance
Model Training Phase Testing Phase
MSE RMSE MAPE (%) MSE RMSE MAPE (%)
FFNN 0.0045 0.0668 0.0005 0.01 0.0873 0.00051
RBFNN 7.101E-06 0.0027 2.444E-05 109.11 10.4455 0.0254
GRNN 0.0003 0.0185 7.152E-05 15.22 3.9011 0.0150
4. CONCLUSION
The paper has presented the neural network algorithms for medium term load forecasting of Kano
zone. During the training phase in both the two scenarios the obtained results demonstrated that the models are
quite effective and reliable in forecasting the load. Although, the models were able to achieved the MAPE of](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5214032-200724021239/85/Medium-term-load-demand-forecast-of-Kano-zone-using-neural-network-algorithms-5-320.jpg)
![TELKOMNIKA Telecommun Comput El Control
Medium term load demand forecast of Kano zone using network algorithm (Huzaimu Lawal Imam)
2117
less than 10% during the testing phases, the performances of the FFNN is slightly better than the RBFNN and
GRNN model. The prediction performances of the models are quite promising and reliable. The models could
serve as the useful and efficient tools for the load forecasting of the zone.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors wish to thank KEDCO, Kano University of Science and Technology, Wudil and Bayero
University Kano for their support.
REFERENCES
[1] A. A. Mati, et al., “Electricity Demand Forecasting in Nigeria using Time Series Model,” The Pacific Journal of
Science and Technology, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 479-485, January 2009.
[2] M. Buhari, S. S. Adamu, “Short-Term Load Forecasting Using Artificial Neural Network,” Proceedings of
the International Multi-conference of Engineers and Computer Scientists, 2012.
[3] A. E. James, et al., “Artificial Neural Network for Energy Demand Forecast,” International Journal of Electrical and
Electronic Science, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 8-13, 2018.
[4] H. L. Imam, et al., “Short Term Load Forecast of Kano zone using Artificial Intelligent Techniques,” Indonesian
Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 562-568, 2019.
[5] X. Che, “Application of Improved Grey Model in Medium and Long Term Load Forecasting,” IOP Conf. Series:
Earth and Environmental Science, vol. 128, pp. 1-5, 2018.
[6] A. Zare-Noghabi, et al., “Medium-Term Load Forecasting Using Support Vector Regression, Feature Selection, and
Symbiotic Organism Search Optimization,” Conference: 2019 IEEE PES General Meeting, 2019.
[7] R. M. Nezzar, et al., “Mid-Long-Term Load Forecasting using Multi-Model Artificial Neural Networks,”
International Journal on Electrical Engineering and Information, vol.8, no. 2, pp. 389-401, 2016.
[8] G.M. Khan, et al., “Electrical Load Forecasting using Fast Learning Recurrent Neural Networks,” Proceedings of
International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 1-6, 2013.
[9] D. L. Marino, K. Amarasinghe and M. Manic, "Building energy load forecasting using Deep Neural Networks,"
IECON 2016-42nd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, pp. 7046-7051, 2016.
[10] O. E. Dragomir, F. Dragomir, et al., "Medium term load forecasting using ANFIS predictor," 18th Mediterranean
Conference on Control and Automation, pp. 551-556, 2010.
[11] A. Jarndal, "Load forecasting for power system planning using a genetic-fuzzy-neural networks approach," 2013 7th
IEEE GCC Conference and Exhibition (GCC), pp. 44-48, 2013.
[12] N. Ammar, et al., “Analysis Load Forecasting of Power System Using Fuzzy Logic and Artificial Neural Network,”
Journal of Telecommunication, Electronic and Computer Engineering, vol. 9, no. 3, pp. 181-192, 2017.
[13] M. S. Gaya, et al., “Estimation of Turbidity in Water Treatment Plant using Hammerstein-Wiener and Neural
Network Technique,” Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, vol. 5, no. 3,
pp. 666-672, 2017.
[14] M. S. Gaya, et al., “Feed-Forward Neural Network Approximation Applied to Activated Sludge System,” CCIS,
vol. 402, pp. 587–598, 2013.
[15] N. S. A. Yasmin, et al., “Estimation of pH and MLSS using Neural Network,” TELKOMNIKA Telecommunication,
Computing, Electronics and Control, vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 912-918, 2017.
[16] A. J. Al-Mahasneh, et al., “Review of Applications of Generalized Regression Neural Networks in Identification and
Control of Dynamic Systems,” Neural and Evolutionary Computing, 2018.
[17] A. P. Engelbrecht, “Computational intelligence: An introduction,” Second Edition. Chichester, West Sussex England:
John Wiley & Sons, 2007.
[18] M. S. Gaya, “Neuro-Fuzzy Modelling and Neural Network Internal Model Control of an Activated Sludge System,”
Ph. D. Thesis. Skudai, Dept. of Control and Mechatronics, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 2014.
[19] Z. Yusuf, et al., “Neural Network Model Development with Soft Computing Techniques for Membrane Filtration
Process,” International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, vol. 8, no. 4, pp. 2614-2623, 2018.
[20] M. S. Gaya, et al., “ANFIS Modelling of Carbon Removal in Domestic Wastewater Treatment Plant,” Applied
Mechanics and Material, vol. 372, pp. 597-601, 2013
[21] M. S. Gaya, et al., Comparison of Control Strategies Applied to Nonlinear Quarterly Car Passive Suspension System.
International Review of Automatic Control, vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 203-208, 2015.
[22] S. Sumatjhi, S. Paneerselvam, “Computational Intelligence Paradigms: Theory and Applications using MATLAB,”
CRC Press, London, 2010.
[23] T. Masters, “Practical Neural Network Recipes in C++,” Academic Press, New York, 1993.
[24] A. Jain, et al., “Artificial Neural Network: A tutorial, IEEE-Computer Magazine,” Computer, vol. 29, no. 3, pp. 31-44,
March 1996.
[25] Lawrence K. D, Klimberg R. K, Lawrence S. M, “Fundamental of Forecasting using Excel,” New York: Industrial
Press Inc., 2009.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5214032-200724021239/85/Medium-term-load-demand-forecast-of-Kano-zone-using-neural-network-algorithms-6-320.jpg)