JavaScript Fundamentals & JQuery
- 1. JavaScript Jamshid Hashimi Trainer, Cresco Solution http://www.jamshidhashimi.com [email protected] @jamshidhashimi ajamshidhashimi Afghanistan Workforce Development Program
- 2. Agenda • JS Introduction • JS How To • JS Statements • JS Comments • JS Variables • JS Data Types • JS Objects • JS Arrays
- 3. Agenda • JS JSON • JS Functions • JS Operators • JS Inspect Elements (Chrome, Firefox, IE) • JQuery • DEMO
- 4. Introduction • JavaScript is the world's most popular programming language. It is the language for HTML and the web, for servers, PCs, laptops, tablets, smart phones, and more. • A scripting language is a lightweight programming language. • JavaScript is programming code that can be inserted into HTML pages. • JavaScript inserted into HTML pages, can be executed by all modern web browsers. • JavaScript is easy to learn.
- 5. How TO • JavaScripts in HTML must be inserted between <script> and </script> tags. • JavaScript can be put in the <body> and in the <head> section of an HTML page. <script> alert("My First JavaScript"); </script> <script> document.write("<h1>This is a heading</h1>"); document.write("<p>This is a paragraph</p>"); </script>
- 6. OUTPUT • JavaScript is typically used to manipulate HTML elements. <p id="demo">My First Paragraph</p> <script> document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML=" My First JavaScript"; </script>
- 7. Statements • JavaScript is a sequence of statements to be executed by the browser. • JavaScript statements are "commands" to the browser. • The purpose of the statements is to tell the browser what to do. • JavaScript code (or just JavaScript) is a sequence of JavaScript statements. • Each statement is executed by the browser in the sequence they are written.
- 8. Statements • Semicolon ; – Semicolon separates JavaScript statements. – Normally you add a semicolon at the end of each executable statement. – Using semicolons also makes it possible to write many statements on one line. document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML=" Hello Dolly"; document.getElementById("myDIV").innerHTML= "How are you?";
- 9. Statements • JavaScript is Case Sensitive – Watch your capitalization closely when you write JavaScript statements: • A function getElementById is not the same as getElementbyID. • A variable named myVariable is not the same as MyVariable.
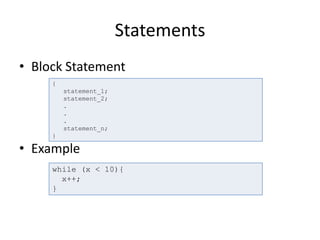
- 10. Statements • Block Statement • Example { statement_1; statement_2; . . . statement_n; } while (x < 10){ x++; }
- 11. Statements • Conditional Statements – if...else Statement – switch Statement if (condition) statement_1 [else statement_2] switch (expression) { case label_1: statements_1 [break;] case label_2: statements_2 [break;] ... default: statements_def [break;] }
- 12. Statements • LOOPS – for Statement – do...while Statement – while Statement – break Statement – continue Statement
- 13. Statements • Object Manipulation Statements – for...in Statement var obj = {make:"BMW", model:"2013"} function dump_props(obj, obj_name) { var result = ""; for (var i in obj) { result += obj_name + "." + i + " = " + obj[i] + "<br>"; } return result; } document.write(dump_props(obj,"obj"));
- 14. Comments • Comments will not be executed by JavaScript. • Comments can be added to explain the JavaScript, or to make the code more readable. • Single line comments start with //. • Multi line comments start with /* and end with */.
- 15. Comments // Write to a heading document.getElementById("myH1").innerHTML="Welcome to my Homepage"; /* The code below will write to a heading and to a paragraph, and will represent the start of my homepage: */ document.getElementById("myH1").innerHTML="Welcome to my Homepage"; var x=5; // declare x and assign 5 to it
- 16. Variables • JavaScript variables are "containers" for storing information. • As with algebra, JavaScript variables can be used to hold values (x=5) or expressions (z=x+y). • Variable can have short names (like x and y) or more descriptive names (age, sum, totalvolume). – Variable names must begin with a letter – Variable names can also begin with $ and _ (but we will not use it) – Variable names are case sensitive (y and Y are different variables) var money; var name;
- 17. Variables • JavaScript Data Types • Global & Local Variables var name = "Ali"; var money; money = 2000.50; var myVar = "global"; // Declare a global variable function checkscope( ) { var myVar = "local"; // Declare a local variable document.write(myVar); }
- 18. Variables • One Statement, Many Variables • Value = undefined – In computer programs, variables are often declared without a value. The value can be something that has to be calculated, or something that will be provided later, like user input. Variable declared without a value will have the value undefined. var lastname=”Ahmad", age=30, job="carpenter"; var lastname=”Mohammad", age=30, job=”Engineer"; var lastname;
- 19. Data Types • String, Number, Boolean, Array, Object, Null, Undefined. • JavaScript has dynamic types. This means that the same variable can be used as different types: var x; // Now x is undefined var x = 5; // Now x is a Number var x = ”Salih"; // Now x is a String
- 20. Data Types • JavaScript Booleans – Booleans can only have two values: true or false. • JavaScript Arrays var x=true; var y=false; var arr = new Array(); arr[0] = ”item 1"; arr[1] = ”item 2"; var arr = new Array(”item1",”item2”); var arr = [“item1", “item2"];
- 21. Data Types • JavaScript Objects – An object is delimited by curly braces. Inside the braces the object's properties are defined as name and value pairs (name : value). The properties are separated by commas: var person={firstname:”James", lastname:”Bond", id:9999}; var person={ firstname : ”James", lastname : ”Bond", id : 9999 };
- 22. Objects • JavaScript is designed on a simple object- based paradigm. "Everything" in JavaScript is an Object: a String, a Number, an Array, a Date.... • In JavaScript, an object is data, with properties and methods. – Properties are values associated with objects. – Methods are actions that objects can perform.
- 23. Objects • Accessing Object Properties • Accessing Object Methods objectName.propertyName objectName.methodName()
- 24. Objects • Objects in JavaScript, just as many other programming languages, can be compared to objects in real life. var myCar = new Object(); myCar.make = "Ford"; myCar.model = "Mustang"; myCar.year = 1969; myCar.make myCar[“make”]
- 25. Objects var myCar = {make:"BMW",model:"s2013",year:"2013"} function showProps(obj, objName) { var result = ""; for (var i in obj) { if (obj.hasOwnProperty(i)) { result += objName + "." + i + " = " + obj[i] + "n"; } } return result; } alert(showProps(myCar,"myCar"))
- 26. Arrays • The JavaScript Array global object is a constructor for arrays, which are high-level, list-like objects. • Arrays are list-like objects that come with a several built-in methods to perform traversal and mutation operations. Neither the size of a JavaScript array nor the types of its elements are fixed. Since an array's size can grow or shrink at any time, JavaScript arrays are not guaranteed to be dense.
- 27. Arrays <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> </head> <body> <script> var years = [1950, 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990, 2000, 2010]; console.log(years[0]); </script> </body> </html>
- 28. JSON • JSON is a subset of the object literal notation of JavaScript. Since JSON is a subset of JavaScript, it can be used in the language var myJSONObject = {"bindings": [ {"ircEvent": "PRIVMSG", "method": "newURI", "regex": "^http://.*"}, {"ircEvent": "PRIVMSG", "method": "deleteURI", "regex": "^delete.*"}, {"ircEvent": "PRIVMSG", "method": "randomURI", "regex": "^random.*"} ] }; myJSONObject.bindings[0].method // "newURI"
- 29. Functions • Function is a "subprogram" that can be called by code external (or internal in the case of recursion). Like the program itself, a function is composed of a sequence of statements called the function body. Values can be passed to a function, and the function can return a value. • Every function in JavaScript is actually a Function object.
- 30. Functions /* Declare the function 'myFunc' */ function myFunc(theObject) { theObject.brand = "Toyota"; } /* * Declare variable 'mycar'; * create and initialize a new Object; * assign reference to it to 'mycar' */ var mycar = { brand: "Honda", model: "Accord", year: 1998 }; /* Shows 'Honda' */ window.alert(mycar.brand); /* Pass object reference to the function */ myFunc(mycar); /* * Shows 'Toyota' as the value of the 'brand' property * of the object, as changed to by the function. */ window.alert(mycar.brand);
- 31. Operators • Assignment operators • Comparison operators • Arithmetic operators • Bitwise operators • Logical operators • String operators • Special operators
- 36. JQuery • Released in January of 2006, jQuery is a cross- browser JavaScript library designed to simplify the client-side script of HTML. • Used by close to a million websites, jQuery is the most popular JavaScript library in use to date. • jQuery makes it easy to handle DOM objects, events, effects and Ajax, automatically takes care of JavaScript leaks, and has countless third-party plugins.
- 38. Demo
- 39. QUESTIONS?










![Statements
• Conditional Statements
– if...else Statement
– switch Statement
if (condition)
statement_1
[else
statement_2]
switch (expression) {
case label_1:
statements_1
[break;]
case label_2:
statements_2
[break;]
...
default:
statements_def
[break;]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascript-130616075134-phpapp02/85/JavaScript-Fundamentals-JQuery-11-320.jpg)

![Statements
• Object Manipulation Statements
– for...in Statement
var obj = {make:"BMW", model:"2013"}
function dump_props(obj, obj_name) {
var result = "";
for (var i in obj) {
result += obj_name + "." + i + " = "
+ obj[i] + "<br>";
}
return result;
}
document.write(dump_props(obj,"obj"));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascript-130616075134-phpapp02/85/JavaScript-Fundamentals-JQuery-13-320.jpg)






![Data Types
• JavaScript Booleans
– Booleans can only have two values: true or false.
• JavaScript Arrays
var x=true;
var y=false;
var arr = new Array();
arr[0] = ”item 1";
arr[1] = ”item 2";
var arr = new Array(”item1",”item2”);
var arr = [“item1", “item2"];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascript-130616075134-phpapp02/85/JavaScript-Fundamentals-JQuery-20-320.jpg)



![Objects
• Objects in JavaScript, just as many other
programming languages, can be compared to
objects in real life.
var myCar = new Object();
myCar.make = "Ford";
myCar.model = "Mustang";
myCar.year = 1969;
myCar.make
myCar[“make”]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascript-130616075134-phpapp02/85/JavaScript-Fundamentals-JQuery-24-320.jpg)
![Objects
var myCar = {make:"BMW",model:"s2013",year:"2013"}
function showProps(obj, objName) {
var result = "";
for (var i in obj) {
if (obj.hasOwnProperty(i)) {
result += objName + "." + i + " = " + obj[i] +
"n";
}
}
return result;
}
alert(showProps(myCar,"myCar"))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascript-130616075134-phpapp02/85/JavaScript-Fundamentals-JQuery-25-320.jpg)

![Arrays
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var years = [1950, 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990, 2000, 2010];
console.log(years[0]);
</script>
</body>
</html>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascript-130616075134-phpapp02/85/JavaScript-Fundamentals-JQuery-27-320.jpg)
![JSON
• JSON is a subset of the object literal notation
of JavaScript. Since JSON is a subset of
JavaScript, it can be used in the language
var myJSONObject = {"bindings": [
{"ircEvent": "PRIVMSG", "method":
"newURI", "regex": "^http://.*"},
{"ircEvent": "PRIVMSG", "method":
"deleteURI", "regex": "^delete.*"},
{"ircEvent": "PRIVMSG", "method":
"randomURI", "regex": "^random.*"}
]
};
myJSONObject.bindings[0].method // "newURI"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascript-130616075134-phpapp02/85/JavaScript-Fundamentals-JQuery-28-320.jpg)










