6 3 tier architecture php
- 1. 3-Tier Architecture and PHP Scripting 1
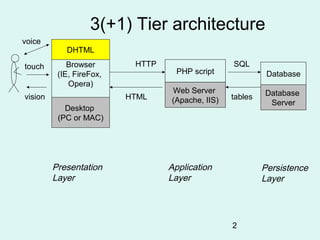
- 2. 3(+1) Tier architecture voice DHTML touch Browser HTTP SQL (IE, FireFox, PHP script Database Opera) Web Server Database vision HTML (Apache, IIS) tables Server Desktop (PC or MAC) Presentation Application Persistence Layer Layer Layer 2
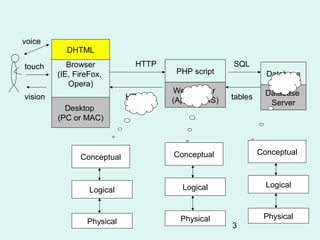
- 3. voice DHTML touch Browser HTTP SQL (IE, FireFox, PHP script Database Opera) Web Server Database vision HTML (Apache, IIS) tables Server Desktop (PC or MAC) Conceptual Conceptual Conceptual Logical Logical Logical Physical Physical Physical 3
- 4. Dynamic Web page needed when: • consistent look and feel on each page of a large site is required • data is derived from a database • content depends on real time • content depend on user choice • business transactions e.g. e-commerce… 4
- 5. 3-tier architecture • A Presentation layer using Browser technology • An Application layer using a web application server platform + application programs • A Persistence layer using a relational database or other data store technology 5
- 6. Presentation layer arch • Decoding URLs : protocol/host/file – Host name converted to IP address(164.11.8.19) – www.dnsstuff.com • Issue request to remote server using appropriate protocol (usually HTTP) • accept the returned HTML (or JPEG, ..) file • Issue requests for any embedded links (<img src=red.gif/> • render (i.e. create a 2-d image ) the HTML • allow plug-ins to handle new file types • execute client-side scripts in JavaScript • support interaction between client-side scripts and the web page (DHTML) • accept user input via a variety of controls on a form 6
- 7. Persistence layer arch • interaction with the database using standard languages e.g. SQL queries using database-specific protocol over TCP/IP • define and modify the data structures (e.g. tables) themselves ( the Database Schema) • insert, update and delete data • maintain data persistently, with backup and recovery • handle transactions to support concurrent access to the database via locking et • optimise access by compilation of queries, indexing, replication of tables etc. 7
- 8. Application Layer arch • Server (Apache, IIS) – Identifying appropriate action to take – fetch a file, pass request to an interpreter – Sending output back to caller in MIME package – Support for: • thousands of concurrent users • multi-threading [ allow multiple processes to run concurrently] • caching [holding results in a temporary store to reduce re-calculation] • Server Script (e.g. in PHP) – Interacting with the server (accessing input and generating output) – interpreting the requests according to business rules and past transactions from this client – requesting the appropriate data from the Persistence layer – computing derived data – creating the HTML (or GIF, MIDI..) for the page 8
- 9. PHP Created by Rasmus Lerdorf (born Greenland, educated in Canada) PHP originally abbreviation for ‘Personal Home Pages’, now ‘PHP Hypertext Processor’ Other key developers: Zeev Surashi and Andi Gutmans (Israel) Wikipedia entry PHP version 5.1 current at UWE 9
- 10. Scripting languages • A scripting language is: – often evolved not designed – cross-platform since interpreter is easy to port – designed to support a specific task – PHP -> Web support – un-typed variables (but values are typed) – implicit variable declaration – implicit type conversion – stored only as script files – compiled on demand – may run on the server (PHP) or the client (JavaScript) 10
- 11. PHP details • Procedural language – Compare with JavaScript which is event-driven • C-like syntax - { } ; • Extensive Function Library • Good Web-server integration – Script embedded in HTML – Easy access to form data and output of HTML pages • Not fully object-oriented – Java is fully object oriented – all functions have to be in a class – In PHP, classes are additional but quite simple to use 11
- 12. PHP and HTML • HTML-embedded – PHP scripts are essentially HTML pages with the occasional section of PHP script. – PHP script is enclosed in the tag pair: • <h2><?php print date(“H:I”) ?></h2> 12
- 13. C-like language • Free format - white space is ignored • Statements are terminated by semi-colon ; • Statements grouped by { … } • Comments begin with // or a set of comments /* */ • Assignment is ‘=’: $a=6 • Relational operators are ,< , > == ( not a single equal) • Control structures include if (cond) {..} else { }, while (cond) { .. } , for(sstartcond; increment; endcond) { } • Arrays are accessed with [ ] : $x[4] is the 5th element of the array $x – indexes start at 0 • Associative Arrays (hash array in Perl, dictionary in Java) are accessed in the same way: $y[“fred”] • Functions are called with the name followed by arguments in a fixed order enclosed in ( ) : substr(“fred”,0,2) • Case sensitive - $fred is a different variable to $FRED 13
- 14. Function library • Basic tasks – String Handling – Mathematics – random numbers, trig functions.. – Regular Expressions – Date and time handling – File Input and Output • And more specific functions for- – Database interaction – • MySQL, Oracle, Postgres, Sybase, MSSQL .. – Encryption – Text translation – Spell-checking – Image creation – XML 14
- 15. String Handling • String literals (constants) enclosed in double quotes “ ” or single quotes ‘ ’ • Within “”, variables are replaced by their value: – called variable interpolation. “My name is $name, I think” • Within single quoted strings, interpolation doesn’t occur • Strings are concatenated (joined end to end) with the dot operator “key”.”board” == “keyboard” • Standard functions exist: strlen(), substr() etc • Values of other types can be easily converted to and from strings – numbers implicitly converted to strings in a string context. • Regular expressions be used for complex pattern matching. 15
- 16. The basic Album Code • To help you get started on the Coursework, I have supplied a very minimal working photo album. • This illustrates such techniques as : – Creating a new member – Editing member details – Uploading a photo – Displaying a member’s photos 16
- 17. Learning PHP • Start with just the basics, installing a script to output an HTML page • Understand how PHP supports interaction with the Browser or other clients • Understand how PHP supports integration with databases – MySQL • http://www.cems.uwe.ac.uk/~cjwallac/php/ • http://www.zend.com/zend/art/index.php 17
- 18. Resources • Background – Wikipedia • PHP site – PHP home – PHP Manual • Tutorials – w3c.schools – Zend – PHP in CEMS • Examples – Basics – Basic Album – Basic Calculator 18





![Application Layer arch
• Server (Apache, IIS)
– Identifying appropriate action to take – fetch a file, pass request to an
interpreter
– Sending output back to caller in MIME package
– Support for:
• thousands of concurrent users
• multi-threading [ allow multiple processes to run concurrently]
• caching [holding results in a temporary store to reduce re-calculation]
• Server Script (e.g. in PHP)
– Interacting with the server (accessing input and generating output)
– interpreting the requests according to business rules and past
transactions from this client
– requesting the appropriate data from the Persistence layer
– computing derived data
– creating the HTML (or GIF, MIDI..) for the page
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/63-tierarchitecturephp-130401061717-phpapp02/85/6-3-tier-architecture-php-8-320.jpg)




![C-like language
• Free format - white space is ignored
• Statements are terminated by semi-colon ;
• Statements grouped by { … }
• Comments begin with // or a set of comments /* */
• Assignment is ‘=’: $a=6
• Relational operators are ,< , > == ( not a single equal)
• Control structures include if (cond) {..} else { }, while (cond) { .. } ,
for(sstartcond; increment; endcond) { }
• Arrays are accessed with [ ] : $x[4] is the 5th element of the array
$x – indexes start at 0
• Associative Arrays (hash array in Perl, dictionary in Java) are
accessed in the same way: $y[“fred”]
• Functions are called with the name followed by arguments in a fixed
order enclosed in ( ) : substr(“fred”,0,2)
• Case sensitive - $fred is a different variable to $FRED
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/63-tierarchitecturephp-130401061717-phpapp02/85/6-3-tier-architecture-php-13-320.jpg)




