Static and dynamic Page Objects with Java \ .Net examples
- 1. 1CONFIDENTIAL Static and dynamic Page Objects Anton Semenchenko
- 2. 2CONFIDENTIAL 1. Page Object – just to “refresh” 2. State-less or state-full solution - just to “refresh” 3. How to select a proper PO implementation? Agenda, part 1 (to refresh)
- 3. 3CONFIDENTIAL 1. Hypothetical project context 2. Compare complexity 3. Compare “tech” limitations 4. Compare “business” limitations 5. Rationale “business” limitations 6. How to find and “update” a balance for your own project? Agenda, part 2 (to compare)
- 4. 4CONFIDENTIAL 1. Encapsulation – the most important OOP principle 2. Refactoring 3. Refactoring and Design Patterns 4. Refactoring Catalog / Language 5. Replace Conditional with Polymorphism and vice versa 6. Replace Conditional with … more sophisticated options 7. Replace Conditional with Polymorphism – detailed description 8. How to select a proper PO implementation? Agenda, part 3 (theory)
- 5. 5CONFIDENTIAL 1. Base class, inheritance, virtual functions and overloading 2. Page Base 3. Page examples 4. Dialog Base 5. Dialog examples 6. Test Base 7. Test examples 8. Infrastructure Agenda, part 4 (practice)
- 6. 6CONFIDENTIAL 1. A real-life example 2. “Homework” 3. “Rules” and principles 4. A set of useful links 5. What’s next? 6. Questions Agenda, part 5 (take away points)
- 7. 7CONFIDENTIAL 1. Page Objects – encapsulates the way of identification and logical grouping of widgets. 2. Page Object == Logical Page 3. Page Object != Physical Page Page Object – just to “refresh”
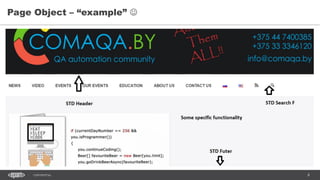
- 8. 8CONFIDENTIAL Page Object – “example”
- 9. 9CONFIDENTIAL Page Object – “example”
- 10. 10CONFIDENTIAL 1. Let’s compare: – Photo • Share – looks like parallelism (easy parallelism). – Video • Share – looks like parallelism (not trivial parallelism). State-less or state-full solution?
- 11. 11CONFIDENTIAL 1. How easy transform solution from “single” to “multi” threading (to decrease “QA Automation Windows”) – State-less – like share a photo • Just 5 minutes of work. – State-full – like share a video • Not trivial task, could be a night mare. 2. Summary – prefer state-less solutions to state-full solutions in mooooost cases; – before start implementation a state-full solution, please, take a break for a minute, and re- thing everything again, possibly you can find a proper state-less solution. State-less or state-full solution?
- 12. 12CONFIDENTIAL 1. Static class – could be implemented as a state-less solution easily 2. Object – State-full solution in 99,99% cases 3. Summary – prefer static class based solutions (state-less) to object based (state-full) in mooooost cases; – before start implementation based on objects, please, take a break for a minute, and re-thing everything again, possibly you can find a proper solution based on static classes. Object or static class State-full or state-less solution?
- 13. 13CONFIDENTIAL 1. Too complicated business logic due to Domain 2. Too complicated business logic due to System size (thousands test-cases) 3. Too many “contexts” – Browser versions – Environments – Customers with a tiny nuances of functionality – Platforms (cross-browser Web plus cross-platform Mobile) – Combination 4. Combination Page Objects – state-full, general case
- 14. 14CONFIDENTIAL 1. Web UI that behaves like a Wizard 2. Web UI in combination with Mobile in one use case 3. Internet of Things (in most cases) 4. More then 1 page during 1 test (for example several portals or several instances of one portal to implement one “business use case”): – Really seldom; – Looks like integration tests (in most cases): • Std solution- some type of White Box Testing. 5. Many others “special cases” Page Objects – state-full, special cases
- 15. 15CONFIDENTIAL How to select a proper PO implementation?
- 16. 16CONFIDENTIAL 1. 30 Physical Pages 2. Standard Header, footer and search functionality for all physical pages 3. Each Physical Page consists of – Header – H – Footer – F – Search – S – Some functionality, specific for the Page – U (unique) Hypothetical project context – to compare
- 17. 17CONFIDENTIAL 1. 33 Static Page Objects = Logical Pages 2. 0 explicit and 30 implicit Physical Pages 3. Just share 33 Static Page Objects between 30 implicit Physical Pages – For example, Header Static Page Object (static class) is used in test cases for all 30 Physical Page Objects 4. Complexity – just 33 static state-less entities (plus limitations due to state-less solutions) Compare complexity – Static Page Object based
- 18. 18CONFIDENTIAL 1. 33 Dynamic Page Objects = Logical Pages 2. It depends on implementation (one of the ways): – 0 explicit and 30 implicit Physical Pages – implicit Physical Page implements on Action layer (limitations example) – Action for Physical Page aggregates all necessary Dynamic Logical Pages • Physical Pages are implemented in a next way: create all necessary instances of logical pages, aggregate in some way, use Action layer as an point of aggregation in most cases, free resources Compare complexity – Dynamic Page Object based (option 1)
- 19. 19CONFIDENTIAL 1. 120 objects (min), each with some state, dynamically created and frees to implement necessary behavior - to implement 30 implicit Physical Pages 2. Complexity – 120 dynamic, state-full entities min (plus some limitations due to state-full solution implementation nuances) Compare complexity – Dynamic Page Object based (option 1)
- 20. 20CONFIDENTIAL 1. 33 Dynamic Page Objects = Logical Pages 2. It depends on implementation (another way): – 30 explicit Physical Pages – Multiple Interface inheritance – Combine Page Objects and Actions layer (in most cases) – Action-Physical Page (limitations example) • Implements all Logical Pages interfaces using aggregation and “delegation” • Aggregate all Dynamic Logical Page Objects • Create and frees resources (Dynamic Logical Page Objects) Compare complexity – Dynamic Page Object based (option 2)
- 21. 21CONFIDENTIAL 1. 150 objects, each with some state, dynamically created and frees to implement necessary behavior - to implement 30 explicit Physical Pages 2. Complexity – 150 dynamic, state-full not trivial entities with a multiple interface inheritance (plus some limitations due to state-full solution implementation nuances) Compare complexity – Dynamic Page Object based (option 2)
- 22. 22CONFIDENTIAL 1. Can be used together with next Design Patterns Approaches – Action (both static – preferable and dynamic) – Key-word driven – DSL – external only – BDD – partially, it depends on exact BDD engine implementation limitations 2. Can’t be used together with next Design Patterns – Factory – Flow (Fluent Interface) – Navigator (for Web) Compare “tech” limitations - Static Page Object based
- 23. 23CONFIDENTIAL 1. No limitations, but … – For example, in most cases it’s hard to isolate Action and Page Objects layers Compare “tech” limitations - Dynamic Page Object based
- 24. 24CONFIDENTIAL 1. Too complicated business logic due to Domain 2. Too complicated business logic due to System size (thousands test-cases) 3. Too many “contexts” – Browser versions – Environments – Customers with a tiny nuances of functionality – Platforms (cross-browser Web plus cross-platform Mobile) – Combination 4. Combination Compare “business” limitations - Static
- 25. 25CONFIDENTIAL 1. State-less approach - you have a conditional that chooses different behavior depending on … 2. Solution to simplify the project – refactoring “Replace Conditional with Polymorphism” 3. Polymorphism = object = State-full approach Rationale “business” limitations - Static
- 26. 26CONFIDENTIAL 1. “From refactoring to Patterns” – There is a set of specific Design Patterns 2. The trickiest part – find a balance for your project now and update point of balance in time Rationale “business” limitations - Static
- 27. 27CONFIDENTIAL 1. Relatively simple business logic due to Domain 2. Relatively simple business logic due to System size (hundreds test-cases) 3. Not so many “contexts” – Browser versions – Environments – Customers with a tiny nuances of functionality – Platforms (cross-browser Web plus cross-platform Mobile) Compare “business” limitations - Dynamic
- 28. 28CONFIDENTIAL 1. State-full approach - you have a set of objects classes, which developed, possibly, using several Design Patterns to implement necessary functionality – to choose different behavior depending on … 2. Solution to simplify the project – refactoring “Replace Polymorphism with Conditional” 3. Polymorphism ~= object ~= State-full approach 4. No Polymorphism ~= no objects ~= State-less approach Rationale “business” limitations - Dynamic
- 29. 29CONFIDENTIAL 1. “From Patterns to refactoring” – There is no need to use a set of specific Design Patterns 2. The trickiest part – find a balance for your project now and update point of balance in time Rationale “business” limitations - Dynamic
- 30. 30CONFIDENTIAL Find and “update” a balance for your own project
- 31. 31CONFIDENTIAL 1. Ask yourself "how can I hide some details from the rest of the software?“ 2. What is encapsulation? – hide variability – hide complexity – Details • "conflict of interests“ • “tech” discussions 3. Example of public member or private member + setter/getter – What is really hidden? – Where is simplicity? Encapsulation – the most important OOP principle
- 32. 32CONFIDENTIAL 1. “Refactoring is a controlled technique for improving the design of an existing code base.” 2. “Its essence is applying a series of small behavior-preserving transformations, each of which "too small to be worth doing".” 3. “The cumulative effect of each of these transformations is quite significant.” 4. “By doing Refactoring in small steps you reduce the risk of introducing errors. You also avoid having the system broken while you are carrying out the restructuring - which allows you to gradually refactor a system over an extended period of time.” Refactoring by Martin Fowler
- 33. 33CONFIDENTIAL 1. “There is a close relationship between refactoring and patterns.” 2. “Often the best way to use patterns is to gradually refactor your code to use the pattern once you realize it’s needed.” 3. “Joshua Kerievsky’s Refactoring to Patterns explores this topic, making this a great topic to learn about once you’ve got the basic refactoring's under your belt.” 4. “From Refactoring To Design Pattern” path – from pure design to adequate design 5. “From ~Design Patterns To Refactoring” path – from over design to adequate design Refactoring and Design Patterns by Martin Fowler
- 34. 34CONFIDENTIAL 1. “Refactoring to Patterns is the marriage of refactoring - the process of improving the design of existing code - with patterns, the classic solutions to recurring design problems.” 2. “Refactoring to Patterns suggests that using patterns to improve an existing design is better than using patterns early in a new design. This is true whether code is years old or minutes old.” 3. “We improve designs with patterns by applying sequences of low-level design transformations, known as refactoring's.” 4. And vice versa Refactoring and Design Patterns by Joshua Kerievsky
- 35. 35CONFIDENTIAL 1. There are more then 90 types of refactoring 2. Refactoring types that relate to a particular field is called a ”Refactoring Language” 3. ”Refactoring Language” gives a common terminology for discussing the situations specialists are faced with: – “The elements of this language are entities called Refactoring types”; – “Each type of Refactoring describes a problem that occurs over and over again in our environment”; – “Each type of Refactoring describes the core of the solution to that “~low level” problem, in such a way that you can use this solution a million times over, without ever doing it the same way twice!” Refactoring Catalog / Language
- 36. 36CONFIDENTIAL 1. You have a conditional that chooses different behavior depending on the type of an object. 2. Move each leg of the conditional to an overriding method in a subclass. Make the original method abstract. 3. And vice versa 4. Example Replace Conditional with Polymorphism and vice versa
- 37. 37CONFIDENTIAL 1. Replace Conditional Dispatcher with Command Design Pattern – Create a Command for each action. Store the Commands in a collection and replace the conditional logic with code to fetch and execute Commands. 2. Replace Conditional Logic with Strategy Design Pattern – Create a Strategy for each variant and make the method delegate the “calculation” to a Strategy instance. 3. Replace Conditional Logic with State Design Pattern – Create a State for each variant as a part of “State Machine” and make the method delegate tricky “calculation” to the “State Machine”. Replace Conditional with … more sophisticated options
- 38. 38CONFIDENTIAL 1. Problem: – You have a conditional that performs various actions depending on object type or properties. 2. Solution: – Create subclasses matching the branches of the conditional. – In them, create a shared method and move code from the corresponding branch of the conditional to it. – Replace the conditional with the relevant method call. – The result is that the proper implementation will be attained via polymorphism depending on the object class. Replace Conditional with Polymorphism – detailed description
- 39. 39CONFIDENTIAL 1. This refactoring technique can help if your code contains operators performing various tasks that vary based on: – Class of the object or interface that it implements – Value of an object's field – Result of calling one of an object's methods 2. If a new object property or type appears, you will need to search for and add code in all similar conditionals. Thus the benefit of this technique is multiplied if there are multiple conditionals scattered throughout all of an object's methods. Why refactor
- 40. 40CONFIDENTIAL 1. This technique adheres to the Tell-Don't-Ask principle: instead of asking an object about its state and then performing actions based on this, it is much easier to simply tell the object what it needs to do and let it decide for itself how to do that. 2. Removes duplicate code. You get rid of many almost identical conditionals. 3. If you need to add a new execution variant, all you need to do is add a new subclass without touching the existing code (Open/Closed Principle). Benefits
- 41. 41CONFIDENTIAL 1. For this refactoring technique, you should have a ready hierarchy of classes that will contain alternative behaviors. If you do not have a hierarchy like this, create one. Other techniques will help to make this happen: 2. Replace Type Code with Subclasses. Subclasses will be created for all values of a particular object property. This approach is simple but less flexible since you cannot create subclasses for the other properties of the object. 3. Replace Type Code with State/Strategy. A class will be dedicated for a particular object property and subclasses will be created from it for each value of the property. The current class will contain references to the objects of this type and delegate execution to them. 4. The following steps assume that you have already created the hierarchy. Preparing to Refactor
- 42. 42CONFIDENTIAL 1. If the conditional is in a method that performs other actions as well, perform Extract Method. 2. For each hierarchy subclass, redefine the method that contains the conditional and copy the code of the corresponding conditional branch to that location. 3. Delete this branch from the conditional. 4. Repeat replacement until the conditional is empty. Then delete the conditional and declare the method abstract. Refactoring Steps
- 43. 43CONFIDENTIAL 1. Follow Refactoring to Patterns or Patterns to Refactoring flows How to select a proper PO implementation?
- 44. 44CONFIDENTIAL Find and “update” a balance for your own project
- 45. 45CONFIDENTIAL Base class, inheritance, virtual functions and overloading
- 46. 46CONFIDENTIAL 1. public class PageBase { 2. protected static void titleShouldAppear(String title) { 3. Waiter.getWaiter().until(ExpectedConditions.titleIs(title)); 4. } 5. } PageBase example
- 47. 47CONFIDENTIAL 1. public class HomePage extends PageBase { 2. private static final String TITLE = "Sign Documents Online - Build, Deliver & Track Sales Collateral"; 3. public static void titleShouldAppear() { 4. titleShouldAppear(TITLE); 5. } 6. } Some page example, general
- 48. 48CONFIDENTIAL 1. private static final By LOGIN_BUTTON = get("HomePage.LoginButton"); 2. private static void clickLoginButton() { 3. $(LOGIN_BUTTON).click(); } 4. public static void login() { 5. login(USERNAME, PASSWORD); } 6. public static void login(String username, String password) { 7. clickLoginButton(); LoginPage.titleShouldAppear(); LoginPage.login(username, password);} Some page example, specific
- 49. 49CONFIDENTIAL 1. protected static void checkExpectedElements(By... locators) { 2. for (By locator : locators) { 3. $(locator).shouldBe(Condition.visible); 4. } 5. } checkExpectedElements example (base)
- 50. 50CONFIDENTIAL 1. public static void checkExpectedElements() { 2. checkExpectedElements(USERNAME_INPUT, PASSWORD_INPUT, LOGIN_BUTTON); 3. } checkExpectedElements example (derived)
- 51. 51CONFIDENTIAL 1. public class Header { 2. public static final By INFORMATION_SPAN = get("Header.InformationSpan"); 3. private static final By AVATAR_LINK = get("Header.AvatarLink"); 4. private static final By USER_INFORMATION_CONTAINER = get("Header.UserInformationContainer"); 5. private static final By LOGOUT_LINK = get("Header.LogoutLink"); 6. private static final By MENU_ICON = get("Header.MenuIcon"); 7. public static void openMenu() {$(MENU_ICON).click(); LeftMenu.shouldAppear();} Header example
- 52. 52CONFIDENTIAL 1. public class DialogBase { 2. protected static void windowShouldAppear(By window) { 3. $(window).waitUntil(Condition.appears, TIMEOUT); 4. } 5. protected static void windowShouldDisappear(By window) { 6. $(window).waitUntil(Condition.disappears, TIMEOUT); 7. } 8. } DialogBase example
- 53. 53CONFIDENTIAL 1. public class ModalDialog extends DialogBase { 2. private static final By WINDOW = get("ModalDialog.Window"); 3. public static void windowShouldAppear() { 4. windowShouldAppear(WINDOW); 5. } 6. public static void windowShouldDisappear() { 7. windowShouldDisappear(WINDOW); 8. }} Some dialog example, general
- 54. 54CONFIDENTIAL 1. public class ModalDialog extends DialogBase { 2. private static final By X_BUTTON = get("ModalDialog.XButton"); 3. public static void close() { 4. $(X_BUTTON).click(); 5. } 6. } Some dialog example, specific
- 55. 55CONFIDENTIAL 1. Base Table - ??? 2. Simple Table 3. Sorted Table 4. Filtered Table 5. Combination, for example, Filtered Sorted Table Hierarchy of Tables counter-example
- 56. 56CONFIDENTIAL 1. @BeforeTest(alwaysRun = true) 2. protected void beforeTestRunSetup() { 3. Configuration.baseUrl = URL; 4. Configuration.timeout = 10000; 5. } TestBase: BeforeTest
- 57. 57CONFIDENTIAL 1. @BeforeMethod(alwaysRun = true) 2. protected void setup() { 3. open(Configuration.baseUrl); 4. HomePage.titleShouldAppear(); 5. HomePage.login(); 6. DashboardPage.titleShouldAppear(); 7. } TestBase: BeforeMethod
- 58. 58CONFIDENTIAL 1. @AfterMethod(alwaysRun = true) 2. protected void tearDown() { 3. close(); 4. } TestBase: AfterMethod
- 59. 59CONFIDENTIAL 1. public void simpleSignInTest() { 2. HomePage.clickLoginButton(); 3. LoginPage.titleShouldAppear(); 4. LoginPage.login(USERNAME, PASSWORD); 5. DashboardPage.titleShouldAppear(); 6. } SignIn Test example
- 60. 60CONFIDENTIAL 1. public void signOutTest() { 2. HomePage.login(); 3. DashboardPage.titleShouldAppear(); 4. Header.clickOnAvatar(); 5. Header.logout(); 6. LoginPage.titleShouldAppear(); 7. } SignOut Test example
- 61. 61CONFIDENTIAL 1. @Test(groups = {"smoke"}) 2. @Features("Sign in") 3. @Stories("Verify ability to make a simple login to PandaDoc application") 4. @TestCaseId("1.1") 5. public void simpleSignInTest() “Meta” info test example 1 (SignIn)
- 62. 62CONFIDENTIAL 1. @Test(groups = {"smoke"}) 2. @Features("Sign in") 3. @Stories("Verify ability to logout from PandaDoc application") 4. @TestCaseId("1.5") 5. public void signOutTest() “Meta” info test example 2 (SignOut)
- 63. 63CONFIDENTIAL 1. public class CommonDataProvider; // ~30 lines of code 2. public class Locators; // ~ 70 lines of code 3. public class Waiter; // ~ 10 lines of code 4. That’s all Infrastructure
- 64. 64CONFIDENTIAL 1. Business context 2. Tech context – Challenge – Solution – Technology Stack 3. QA Automation process context 4. Source code example 5. Summary A real-life example
- 65. 65CONFIDENTIAL 1. Example and “home work” – How to setting up environment • “Java - set up and configuration.docx” • “Selenium WebDriver essentials.docx” • https://kb.epam.com/display/EPMCDPSITE/Pre-selection+for+Test+Automation+Mentoring+participation – Where to download (https://github.com/comaqaby/PDoc-QA-Automation-Prototype) – How to build – How to configure – How to run A real-life example
- 66. 66CONFIDENTIAL 1. Download example’ source code 2. “Investigate” 3. Develop a TODO list with a set of improvements 4. Setting up environment 5. Compile and Run 6. “Play” 7. Improve Update TODO list with a set of improvements “Homework”, part 1
- 67. 67CONFIDENTIAL 1. Read recommended books and articles 2. Improve Update TODO list with a set of improvements 3. Provide me via email with an intermediate and final list of improvements 4. Develop at least 1 more auto-test “Homework”, part 2
- 68. 68CONFIDENTIAL 1. Could you please “refresh” your knowledge, slides 30-41, thanks “Rules” and principles
- 69. 69CONFIDENTIAL 1. Martin Fowler “Refactoring” – http://martinfowler.com/books/refactoring.html – http://refactoring.com/ – http://refactoring.com/catalog/ – http://refactoring.com/catalog/replaceConditionalWithPolymorphism.html Useful links
- 70. 70CONFIDENTIAL 1. Refactoring to Patterns and vice versa – https://industriallogic.com/xp/refactoring/ – https://industriallogic.com/xp/refactoring/catalog.html – https://industriallogic.com/xp/refactoring/conditionDispatcherWithCommand.html – https://industriallogic.com/xp/refactoring/conditionalWithStrategy.html – http://martinfowler.com/books/r2p.html Useful links
- 71. 71CONFIDENTIAL 1. https://sourcemaking.com/ – https://sourcemaking.com/refactoring – https://sourcemaking.com/refactoring/replace-conditional-with-polymorphism – https://sourcemaking.com/design_patterns – https://sourcemaking.com/antipatterns • https://sourcemaking.com/antipatterns/software-development-antipatterns • https://sourcemaking.com/antipatterns/software-architecture-antipatterns – https://sourcemaking.com/uml Useful links
- 72. 72CONFIDENTIAL Tech “basement” • Grady Butch «Object oriented analysis and design with examples of apps on C++ Notes: IMHO No need to be afraid of C++, 95% of the material is conceptual, there is no strict connection to chosen language. From my point of view is one of the best books for true getting to know with OOP. • Martin Fowler «Refactoring» Notes: IMHO strongly recommend to read from cover to cover, twice, in order to have contents of the book – you active professional luggage. • Gang of four “Design patterns” Notes: IMHO strongly recommend to read from cover to cover, twice, in order to have contents of the book – you active professional luggage.
- 73. 73CONFIDENTIAL Tech “basement” • D. Thomas, Andrew Hunt “Pragmatic Programmer, The: From Journeyman to Master” Notes: IMHO Amazing book that consists of a ton of advices. IMHO strongly recommend to read from cover to cover, twice, in order to have contents of the book – you active professional luggage. And then look through different chapters before talking to a customer. • Steve McConnel “Code complete” Notes: IMHO No need to be afraid of the size of the book ... it should be read or before “going to bed”, or from any place, of separate chapters, just to fresh things in the memory in the chosen f ield of problem.
- 74. 74CONFIDENTIAL What’s next?! • “Out of box Page Object Design Pattern, Java” • Dynamic solutions • Let’s compare with a static one • “Out of box Page Object Design Pattern, .Net C#” • Dynamic solutions • Let’s compare with a static one • “Variants of implementation Page Object Design Pattern from the scratches, without being bind to any programming language” • Static solutions • Dynamic solutions • Let’s compare static and dynamic • Answer to all our questions
- 75. 75CONFIDENTIAL [email protected] Skype - semenchenko_anton_v +375 33 33 46 120 +375 44 74 00 385 https://www.linkedin.com/in/anton-semenchenko-612a926b https://www.facebook.com/semenchenko.anton.v https://twitter.com/comaqa www.comaqa.by www.corehard.by
- 76. 76CONFIDENTIAL Thanks for your attention Anton Semenchenko EPAM Systems www.comaqa.by www.corehard.by
- 77. 77CONFIDENTIAL