Subneting
- 1. 1
- 2. Example – 2 Class C : N.N.N.H 110xxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx Class C : 192.168.1.0 • No. = = = = of Subnet 2n – 2 22 – 2 4–2 2 Subnet • No. = = = = of Host 2h – 2 (-2 is for Network ID & Broadcast ID) 26 – 2 64 – 2 62 Hosts/Subnet 2 HELP
- 3. Example – 2 (Continued…) • Customize Subnet Mask = Bits to Network Bits If you convert 2 Host If you convert 2 Host Bits to Network Bits 255. 255. 192 2 Subnet & 62 Hosts/Subnet Subnet & 255. 62 Hosts/Subnet 2 1 2 8 6 4 11111111 11111111 11111111 11000000 Customize Subnet Mask . . . Customize Subnet Mask 255.255.255.192 255.255.255.192 • Range of Networks Network ID Broadcast ID Subnet Range Range – Subnet 192.168.1.63 x 192.168.1.0 192.168.1.64 to 192.168.1.127 192.168.1.64 to 192.168.1.127 192.168.1.64 – 192.168.1.127 192.168.1.128 to 192.168.1.191 Valid Subnets 192.168.1.128 to 192.168.1.191 192.168.1.128 – 192.168.1.191 192.168.1.192 – 192.168.1.255 x 3
- 4. Example – 3 Class C : N.N.N.H 110xxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx Class C : 192.168.1.0 • No. = = = = of Subnet 2n – 2 25 – 2 32 – 2 30 Subnet • No. = = = = of Host 2h – 2 (-2 is for Network ID & Broadcast ID) 23 – 2 8–2 6 Hosts/Subnet 4 HELP
- 5. Example – 3 (Continued…) • Customize Subnet Mask = Bits to Network Bits If you convert 5 Host If you convert 5 Host Bits to Network Bits 255. 255. 255. 248 30 Subnet & 6 Hosts/Subnet Subnet & 6 Hosts/Subnet 30 1 2 8 6 4 3 2 1 6 8 11111111 11111111 11111111 11111000 Customize Subnet Mask . . . Customize Subnet Mask 255.255.255.248 255.255.255.248 • Range of Networks Network ID Broadcast ID Subnet Range Subnet Range x – 192.168.1.7 192.168.1.0 192.168.1.8 to 192.168.1.15 to 192.168.1.15 192.168.1.8 192.168.1.8 – 192.168.1.15 192.168.1.16 to 192.168.1.23 192.168.1.16 to 192.168.1.23 192.168.1.16 – 192.168.1.23 192.168.1.24 to 192.168.1.31 192.168.1.24 to 192.168.1.31 192.168.1.24 – 192.168.1.31 192.168.1.32 to 192.168.1.39 192.168.1.32 to 192.168.1.39Valid Subnets 192.168.1.240 – 192.168.1.247 192.168.1.240 to 192.168.1.247 192.168.1.240 to 192.168.1.247 192.168.1.248 – 192.168.1.255 x 5
- 6. Example – 4 Class C : N.N.N.H 110xxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx Class C : 192.168.1.0 • No. = = = = of Subnet 2n – 2 26 – 2 64 – 2 62 Subnet • No. = = = = of Host 2h – 2 (-2 is for Network ID & Broadcast ID) 22 – 2 4–2 2 Hosts/Subnet 6 HELP
- 7. Example – 4 (Continued…) • Customize Subnet Mask = Bits to Network Bits If you convert 6 Host If you convert 6 Host Bits to Network Bits 255. 255. 255. 252 62 Subnet & 2 Hosts/Subnet Subnet & 2 Hosts/Subnet 62 1 2 8 6 4 3 2 1 6 8 4 11111111 11111111 11111111 11111100 Customize Subnet Mask . . . Customize Subnet Mask 255.255.255.252 255.255.255.252 • Range of Networks Network ID Broadcast ID Subnet Range Subnet Range x – 192.168.1.3 192.168.1.0 192.168.1.4 to 192.168.1.7 to 192.168.1.7 192.168.1.4 192.168.1.4 – 192.168.1.7 192.168.1.8 to 192.168.1.11 192.168.1.8 to 192.168.1.11 192.168.1.8 – 192.168.1.11 192.168.1.12 to 192.168.1.15 192.168.1.12 to 192.168.1.15 192.168.1.12 – 192.168.1.15 192.168.1.16 to 192.168.1.19 192.168.1.16 to 192.168.1.19Valid Subnets 192.168.1.248 – 192.168.1.251 192.168.1.248 to 192.168.1.251 192.168.1.248 to 192.168.1.251 192.168.1.252 – 192.168.1.255 x 7
- 8. Example – 5 Class C : N.N.N.H 110xxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx Class C : 192.168.1.0 • No. = = = = of Subnet 2n – 2 27 – 2 128 – 2 126 Subnet • No. of Host = 2h – 2 (-2 is for Network ID & Broadcast ID) = 21 – 2 = 2 – 2 = 0 Hosts/Subnet • In this case, You are not getting any host when you convert 7 host bit to network bit. 8 HELP
- 9. Example – 6 Class C : N.N.N.H 110xxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx Class C : 192.168.1.0 • No. = = = = of Subnet 2n – 2 28 – 2 256 – 2 254 Subnet • No. of Host = 2h – 2 (-2 is for Network ID & Broadcast ID) = 20 – 2 = 0 – 2 = -2 Hosts/Subnet • In this case, You are not getting any host when you convert 8 host bit to network bit. 9 HELP
- 10. Requirement of Hosts is 40 ? Example – 1 Class C : N.N.N.H 110xxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx Class C : 192.168.1.0 • No. of Host = 2h – 2 ≥ Req. of Host = 26 – 2 ≥ 40 (-2 is for Network ID & Broadcast ID) = 64 – 2 = 62 Hosts/Subnet • No. of Subnet = = = = 2n – 2 (-2 is for First & Last Subnet Range) 22 – 2 4–2 2 Subnet 10 HELP
- 11. Example – 1 (Continued…) • Customize Subnet Mask = Bits to Network Bits If you convert 2 Host If you convert 2 Host Bits to Network Bits 255. 255. 192 2 Subnet & 62 Hosts/Subnet Subnet & 255. 62 Hosts/Subnet 2 1 2 8 6 4 11111111 11111111 11111111 11000000 Customize Subnet Mask . . . Customize Subnet Mask 255.255.255.192 255.255.255.192 • Range of Networks Network ID Broadcast ID Subnet Range Range – Subnet 192.168.1.63 x 192.168.1.0 192.168.1.64 to 192.168.1.127 192.168.1.64 to 192.168.1.127 192.168.1.64 – 192.168.1.127 192.168.1.128 to 192.168.1.191 Valid Subnets 192.168.1.128 to 192.168.1.191 192.168.1.128 – 192.168.1.191 192.168.1.192 – 192.168.1.255 x 11
- 12. Requirement of Hosts is 2 ? Example – 2 Class C : N.N.N.H 110xxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx Class C : 192.168.1.0 • No. of Host = 2h – 2 ≥ Req. of Host = 22 – 2 ≥ 2 (-2 is for Network ID & Broadcast ID) = 4–2 = 2 Hosts/Subnet • No. of Subnet = = = = 2n – 2 (-2 is for First & Last Subnet Range) 26 – 2 64 – 2 62 Subnet 12 HELP
- 13. Example – 2 (Continued…) • Customize Subnet Mask = 255. 255. 255. 252 1 2 8 6 4 3 2 1 6 8 4 11111111 11111111 11111111 11111100 . . . • Range of Networks Network ID – 192.168.1.0 192.168.1.4 – 192.168.1.8 – 192.168.1.12 – 192.168.1.248 192.168.1.252 – – Broadcast ID 192.168.1.3 192.168.1.7 192.168.1.11 192.168.1.15 x 192.168.1.251 192.168.1.255 x Valid Subnets 13
- 14. Cisco / Notation Example – 1 Class C : N.N.N.H 110xxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx Class C : 192.168.1.0/29 Extra Network Bits = 29 – 24 = 5 Put n value = 5 • No. = = = = • No. = = = = of Subnet 2n – 2 25 – 2 (-2 is for First & Last Subnet Range) 32 – 2 30 Subnet of Host 2h – 2 (-2 is for Network ID & Broadcast ID) 23 – 2 8–2 6 Hosts/Subnet 14 HELP
- 15. Example – 1 (Continued…) • Customize Subnet Mask = Bits to Network Bits If you convert 5 Host If you convert 5 Host Bits to Network Bits 255. 255. 255. 248 30 Subnet & 6 Hosts/Subnet Subnet & 6 Hosts/Subnet 30 1 2 8 6 4 3 2 1 6 8 11111111 11111111 11111111 11111000 Customize Subnet Mask . . . Customize Subnet Mask 255.255.255.248 255.255.255.248 • Range of Networks Network ID Broadcast ID Subnet Range Subnet Range x – 192.168.1.7 192.168.1.0 192.168.1.8 to 192.168.1.15 to 192.168.1.15 192.168.1.8 192.168.1.8 – 192.168.1.15 192.168.1.16 to 192.168.1.23 192.168.1.16 to 192.168.1.23 192.168.1.16 – 192.168.1.23 192.168.1.24 to 192.168.1.31 192.168.1.24 to 192.168.1.31 192.168.1.24 – 192.168.1.31 192.168.1.32 to 192.168.1.39 192.168.1.32 to 192.168.1.39Valid Subnets 192.168.1.240 – 192.168.1.247 192.168.1.240 to 192.168.1.247 192.168.1.240 to 192.168.1.247 192.168.1.248 – 192.168.1.255 x 15
- 16. Cisco / Notation Example – 2 Class C : N.N.N.H 110xxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx Class C : 192.168.1.0/28 Extra Network Bits = 28 – 24 = 4 Put n value = 4 • No. = = = = • No. = = = = of Subnet 2n – 2 24 – 2 (-2 is for First & Last Subnet Range) 16 – 2 14 Subnet of Host 2h – 2 (-2 is for Network ID & Broadcast ID) 24 – 2 16 – 2 14 Hosts/Subnet 16 HELP
- 17. Example – 2 (Continued…) • Customize Subnet Mask = Bits to Network Bits If you convert 4 Host If you convert 4 Host Bits to Network Bits 255. 255. 240 14 Subnet & 255.Hosts/Subnet Subnet & 14 Hosts/Subnet 14 14 1 2 8 6 4 3 2 1 6 11111111 11111111 11111111 11110000 Customize Subnet Mask . . . Customize Subnet Mask 255.255.255.240 255.255.255.240 • Range of Networks Network ID Broadcast ID Subnet Range Subnet Range – 192.168.1.15 x 192.168.1.0 192.168.1.16 to 192.168.1.31 192.168.1.16 to 192.168.1.31 192.168.1.16 – 192.168.1.31 192.168.1.32 to 192.168.1.47 192.168.1.32 to 192.168.1.47 192.168.1.32 – 192.168.1.47 192.168.1.48 to 192.168.1.63 192.168.1.48 to 192.168.1.63 192.168.1.48 – 192.168.1.63 192.168.1.64 to 192.168.1.80 192.168.1.64 to 192.168.1.80Valid Subnets 192.168.1.224 – 192.168.1.239 192.168.1.224 to 192.168.1.239 192.168.1.224 to 192.168.1.239 192.168.1.240 – 192.168.1.255 x 17
- 18. Requirement of Networks is 2 ? Example – 1 Class B : N.N.H.H 10xxxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx Class B : 172.16.0.0 • No. = = = = • No. = = = = of Subnet 2n – 2 ≥ Req. of Subnet 22 – 2 ≥ 2 (-2 is for First & Last Subnet Range) 4–2 2 Subnet of Host 2h – 2 (-2 is for Network ID & Broadcast ID) 214 – 2 16384 – 2 16382 Hosts/Subnet 18 HELP
- 19. Example – 1 (Continued…) • Customize Subnet Mask = Bits to Network Bits If you convert 2 Host If you convert 2 Host Bits to Network Bits 255. 255. 192. 0 2 Subnet & 16382 Hosts/Subnet Subnet & 16382 Hosts/Subnet 2 1 2 8 6 4 11111111 11111111 11000000 00000000 Customize Subnet Mask . . . Customize Subnet Mask 255.255.192.0 255.255.192.0 • Range of Networks Network ID Broadcast ID Subnet Range Range – Subnet 172.16.63.255 x 172.16.0.0 172.16.64.0 to 172.16.127.255 to 172.16.127.255 172.16.64.0172.16.127.255 172.16.64.0 – 172.16.128.0 to 172.16.191.255 to 172.16.191.255 Valid Subnets 172.16.128.0172.16.191.255 172.16.128.0 – 172.16.192.0 – 192.168.1.255 x 19
- 20. Requirement of Hosts is 126 ? Example – 2 Class B : N.N.H.H 10xxxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx Class B : 172.16.0.0 • No. of Host = 2h – 2 ≥ Req. of Host = 27 – 2 ≥ 126 (-2 is for Network ID & Broadcast ID) = 128 – 2 = 126 Hosts/Subnet • No. of Subnet = = = = 2n – 2 (-2 is for First & Last Subnet Range) 29 – 2 512 – 2 510 Subnet 20 HELP
- 21. Example – 2 (Continued…) • Customize Subnet Mask = Bits to Network Bits If you convert 9 Host If you convert 9 Host Bits to Network Bits 255. 255. 128 510 Subnet & 255. Hosts/Subnet Subnet & 126 Hosts/Subnet 126 510 1 2 8 11111111 11111111 11111111 10000000 Customize Subnet Mask . . . Customize Subnet Mask 255.255.255.128 255.255.255.128 • Range of Networks Network ID Broadcast ID Subnet Range Subnet Range x – 172.16.0.127 172.16.0.0 172.16.0.128 to 172.16.0.255 to 172.16.0.255 172.16.0.128 172.16.0.128 – 172.16.0.255 172.16.1.0 to 172.16.1.127 172.16.1.0 to 172.16.1.127 172.16.1.0 – 172.16.1.127 172.16.1.128 to 172.16.1.255 172.16.1.128 to 172.16.1.255 172.16.1.128 – 172.16.1.255 172.16.2.0 to 172.16.2.127 172.16.2.0 to 172.16.2.127 Valid Subnets 172.16.255.0 – 172.16.255.127 172.16.255.0 to 172.16.255.127 172.16.255.0 to 172.16.255.127 172.16.255.128 – 172.16.255.255 x 21
- 22. Cisco / Notation Example – 3 Class B : N.N.H.H 10xxxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx Class B : 172.16.0.0/22 Extra Network Bits = 22 – 16 = 6 Put n value = 6 • No. = = = = • No. = = = = of Subnet 2n – 2 26 – 2 (-2 is for First & Last Subnet Range) 64 – 2 62 Subnet of Host 2h – 2 (-2 is for Network ID & Broadcast ID) 210 – 2 1024 – 2 1022 Hosts/Subnet 22 HELP
- 23. Example – 3 (Continued…) • Customize Subnet Mask = Bits to Network Bits If you convert 6 Host If you convert 6 Host Bits to Network Bits 255. 252. 0 62255. Subnet & 1022 Hosts/Subnet & 1022 Hosts/Subnet 62 Subnet 1 2 8 6 4 3 2 1 6 8 4 11111111 11111111 11111100 00000000 Customize Subnet Mask . . . Customize Subnet Mask 255.255.252.0 255.255.252.0 • Range of Networks Network ID Broadcast ID Subnet Range Subnet Range x – 172.16.3.255 172.16.0.0 172.16.4.0 to 172.16.7.255 to 172.16.7.255 172.16.4.0 172.16.4.0172.16.7.255 – 172.16.8.0 to 172.16.11.255 to 172.16.11.255 172.16.8.0172.16.11.255 172.16.8.0 – 172.16.12.0 to 172.16.15.255 to 172.16.15.255 172.16.12.0172.16.15.255 172.16.12.0 – 172.16.16.0 to 172.16.19.255 172.16.16.0 to 172.16.19.255 Valid Subnets 172.16.248.0 – 172.16.251.255 172.16.248.0 to 172.16.251.255 to 172.16.251.255 172.16.248.0172.16.255.255 x 172.16.252.0 – 23
- 24. Requirement of Networks is 500 ? Example – 1 Class A : N.H.H.H 0xxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx Class A : 10.0.0.0 • No. = = = = • No. = = = = of Subnet 2n – 2 ≥ Req. of Subnet 29 – 2 ≥ 500 (-2 is for First & Last Subnet Range) 512 – 2 510 Subnet of Host 2h – 2 (-2 is for Network ID & Broadcast ID) 215 – 2 32768 – 2 32766 Hosts/Subnet 24 HELP
- 25. Example – 1 (Continued…) • Customize Subnet Mask = Bits to Network Bits If you convert 9 Host If you convert 9 Host Bits to Network Bits 255. 510255. 128. 0 Subnet & 32766 Hosts/Subnet & 32766 Hosts/Subnet 510 Subnet 1 2 8 11111111 11111111 10000000 00000000 Customize Subnet Mask . . . Customize Subnet Mask 255.255.128.0 255.255.128.0 • Range of Networks Network ID Broadcast ID Subnet Range Subnet Range x – 10.0.127.255 10.0.0.0 10.0.128.0 to 10.0.255.255 to 10.0.255.255 10.0.128.0 10.0.128.010.0.255.255 – 10.1.0.0 to 10.1.127.255 to 10.1.127.255 10.1.0.010.1.127.255 10.1.0.0 – 10.1.128.0 to 10.1.255.255 to 10.1.255.255 10.1.128.010.1.255.255 10.1.128.0 – 10.2.0.0 to 10.2.127.255 10.2.0.0 to 10.2.127.255 Valid Subnets 10.255.0.0 – 10.255.127.255 10.255.0.0 to 10.255.127.255 to 10.255.127.255 10.255.0.0 10.255.255.255 x 10.255.128.0 – 25
- 26. Requirement of Hosts is 260000 ? Example – 2 Class A : N.H.H.H 0xxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx Class A : 10.0.0.0 • No. of Host = 2h – 2 ≥ Req. of Host = 218 – 2 ≥ 260000 (-2 is for Network ID & Broadcast ID) = 262144 – 2 = 262142 Hosts/Subnet • No. of Subnet = = = = 2n – 2 (-2 is for First & Last Subnet Range) 26 – 2 64 – 2 62 Subnet 26 HELP
- 27. Example – 2 (Continued…) • Customize Subnet Mask = Bits to Network Bits If you convert 6 Host If you convert 6 Host Bits to Network Bits 255. 62 Subnet & 262142 Hosts/Subnet 252. 0. 0 62 Subnet & 262142 Hosts/Subnet 1 2 8 6 4 3 2 1 6 8 4 11111111 11111100 00000000 00000000 Customize Subnet Mask . . . Customize Subnet Mask 255.252.0.0 255.252.0.0 • Range of Networks Network ID Broadcast ID Subnet Range Subnet Range x – 10.3.255.255 10.0.0.0 10.4.0.0 to 10.3.255.255 to 10.3.255.255 10.4.0.0 10.7.255.255 10.4.0.0 – 10.8.0.0 to 10.7.255.255 to 10.7.255.255 10.8.0.0 10.11.255.255 10.8.0.0 – 10.12.0.0 to 10.15.255.255 to 10.15.255.255 10.12.0.0 10.15.255.255 10.12.0.0 – 10.16.0.0 to 10.19.255.255 10.16.0.0 to 10.19.255.255 Valid Subnets 10.248.0.0 – 10.251.255.255 10.248.0.0 to 10.251.255.255 10.248.0.0 to 10.251.255.255 10.252.0.0 – 10.255.255.255 x 27
- 28. Cisco / Notation Example – 3 Class A : N.H.H.H 0xxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx Class B : 10.0.0.0/20 Extra Network Bits = 20 – 8 = 12 Put n value = 12 • No. = = = = • No. = = = = of Subnet 2n – 2 212 – 2 (-2 is for First & Last Subnet Range) 4096 – 2 4094 Subnet of Host 2h – 2 (-2 is for Network ID & Broadcast ID) 212 – 2 4096 – 2 4094 Hosts/Subnet 28 HELP
- 29. Example – 3 (Continued…) • Customize Subnet Mask = Bits to Network Bits If you convert 12 Host If you convert 12 Host Bits to Network Bits 255. 4094 Subnet & 4094 Hosts/Subnet 255. 240. 0 4094 Subnet & 4094 Hosts/Subnet 1 2 8 6 4 3 2 1 6 11111111 11111111 11110000 00000000 Customize Subnet Mask . . . Customize Subnet Mask 255.255.240.0 255.255.240.0 • Range of Networks Network ID Broadcast ID Subnet Range Subnet Range x – 10.0.15.255 10.0.0.0 10.0.16.0 to 10.31.255.255 to 10.31.255.255 10.0.16.0 10.0.31.255 10.0.16.0 – 10.0.32.0 to 10.47.255.255 to 10.47.255.255 10.0.32.0 10.0.47.255 10.0.32.0 – 10.0.48.0 to 10.63.255.255 to 10.63.255.255 10.0.48.0 10.0.63.255 10.0.48.0 – 10.0.64.0 to 10.79.255.255 10.0.64.0 to 10.79.255.255 Valid Subnets 10.255.224.0 – 10.255.239.255 10.255.224.0 to 10.255.239.255 to 10.255.239.255 10.255.224.010.255.255.255 x 10.255.240.0 – 29
- 30. VLSM • Subnetting a subnet is called as Variable Length Subnet Mask • VLSMs provide the capability to include more than one subnet mask within a major network 30
- 31. Scenario ZOOM Technologies is having 100 PC • ZOOM Technologies – 192.168.1.0/24 – MCSE – CISCO – FIREWALL – SOLARIS – TRAINING • Administrator wants inter-department communication should not be possible ? What is best the solution ? Answer : You will go for FLSM i.e. Subnetting 31
- 32. Scenario (…continued) Now we are also having sub departments ZOOM Technologies – MCSE – CISCO – Ccna – Ccnp – FIREWALL – ISA – Checkpoint – Net SQ – Clavister – Cisco PIX – SOLARIS – Linux – Unix – Solaris – TRAINING 32
- 33. Scenario (…continued) Now we are also having sub departments ZOOM Technologies – MCSE – CISCO – Ccna – Ccnp – FIREWALL – ISA – Checkpoint – Net SQ – Clavister – Cisco PIX – SOLARIS – Linux – Unix – Solaris – TRAINING 33
- 34. Scenario (…continued) • Administrator does not want inter-department communication in the sub departments ? Answer : You will use the subnet range to further divide it into smaller ranges, this time its Subnetting of a Subnet i.e. VLSM. 34
- 35. Calculation of FLSM Class C : N.N.N.H 110xxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx Class C : 192.168.1.0 • No. = = = = • No. = = = = of Subnet 2n – 2 ≥ Req. of Subnet 23 – 2 ≥ 5 (-2 is for First & Last Subnet Range) 8–2 6 Subnet of Host 2h – 2 (-2 is for Network ID & Broadcast ID) 25 – 2 32 – 2 30 Hosts/Subnet 35 HELP
- 36. FLSM (Continued…) • Customize Subnet Mask = Bits to Network Bits If you convert 3 Host If you convert 3 Host Bits to Network Bits 255. 255. 224 6 Subnet & 30 Hosts/Subnet Subnet & 255. 30 Hosts/Subnet 6 1 2 8 6 4 3 2 11111111 11111111 11111111 11100000 Customize Subnet Mask . . . Customize Subnet Mask 255.255.255.224 255.255.255.224 • Range of Networks Network ID Broadcast ID Subnet Range Subnet Range 192.168.1.31 x 192.168.1.0 192.168.1.32 to 192.168.1.63. 192.168.1.32 to 192.168.1.63. 192.168.1.32 192.168.1.63 192.168.1.64 to 192.168.1.95 192.168.1.64 to 192.168.1.95 192.168.1.64 192.168.1.95 192.168.1.96 to 192.168.1.127 192.168.1.96 to 192.168.1.127 192.168.1.96 192.168.1.127 192.168.1.128 to 192.168.1.159 Valid Subnets 192.168.1.128 to 192.168.1.159 192.168.1.128 192.168.1.159 192.168.1.160 to 192.168.1.191 192.168.1.160 to 192.168.1.191 192.168.1.160 192.168.1.191 192.168.1.192 to 192.168.1.223 192.168.1.192 to 192.168.1.223 192.168.1.192 192.168.1.223 192.168.1.224 192.168.1.255 x 36
- 37. Assigning of the Ranges ZOOM Technologies 192.168.1.32 – 1.63/27 – MCSE – CISCO 192.168.1.64 – 1.95/27 – Ccna – Ccnp 192.168.1.96 – 1.127/27 – FIREWALL – ISA – Checkpoint – Net SQ – Clavister – Cisco PIX 192.168.1.128 – 1.159/27 – SOLARIS – Linux – Unix – Solaris – TRAINING 192.168.1.160 – 1.191/27 37
- 38. Calculation of VLSM for CISCO Dept. Class C : N.N.N.H 110xxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx Class C : 192.168.1.64 • No. = = = = • No. = = = = of Subnet 2n ≥ Req. of Subnet 21 ≥ 2 2 2 Subnet of Host 2h – 2 (-2 is for Network ID & Broadcast ID) 24 – 2 16 – 2 14 Hosts/Subnet 38 HELP
- 39. VLSM (Continued…) • Customize convert Mask = Host Bit to Network Bit If you convert 1 more Host Bit to Network Bit you Subnet 1 more If 255. 255. 240 2 Subnet & 14 Hosts/Subnet Subnet & 255. 14 Hosts/Subnet 2 1 2 8 6 4 3 2 1 6 11111111 11111111 11111111 11110000 Customize Subnet Mask . . . Customize Subnet Mask 255.255.255.240 255.255.255.240 • Range of Networks Network ID Broadcast ID Subnet Range Subnet Range – 192.168.1.79 192.168.1.64 192.168.1.64 to 192.168.1.79 192.168.1.64 to 192.168.1.79 Valid Subnets 192.168.1.80 – 192.168.1.95 192.168.1.80 to 192.168.1.95 192.168.1.80 to 192.168.1.95 39
- 40. Assigning of the Ranges ZOOM Technologies 192.168.1.32 – 1.63/27 – MCSE – CISCO 192.168.1.64 – 1.95/27 192.168.1.64 – 1.79/28 – Ccna 192.168.1.80 – 1.95/28 – Ccnp 192.168.1.96 – 1.127/27 – FIREWALL – ISA – Checkpoint – Net SQ – Clavister – Cisco PIX 192.168.1.128 – 1.159/27 – SOLARIS – Linux – Unix – Solaris – TRAINING 192.168.1.160 – 1.191/27 40
- 41. Calculation of VLSM for Firewall Dept. Class C : N.N.N.H 110xxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx Class C : 192.168.1.96 • No. = = = = • No. = = = = of Subnet 2n ≥ Req. of Subnet 23 ≥ 5 8 8 Subnet of Host 2h – 2 (-2 is for Network ID & Broadcast ID) 22 – 2 4–2 2 Hosts/Subnet 41 HELP
- 42. VLSM (Continued…) • Customize convert Mask = Host Bit to Network Bit If you convert 3 more Host Bit to Network Bit you Subnet 3 more If 255. 255. 252 8 Subnet & 255. Subnet & 2 Hosts/Subnet 2 Hosts/Subnet 8 1 2 8 6 4 3 2 1 6 8 4 11111111 11111111 11111111 11111100 Customize Subnet Mask Customize Subnet Mask . . . 255.255.255.252 255.255.255.252 • Range of Networks Network ID Broadcast Subnet Range Subnet Range ID – 192.168.1.99 192.168.1.96 192.168.1.96 to 192.168.1.99 192.168.1.96 to 192.168.1.99 192.168.1.100 – 192.168.1.103 192.168.1.100 to 192.168.1.103 192.168.1.100 to 192.168.1.103 192.168.1.104 – 192.168.1.107 192.168.1.104 to 192.168.1.107 192.168.1.104 to 192.168.1.107 192.168.1.108 – 192.168.1.111 192.168.1.108 to 192.168.1.111 Valid Subnets 192.168.1.108 to 192.168.1.111 192.168.1.112 – 192.168.1.115 192.168.1.112 to 192.168.1.115 192.168.1.112 to 192.168.1.115 192.168.1.116 – 192.168.1.119 192.168.1.116 to 192.168.1.119 192.168.1.116 to 192.168.1.119 192.168.1.120 – 192.168.1.123 192.168.1.120 to 192.168.1.123 192.168.1.120 to 192.168.1.123 192.168.1.124 – 192.168.1.127 192.168.1.124 to 192.168.1.127 192.168.1.124 to 192.168.1.127 42
- 43. Assigning of the Ranges ZOOM Technologies 192.168.1.32 – 1.63/27 – MCSE – CISCO 192.168.1.64 – 1.95/27 192.168.1.64 – 1.79/28 – Ccna 192.168.1.80 – 1.95/28 – Ccnp 192.168.1.96 – 1.127/27 – FIREWALL 192.168.1.96 – 1.99/30 – ISA 192.168.1.100 – 1.103/30 – Checkpoint 192.168.1.104 – 1.107/30 – Net SQ 192.168.1.108 – 1.111/30 – Clavister 192.168.1.112 – 1.115/30 – Cisco PIX 192.168.1.128 – 1.159/27 – SOLARIS – Linux – Unix – Solaris – TRAINING 192.168.1.160 – 1.191/27 43
- 44. Calculation of VLSM for Solaris Dept. Class C : N.N.N.H 110xxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx Class C : 192.168.1.128 • No. = = = = • No. = = = = of Subnet 2n ≥ Req. of Subnet 22 ≥ 3 4 4 Subnet of Host 2h – 2 (-2 is for Network ID & Broadcast ID) 23 – 2 8–2 6 Hosts/Subnet 44 HELP
- 45. VLSM (Continued…) • Customize convert Mask = Host Bit to Network Bit If you convert 2 more Host Bit to Network Bit you Subnet 2 more If 255. 255. 248 4 Subnet & 255. Subnet & 6 Hosts/Subnet 6 Hosts/Subnet 4 1 2 8 6 4 3 2 1 6 8 11111111 11111111 11111111 11111000 Customize Subnet Mask Customize Subnet Mask . . . 255.255.255.248 255.255.255.248 • Range of Networks Network ID Broadcast Subnet Range Subnet Range ID 192.168.1.135 192.168.1.128 – 192.168.1.128 to 192.168.1.135 192.168.1.128 to 192.168.1.135 192.168.1.136 – 192.168.1.143 192.168.1.136 to 192.168.1.143 192.168.1.136 to 192.168.1.143 Valid Subnets 192.168.1.144 – 192.168.1.151 192.168.1.144 to 192.168.1.151 to 192.168.1.151 192.168.1.144 192.168.1.152 – 192.168.1.159 192.168.1.152 to 192.168.1.159 192.168.1.152 to 192.168.1.159 45
- 46. Assigning of the Ranges ZOOM Technologies 192.168.1.32 – 1.63/27 – MCSE – CISCO 192.168.1.64 – 1.95/27 192.168.1.64 – 1.79/28 – Ccna 192.168.1.80 – 1.95/28 – Ccnp 192.168.1.96 – 1.127/27 – FIREWALL 192.168.1.96 – 1.99/30 – ISA 192.168.1.100 – 1.103/30 – Checkpoint 192.168.1.104 – 1.107/30 – Net SQ 192.168.1.108 – 1.111/30 – Clavister 192.168.1.112 – 1.115/30 – Cisco PIX 192.168.1.128 – 1.159/27 – SOLARIS 192.168.1.128 – 1.135/29 – Linux 192.168.1.136 – 1.143/29 – Unix 192.168.1.144 – 1.51/29 – Solaris – TRAINING 192.168.1.160 – 1.191/27 46
- 48. CIDR Classless Inter Domain Routing • It is reverse (inverse) of Subnetting • Combining of Multiple Networks to Single Networks • Converting Network Bits to Hosts Bits i.e. Converting 1’s into 0’s • Generally design for Class C networks • Easier Summarization • It is also known as Supernetting 48
- 50. Requirement of Hosts is 1000 ? Example – 1 Class C : N.N.N.H 110xxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx Class C : 192.168.0.0 • No. of Host = 2h – 2 ≥ Req. of Host = 210 – 2 ≥ 1000 (-2 is for Network ID & Broadcast ID) = 1024 – 2 = 1022 Hosts/Subnet 50 HELP
- 51. Example – 1 (Continued…) • Customize Subnet Mask = 255. 255. 252. 0 1 2 8 6 4 3 2 1 6 8 4 11111111 11111111 11111100 00000000 . . . • Range of Networks Network ID – 192.168.0.0 192.168.4.0 – 192.168.8.0 – 192.168.12.0 – 192.168.248.0 192.168.252.0 – – Broadcast ID 192.168.3.255 192.168.7.255 192.168.11.255 192.168.15.255 192.168.251.255 192.168.255.255 Valid Subnets 51
- 52. Requirement of Hosts is 12000 ? Example – 2 Class C : N.N.N.H 110xxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx Class C : 192.168.0.0 • No. of Host = 2h – 2 ≥ Req. of Host = 214 – 2 ≥ 12000 (-2 is for Network ID & Broadcast ID) = 16384 – 2 = 16382 Hosts/Subnet 52 HELP
- 53. Example – 2 (Continued…) • Customize Subnet Mask = 255. 255. 192. 0 1 2 8 6 4 11111111 11111111 11000000 00000000 . . . • Range of Networks Network ID – 192.168.0.0 192.168.64.0 – 192.168.128.0 – 192.168.192.0 – Broadcast ID 192.168.63.255 192.168.127.255 192.168.191.255 192.168.255.255 53
- 54. Example – 1 (Continued…) • Customize Subnet Mask = 255. 255. 252. 0 1 2 8 6 4 3 2 1 6 8 4 11111111 11111111 11111100 00000000 . . . • Range of Networks Network ID – 192.168.0.0 192.168.4.0 – 192.168.8.0 – 192.168.12.0 – 192.168.248.0 192.168.252.0 – – Broadcast ID 192.168.3.255 192.168.7.255 192.168.11.255 192.168.15.255 192.168.251.255 192.168.255.255 Valid Subnets 54
- 55. 55
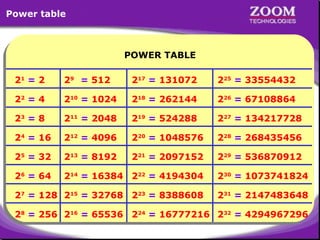
- 56. Power table POWER TABLE POWER TABLE 21 = 2 29 = 512 217 = 131072 225 = 33554432 22 = 4 210 = 1024 218 = 262144 226 = 67108864 23 = 8 211 = 2048 219 = 524288 227 = 134217728 24 = 16 212 = 4096 220 = 1048576 228 = 268435456 25 = 32 213 = 8192 221 = 2097152 229 = 536870912 26 = 64 214 = 16384 222 = 4194304 230 = 1073741824 27 = 128 215 = 32768 223 = 8388608 231 = 2147483648 28 = 256 216 = 65536 224 = 16777216 232 = 4294967296 56