Subnetting and routing
- 1. SUBNET & ROUTING Sritrusta Sukaridhoto Lecturer Pens EEPIS-ITS
- 2. Netmask / Subnet mask tutorial
- 4. IP addressing • • • • Introduction to IP addressing Classes of IP addressing Why Subnet Masks are necessary? How to create subnet masks Subnet & Routing 4
- 5. Why are IP addresses written as bits? • In order for data to pass along the media, it must first be changed to electrical impulses. • When a computer receives these electrical impulses, it recognizes two things: the presence of voltage on the wire or the absence of voltage on the wire. Subnet & Routing 5
- 7. What format do IP addresses use? Subnet & Routing 7
- 8. How are IP addresses expressed in dotted notation? Subnet & Routing 8
- 9. Why are IP addresses necessary? • IP addressing makes it possible for data passing over the network media of the Internet to find its destination. • Because each IP address is a 32-bit value, that means that there are four billion different IP address possibilities. • IP addresses are hierarchical addresses like phone numbers and zip codes. Subnet & Routing 9
- 10. How do IP addresses make it possible for data sent via the Internet to find its destination? • It is because each network connected to the Internet has a unique network number. • To ensure that each network number on the Internet will always be unique and unlike that of any other number, an organization called the International Network Information Center, or InterNIC Subnet & Routing 10
- 11. How do IP addresses incorporate network addresses? • Every IP address has two parts. These are known as the network number and the host number. Subnet & Routing 11
- 12. What are the different classes of networks? • There are three classes of IP addresses that a company can receive from the InterNIC. The InterNIC reserves class "A" IP addresses for governments throughout the world, class "B" IP addresses for medium size companies, and class "C" Subnet & Routing 12
- 13. IP addressing • Classes of Networks 1 Byte 1 Byte 1 Byte 1 Byte Class A: N H H H Class B: N N H H Class C: N N N H Network number assigned by NIC Host number assigned by Systems Administrator Subnet & Routing 13
- 14. IP addressing • IP Address Bit Patterns 1 Bit # Class A: 0 8 2-8 Network # 16 9 – 32 (24 bits) Host # 24 32 Class A address range 1.0.0.0 – 126.0.0.0 (127.0.0.0 is for loopback) Private Class A address: 10.0.0.0 Number of hosts: 224 -2 = 16,777,214 Subnet & Routing 14
- 15. IP addressing • IP Address Bit Patterns 1 Bit # Class B: 1 8 2 3 - 16 0 17 – 32 (16 bits) Network # Host # 16 24 32 Class B address range 128.0.0.0 – 191.255.0.0 Private Class B : 172.16.0.0 – 172.31.0.0 Number of hosts: 216 - 2 = 65,534 Subnet & Routing 15
- 16. IP addressing • IP Address2 Bit Patterns 1 3 4 - 24 25 – 32 (8 bits) Bit # Class C: 1 8 1 16 0 Network # Host # 24 32 Class C address range 192.0.0.0 – 233.255.255.0 Private Class C : 192.168.0.0 Number of hosts: 28 - 2 = 254 Subnet & Routing 16
- 18. How many classes of Networks are there? • you have learned about three classes of networks that can be assigned by the InterNIC. • In fact, there are five classes of networks. However, only three of these are used commercially. Subnet & Routing 18
- 19. reserved for multicast purposes and experimental purposes? • The highest number listed was 223. You may have wondered why the highest value was only 223 and not 255, since there are 255 possible values for an octet. • in IP addresses the values 224 through 255 are not used in the first octet for networking purposes. Subnet & Routing 19
- 20. What IP addresses are reserved for the Networks? • By convention, in IP addressing schemes, any IP address that ends in all binary zeroes is reserved for the network address. • Thus, in a class "A" network, 113.0.0.0 would be the IP address of that network. Routers use a network's IP address when forwarding data on the Internet. Subnet & Routing 20
- 22. What IP addresses are reserved for broadcasts? • for the network that is 176.10.0.0, the broadcast address that would be sent out to all devices on that network would be 176.10.255.255. Subnet & Routing 22
- 23. Who assigns subnet addresses? • As with the host number portion of class "A," class "B," and class "C” addresses, subnet addresses are assigned locally. • Usually this is done by the network administrator. Subnet & Routing 23
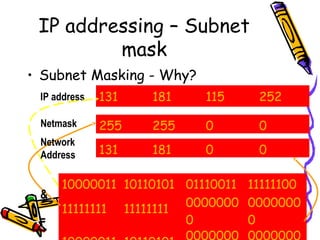
- 25. IP addressing – Subnet mask • Subnet Masking - Why? IP address 131 181 115 252 Netmask 255 255 0 0 Network Address 131 181 0 0 & = 10000011 10110101 01110011 11111100 0000000 0000000 11111111 11111111 0 0 Subnet & Routing 25
- 26. IP addressing Subnetting • Subnetting – Is the act of “borrowing” bits from the host portion to create smaller networks (called subnetworks) – Minimum bits that can be borrowed is 2 why? – Subnetting is used to reduce the number of broadcast domains – Communication between these subnetworks is achieved through a router Subnet & Routing 26
- 28. How are subnet addresses concealed from outside networks? • Subnets are hidden from outside networks by using a mask. • These are referred to as subnet masks. • The function of a subnet mask is to tell devices which part of an address is the network number including the subnet, and which part is the host. Subnet & Routing 28
- 29. What format do subnet masks use? • Subnet masks use the same format as IP addressing. • In other words, they are thirty two bits long and divided into four octets. • Subnet masks have all 1s in the network and subnetwork portion, and all 0s in the host portion. Subnet & Routing 29
- 32. How many bits can be borrowed from the host number in class "B" and class "C" networks to create subnets? • Because there are only two octets in the host field of a class "B” network, up to fourteen bits can be borrowed to create subnetworks. • A class "C" network has only one octet in the host field. Therefore, only up to six bits can be borrowed in class "C” networks to create subnetworks. Subnet & Routing 32
- 33. What happens to the subnet mask address if only some of the bits in an octet are borrowed? • Imagine that you have a class "B” network. This time however, instead of borrowing all eight bits of the third octet, only seven bits are borrowed to create subnetworks. • Using binary representation, in this example, the subnet mask would be 11111111.11111111.11111110.00000000. • Therefore, 255.255.255.0 can no longer be used as the subnet mask. Subnet & Routing 33
- 34. If only seven bits are borrowed in a class "B" network, what would the subnet mask be in dotted decimal notation? • HINT: To convert any eight bit binary number into a decimal number, total the powers of 2 that occur in the number. Subnet & Routing 34
- 35. What determines how many subnetworks can be created by borrowing bits from the host field? • Can you figure out all of the possible combinations of 0s and 1s if four bits are borrowed from the host field to create subnetworks? • 16 from 0000 to 1111. However, you know that 1111 is reserved for broadcast and 0000 means this network. Subnet & Routing 35
- 36. How many subnetworks can be created by borrowing five bits from the host field? • Answer: Thirty-two subnetworks or 25 =32 subnetworks can be created by borrowing five bits from the host field. Subnet & Routing 36
- 37. Which numbers in a subnetwork are reserved for broadcasts? • In previous section, we used an example of a class "C" network in which three bits are borrowed from the host field. You learned that when three bits are borrowed from the host octet, up to eight subnetworks can be created each having up to thirtytwo hosts. • You also learned that IP addresses ending in all binary 1s are reserved for broadcasts. The same is true for subnetworks. Subnet & Routing 37
- 38. For IP address 197.15.22.160 on the same class "C” network. How would this be expressed in a binary numbering scheme? • Answer: If 197.15.22.160 is converted to binary format, it becomes 110001010.00001111.00010110. 10100000. • The first three bits in the last octet, 101, indicate that this is the sixth subnetwork. As before the remaining bits are all binary 0s. This means that the IP address197.15.22.160 must be one that is reserved for a subnetwork address. Subnet & Routing 38
- 39. Subnet mask • How do we determine how many bits to “borrow” for a subnet? • Determine the number of sub networks required • Work from the MOST significant (LHS) bits of the first octet after the network number and calculate the number of bits needed to create the required number of subnetworks Subnet & Routing 39
- 40. Subnet mask • Example: – You are given a class B address and you are required to create 1000 subnetworks. – By working from the LHS of the (first octet after the network number) 3rd octet, calculate the number of bits to equal or slightly exceed 1000. (ie 2x = > 1000) – This would equate to 210 or 1024-2 networks – Hence you will need to borrow 10 bits from the host portion to create 1000 subnetworks Subnet & Routing 40
- 41. Subnet mask • Example: – The subnetmask in this instance would be 10 Bits Borrowed 6 bits left 255.255.255.192 Natural Class B netmask for hosts (subnetmask) 11111111 11111111 11111111 11 000000 – How many host per network can you obtain from this addressing scheme? Subnet & Routing 41
- 42. Subnet mask • How do we determine how many bits to “borrow” for a subnet given the number of hosts required? • Determine the number of hosts required • Work from the LEAST significant (RHS) bits of the last octet and calculate the number of bits needed to create the required number of subnetworks Subnet & Routing 42
- 43. Subnet mask • Example: – You are given a class B address and you require 1000 nodes per subnet – By working from the RHS (last octet) of the 4th octet, calculate the number of bits to equal or slightly exceed 1000. (ie 2x = > 1000) – This would equate to 210 or 1024-2 networks – Hence you will need to borrow 6 bits from the host portion to create subnetworks with 1000 hosts each Subnet & Routing 43
- 44. Subnet mask • Example: – The subnetmask in this instance would be 6 Bits Borrowed 10 bits required 255.255.252.0 Natural Class B netmask 11111111 11111111 (subnetmask) 111111 00 for hosts 00000000 – How many subnetworks per network can you obtain from this addressing scheme? – Note: Do you recognise this address as Subnet & Routing 44 the student “supernet” address?
- 45. What about a Supernet? • A supernet “borrows” bits from the network portion to create contiguous nodes to form a “super network” • For example – Company A has about 1000 nodes to address. A class B address would be too big (or may not be available). Solution Supernetting using 4 contiguous class C addresses 203.10.112.0 203.10.113.0 203.10.114.0 203.10.115.0 (All netmasked to 255.255.255.0) Subnet & Routing 45
- 46. What about a Supernet? • By allowing the first 2 bits of the third octet to be “borrowed”, a virtual class B address can be created. • A supernet address of 203.10.112.0 – 203.10.115.255 is formed with a subnet mask of 255.255.252.0. • The Host portion will be expanded from 8 – 10 bits • Route summarisation can occur to 203.10.112.0/22 Subnet & Routing 46
- 47. What about a Supernet? Network Portion 203.10.112.0 203.10.113.0 203.10.114.0 203.10.115.255 255.255.252.0 1100101 1 1100101 1 1100101 1 1100101 1 1111111 1 00001010 00001010 00001010 00001010 11111111 Host portion 011100 00 011100 01 011100 10 011100 11 111111 00 0000000 0 0000000 0 0000000 0 1111111 1 0000000 0 We have expanded the host portion by 2 bits to 10 bits Subnet & Routing 47
- 48. What is a Broadcast Address • A broadcast address is used to by a node to communicate with ALL nodes in a broadcast domain • Like the netmask, the broadcast address is “AND” with the network address. • However, the host portion of the network is identified in a broadcast address Subnet & Routing 48
- 49. What is a Broadcast Address • A broadcast address does this by inserting all “1’s” in the host portion. • Eg A natural class B broadcast address would look something like this – N.N.255.255 • If it is not a classful subnetmask, you can determine the broadcast address within each subnet by locating the host portion and setting them to all 1’s. Subnet & Routing 49
- 50. What is a Broadcast Address • An example of a Broadcast address 131 181 & 131 181 = 131 181 Host ID 255 Host ID Subnet & Routing Host ID 255 Host ID 50
- 51. What is a Broadcast Address • An example of a cross boundary subnet broadcast address with a mask of 255.255.252.0 131 181 11[2,3,4,5] x & 131 181 115 255 = 131 181 SN + H Host ID Network Portion Network Address SN Host portion 1000001 011100 10110101 1 00 Host 1000001 011100 10110101 Broadcast Address 1 Subnet & Routingxx 51 1000001 011100 0000000 0 xxxxxxx x 1111111
- 52. What is a Broadcast Address • An example of a cross boundary subnet broadcast address with a mask of 255.255.252.0 – In this example, IP addresses • 131.181.112.0 – 131.181.115.255 belong to the same subnetwork Network Portion SN Host portion 131.181.112.0 (Network) 1000001 011100 10110101 1 00 131.181.113.0 1000001 011100 10110101 1 01 131.181.114.0 1000001 011100 10110101 131.181.115.255 1 10 (Broadacast) 1000001 011100 10110101 Subnet & Routing11 52 1 0000000 0 0000000 0 0000000 0 1111111 1
- 53. Network Address VS Broadcast address • Remember • A Network address has all the host bits set to “0” • A Broadcast address has all the host bits set to “1” • Therefore – 131.181.112.0 is the network address – 131.181.115.255 is the broadcast address Subnet & Routing 53
- 54. Network Address VS Broadcast address • This is important when you are doing ifconfig and routing commands • For example, if a host has an address 131.181.114.10/22 • The ifconfig & route commands would be – ifconfig eth<x> inet 131.181.114.10 netmask 255.255.252.0 broadcast 131.181.115.255 – route add –net 131.181.112.0 netmask 255.255.252.0 dev eth<x> Subnet & Routing 54
- 55. How do you determine Network and Broadcast address quickly? • There are different subnetting exercises • Given an IP address & mask, – What is the network/subnetwork address – What is the network/subnetwork broadcast address – What are the assignable address in that network/subnetwork – What are all the valid subnet addresses – How many nodes per subnet Subnet & Routing 55
- 56. Algorithm for deriving Subnet information • Given an IP address, you will usually be given a net/subnetmask • If you are given the mask – Subtract the mask from 256 – This is known as the multiplier – The first number in each multiplier value is the network number – The broadcast address is the next multiplier value subtract 1 Subnet & Routing 56
- 57. Algorithm for deriving Subnet information • Eg given the IP address 192.168.0.100 with the subnet mask of 255.255.255.240 Or 192.168.0.100/28 – What is the network number – What is the broadcast address – What are the valid IP hosts for the subnet Subnet & Routing 57
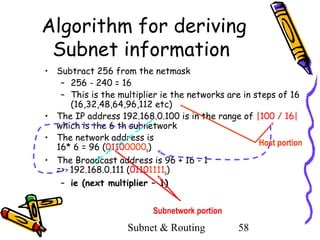
- 58. Algorithm for deriving Subnet information • Subtract 256 from the netmask – 256 - 240 = 16 – This is the multiplier ie the networks are in steps of 16 (16,32,48,64,96,112 etc) • The IP address 192.168.0.100 is in the range of |100 / 16| which is the 6 th subnetwork • The network address is Host portion 16* 6 = 96 (01100000b) • The Broadcast address is 96 + 16 - 1 => 192.168.0.111 (01101111b) – ie (next multiplier – 1) Subnetwork portion Subnet & Routing 58
- 59. Algorithm for deriving Subnet information Network Portion 1100000 0 1111111 1 Network Address 1100000 192.168.0.96 Broadcast Address 0 1100000 192.168.0.111 0 IP address 192.168.0.100 Netmask 255.255.255.240 0000000 0 1111111 11111111 1 0000000 10101000 0 0000000 10101000 0 10101000 Subnet & Routing SN Host portion 0110 0100 1111 0000 0110 0000 0110 1111 59
- 60. Algorithm for deriving Subnet information • Valid ranges are – 192.168.0.97 to 192.168.0.110 – Number of allowable hosts 97 to 110 (incl) = 14 or [24]16 - 2 = 14 • Remember you cannot use the first address (network address) and the last address (broadcast address) in the range • The number of allowable networks – [24]16 - 2 = 14 ( ie 4 bits used. If a class B address with the last bit subnet, then add another 8 bits to give you 212 –2 allowable subnet) Subnet & Routing 60
- 61. Algorithm for deriving Subnet information • What if the IP range goes over 2 octets • Use the same principal – Remember octets with all 0’s are considered “boring” and will be assigned the mask of 0 – You will then have to locate the position in the address with both 1’s and 0’s (interesting byte) and use the same algorithm • Similarly all 1’s are also considered boring and will be given the mask of 255 (eg subnetting the last byte of a class B address) Subnet & Routing 61
- 62. Algorithm for deriving Subnet information • Example • • Netmask expanded : 255.255.252.0 Last byte is “not interesting” hence we set it to “0” for network and “1” for broadcast The third byte is “interesting” 256 – 252 = 4 (multiplier) Networks are in increments of 4 steps 112/4 = 28 (the 28th subnetwork). Since there is no remainder, it is the beginning of the network address • • • – QUT students’ “supernet” address – 131.181.112.0/22 Subnet & Routing 62
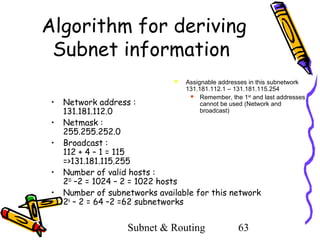
- 63. Algorithm for deriving Subnet information • • • • • Assignable addresses in this subnetwork 131.181.112.1 – 131.181.115.254 Remember, the 1st and last addresses cannot be used (Network and broadcast) Network address : 131.181.112.0 Netmask : 255.255.252.0 Broadcast : 112 + 4 – 1 = 115 =>131.181.115.255 Number of valid hosts : 210 –2 = 1024 – 2 = 1022 hosts Number of subnetworks available for this network 26 – 2 = 64 –2 =62 subnetworks Subnet & Routing 63
- 64. How does the router handle IP addresses and subnet masks? • Let's assume that a device on another network with an IP address of 197.15.22.44 wants to send data to another device attached to Cisco's network with an IP address of 131.108.2.2. • The data is sent out over the Internet until it reaches the router that is attached to Cisco's network. • The router's job is to determine which one of Cisco's subnetworks the data should be routed to. Subnet & Routing 64
- 66. when the router performs this ”ANDing" operation, the host portion falls through. Subnet & Routing 66
- 67. The router looks at what is left which is the network number including the subnetwork. Subnet & Routing 67
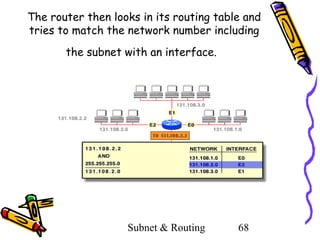
- 68. The router then looks in its routing table and tries to match the network number including the subnet with an interface. Subnet & Routing 68
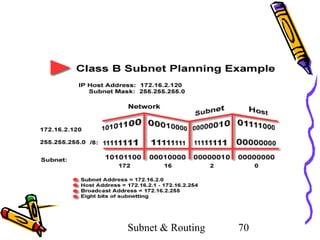
- 69. How does the "Anding” operation change with different subnet masks? • Imagine that you have a class "B” network with the network number 172.16.0.0. • After assessing the needs of his network, the network administrator has decided to borrow eight bits in order to create subnetworks. • When eight bits are borrowed to create subnets, the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0. • Someone outside the network sends data to the IP address 172.16.2.120. Subnet & Routing 69
- 72. Exercise • Exercise – You are given an IP address for a host 172.168.35.10/20 • What is/are the – 1. Subnet address? – 2. Broadcast address? – 3. The number of useable hosts available for this subnet? – 4. The number of useable subnets available for this network? – 5. The assignable address range for this subnet? Answers Subnet & Routing 72
- 73. Exercise • Exercise – Your organisation has been assigned a class B IP address of 130.10.0.0 – You require about 2000 subnetworks • Work out the – 1. Subnet mask required for this subnet – 2. The network and broadcast addresses for the first 5 useable subnets – 3. The number of hosts for each subnet – 4. The assignable address range of the first 5 useable subnets Answers Subnet & Routing 73
- 74. ROUTING
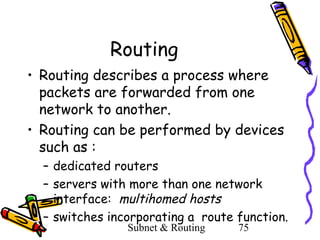
- 75. Routing • Routing describes a process where packets are forwarded from one network to another. • Routing can be performed by devices such as : – dedicated routers – servers with more than one network interface: multihomed hosts – switches incorporating a route function. Subnet & Routing 75
- 76. Routers • Routing devices typically have more than one network interface, each called a port. • Routers process datagrams individually, making routing a processing-intensive operation. • Dedicated routers offer better performance characteristics compared with multi-homed hosts. Subnet & Routing 76
- 77. Routing Tables • To determining the proper destination network for datagrams, routers consult an internal table. • The table consists of records, one per line, each representing a known network. • Each record includes a set of associated characteristics such as netmask Subnet & Routing 77
- 78. Building Route Tables. • Routing table entries can be built by two methods: – Static: entries are entered manually by a network administrator – Dynamic: entries are entered dynamically by routing protocols. Routers learn destination network addresses by the periodic exchange of route tables between routing devices. Routing protocols use IP to deliver this information. Subnet & Routing 78
- 79. Configuring Routers • Before IP routers can perform the route function and use routing protocols to exchange route tables, each interface (port) must be correctly numbered with a valid host IP address and netmask. • The IP address must be selected from within the range for the particular network address. Typically local gateways are located the first address in the valid host range. Subnet & Routing 79
- 80. Routing Protocols • Routing protocols are used by routers to: – learn the location of destination networks. – determine the best route to reach networks. • Examples of routing protocols include: – RIP, Routing Information Protocol – OSPF, Open Shortest Path First – BGP, Border Gateway Protocol Subnet & Routing 80
- 81. Routing Protocols - 2 • Routing protocols differ in: – the way in which they exchange route tables – determine the route to the destination – the information that is communicated Subnet & Routing 81
- 82. Distance Vector • Distance Vector routing protocols broadcast the entire route table on a regular basis. RIP2 typically defaults at once every 30 seconds.This creates considerable network traffic. • They determine the best route path on the basis of the least number number of hops to reach a Subnet & Routing 82 destination network.
- 83. Link State • Link state protocols only broadcast changes to route information after an initial entire table has been sent. • When determining the best path, other factors such as policies (e.g. preferred path) and cost ( time taken, available bandwidth) can influence the choice when multiple paths are available. Subnet & Routing 83
- 84. IP Routing • Before a routing device can forward an IP datagram it must: – examine the Destination Address in the datagram – use the netmask to identify the network portion of the packet’s destination address – find a corresponding network address in the route table and forward the packet to the gateway or interface specified Subnet & Routing 84
- 85. Route Table Fields • To forward IP datagrams, the router uses the following fields of the the route table: – Destination – Network Mask – Gateway Subnet & Routing 85
- 86. Destination • This field lists the networks which are known to the router. Addresses may have been entered by an administrator, or dynamically learned from the transmissions of other routers. • Address entries concerned with routing between network addresses will be of the format {<netid>, 0} Subnet & Routing 86
- 87. Netmask • The netmask field provides the router with the ability to determine the network address of packets being examined. • A logical AND is performed using the netmask and the destination address. This logically removes the host portion allowing the router to identify the destination Subnet & Routing 87
- 88. Gateway • The Gateway field lists the IP addresses of the interface where the datagram should be sent (forwarded) to reach the specified Destination. • This field may contain : – An IP interface address corresponding to an adjacent router – 0.0.0.0 – The address of a interface Subnet & Routing 88
- 89. Destination Hop=0.0.0.0 • A Destination of 0.0.0.0 indicates a directly connected network. Hosts located on this network can be reached using the local network method. If the network is Ethernet, the ARP protocol is used to find the physical address of the node. Subnet & Routing 89


















































![What is a Broadcast Address
• An example of a cross boundary subnet
broadcast address with a mask of
255.255.252.0
131
181
11[2,3,4,5]
x
&
131
181
115
255
=
131
181
SN + H
Host
ID
Network Portion
Network
Address
SN
Host portion
1000001
011100
10110101
1
00
Host
1000001
011100
10110101
Broadcast
Address 1
Subnet & Routingxx
51
1000001
011100
0000000
0
xxxxxxx
x
1111111](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/subnettingandrouting-140222093327-phpapp02/85/Subnetting-and-routing-51-320.jpg)







![Algorithm for deriving
Subnet information
•
Valid ranges are
– 192.168.0.97 to 192.168.0.110
– Number of allowable hosts 97 to 110 (incl) = 14 or [24]16 - 2 = 14
• Remember you cannot use the first address (network address) and the
last address (broadcast address) in the range
•
The number of allowable networks
– [24]16 - 2 = 14 ( ie 4 bits used. If a class B address with the last bit subnet,
then add another 8 bits to give you 212 –2 allowable subnet)
Subnet & Routing
60](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/subnettingandrouting-140222093327-phpapp02/85/Subnetting-and-routing-60-320.jpg)