Named data networking
- 1. Networking Named Content Paper by: V. Jacobson et al. Presented by : Haroon Rashid 1
- 2. Content Centric Networking No NAT traversal. Address space exhaustion. Average latency and total bandwidth is minimized. Networking in mobile scenarios is easy. Content Centric Networking (CCN) removes the concept of host identities (machine address) required for communication and considers only named data packets. Some of its benefits: 2
- 3. Different Paradigms IP Networking CCN Networking Source: Lecture Notes on Internet 3
- 4. IP vs. CCN Network stack IP Network Stack CCN Network Stack 4
- 7. Naming/Hierarchical Addressing Query Traversal Address Structure 7
- 8. Routing CCN Uses name prefixes instead of IP prefixes. Name prefixes are broadcasted via routing protocols. Conventional routing protocols like IS-IS and OSPF are used in CCN by utilizing a general TLV(type label value) scheme. Each node builds its FIB on receiving prefix. 8
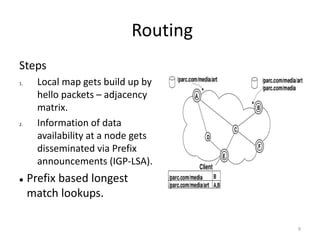
- 9. Routing Steps 1. Local map gets build up by hello packets – adjacency matrix. 2. Information of data availability at a node gets disseminated via Prefix announcements (IGP-LSA). Prefix based longest match lookups. 9
- 10. • CCN supports multicasting when more than one announcer of data is found at a particular node while as IP supports only uni-casting in such a case. • For inter domain routing, BGP supports equivalent of IGP TLV mechanism. 10
- 11. Security • Security is build within data itself rather than securing data channel. • Digital signatures are used for authentication. • Cryptographic encryption is used for private data protection. • Signature in each data packet is over the packet name, the content, and on signed-info. • Decryption keys are distributed along content as a CCN data blocks – no need of trusted servers. 11
- 12. Network Security • No tampering is possible due to digital signatures. • Impossible to send the malicious content to a particular machine as host identities are not revealed. • Data-based distributed denial of service attacks not possible as filtering of each data packet takes place at each aggregation point towards content customer. • For Interest flooding attack, attacker should be expert in providing the different combinations of name components of a prefix served by the target. 12
- 13. • CCN’s semantically selective control also mitigates different attacks: • Data packets follow same path as Interest – helps intermediary routers to have fine grained control of Interests forwarded under a certain prefix. • Attacked domain can ask downstream routers to throttle number of Interest packets for a certain prefix. • Provides tools to organizations to control their content travel. • Policy based routing – requiring content name and signer. • Interests can be digitally signed to enable the policy routing by how often and into what namespaces a particular consumer may query. 13
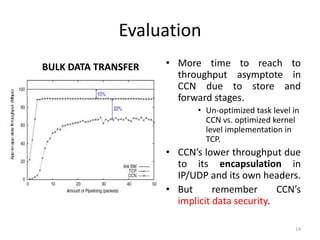
- 14. Evaluation • More time to reach to throughput asymptote in CCN due to store and forward stages. • Un-optimized task level in CCN vs. optimized kernel level implementation in TCP. • CCN’s lower throughput due to its encapsulation in IP/UDP and its own headers. • But remember CCN’s implicit data security. BULK DATA TRANSFER 14
- 15. Performance in secure & insecure scenarios • CCN over Jumbo-UDP is twice as efficient as HTTP and three times more efficient than HTTPS in both overhead and packets (sent). 15
- 16. Performance in data sharing scen. • The performance penalty of using CCN vs. TCP is around 20% while the performance gain from sharing is integer multiples, there is a net performance win from using CCN even when sharing ratios / hit rates are low. 16
- 17. Architecture Difference DONA • Name given to packet is a cryptographic hash of publisher’s key and label. • DNS type table required for resolution of user familiar name to digest based. • Flat Namespace. • Content must be first registered with RHs. CCN • Name given is not a cryptographic digest of anything. • User friendly, structured, location independent names. • Hierarchical Namespace. • Content generated dynamically in response to queries. 17
- 18. Concerns • Names based on digest vs. user friendly, structured names. • Hierarchical namespace vs. flat namespace. • Inter-domain routing feasibility. • Caching level & replacement policy at the intermediary routers. • Does it depends on the ISP? • Can we improve forward strategy? 18