Develop Your Own Operating Systems using Cheap ARM Boards
- 1. Develop Your Own Operating Systems using Cheap ARM Boards Jim Huang ( 黃敬群 ) <[email protected]> Jan 8, 2014 / NCTU, Taiwan
- 2. Rights to copy © Copyright 2014 0xlab http://0xlab.org/ Corrections, suggestions, contributions and translations are welcome! Attribution – ShareAlike 3.0 Latest update: Jan 14, 2014 You are free to copy, distribute, display, and perform the work to make derivative works to make commercial use of the work Under the following conditions Attribution. You must give the original author credit. Share Alike. If you alter, transform, or build upon this work, you may distribute the resulting work only under a license identical to this one. For any reuse or distribution, you must make clear to others the license terms of this work. Any of these conditions can be waived if you get permission from the copyright holder. Your fair use and other rights are in no way affected by the above. License text: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/legalcode
- 3. Goals of This Presentation • Know the reasons why various operating systems exist and how they are functioned for dedicated purposes • Understand the basic concepts while building system software from scratch • How can we benefit from cheap ARM boards and the related open source tools? – Raspberry Pi & STM32F4-Discovery
- 4. Agenda • • • • Yet another Operating System? Embedded Operating System Designs Cheap ARM boards Development flow using open source technologies
- 5. Yet Another Operating Systems?
- 6. Reasons of Home-brew OS • Escape from large-scale and uncertain code base – Linux is a good example: Mature but hard to fit everyone's need • Exploit new systematic methods – Hypervisor for virtualization, runtime isolation – Heterogeneous computing for both performance and power efficiency • Customization – Deeply embedded environments, security, education (xinu, minix, xv6), domain-specific language/runtime, mobile (OKL4; 1.5 billion shipment!) • "Just for Fun" – Linus Torvalds
- 7. Techniques inspired by OS • Even Web/Application Framework learn the performance techniques from OS concepts. • Virtualization – Hypervisor, Resource Kernel (KVM), … – Intel VT-d , ARM Cortex-A15/A7, ARMv8 • Security – Dynamic tracing, analysis, and instrumentation using VM
- 8. Statistics about Large-scale Systems • Drivers cause 85% of Windows XP crashes. – Michael M. Swift, Brian N. Bershad, Henry M. Levy: “Improving the Reliability of Commodity Operating Systems”, SOSP 2003 • Error rate in Linux drivers is 3x (maximum: 10x) higher than for the rest of the kernel – Life expectancy of a bug in the Linux kernel (~2.4): 1.8 years – Andy Chou, Junfeng Yang, Benjamin Chelf, Seth Hallem, Dawson R. Engler: “An Empirical Study of Operating System Errors”, SOSP 2001
- 9. Some statistics • Causes for driver bugs – 23% programming error – 38% mismatch regarding device specification – 39% OS-driver-interface misconceptions – Leonid Ryzhyk, Peter Chubb, Ihor Kuz and Gernot Heiser: “Dingo: Taming device drivers”, EuroSys 2009
- 10. Anecdote: Linux e1000 NVRAM bug • [Aug 8, 2008] Bug report: e1000 PCI-X network cards rendered broken by Linux 2.6.27-rc – overwritten NVRAM on card • [Oct 1, 2008] Intel releases quickfix – map NVRAM somewhere else • [Oct 15, 2008] Reason found: – dynamic ftrace framework tries to patch __init code, but .init sections are unmapped after running init code – NVRAM got mapped to same location – scary cmpxchg() behavior on I/O memory • [Nov 2, 2008] dynamic ftrace reworked for Linux 2.6.28-rc3 FTrace & NIC driver! instrumentation vs. device driver
- 11. Linux Device Driver bugs [Dingo: Taming device drivers, 2009]
- 12. Linux version 3.0 • consists of – 7702 features – 893 Kconfig files – 31281 source files – 88897 #ifdef blocks
- 13. Even worse...
- 16. Bugs in Linux Device Driver
- 17. Bugs in Linux Device Driver Device protocol violation examples: ✗ Issuing a command to uninitialized device ✗ Writing an invalid register value ✗ Incorrectly managing DMA descriptors
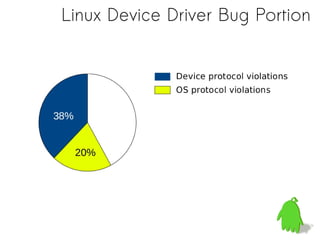
- 18. Linux Device Driver Bug Portion
- 19. Bugs in Linux Device Driver Mellanox Infinihost controller Driver if(cur_state==IB_RESET && new_state==IB_RESET){ return 0; }
- 20. Linux Device Driver Bug Portion
- 22. Further study about concurrency bugs • Markus Peloquin, Lena Olson, Andrew Coonce, University of Wisconsin–Madison, “Simultaneity Safari: A Study of Concurrency Bugs in Device Drivers" (2009) • Types of Device Driver Bugs
- 23. Linux Device Driver Bug Portion
- 25. IoT = I own Technologies, but... • You can only use the devices, services, rights, etc. without really owning them even if you buy the “products" in higher price. • Ecosystem is getting quite essential for applications.
- 26. Deeply Embedded Devices • Power awareness; solid and limited applications • Multi-tasking or cooperative scheduling is still required • IoT (Internet of Things) is the specialized derivative with networking facility • Communication capability is built-in for some products • Example: AIRO wristband (health tracker) http://www.weweartech.com/amazing-new-uses-smart-watches/
- 27. Work at AcoMo: Physiological Inspection • Analyze signals from various bio sensors and apply efficient algorithms to examine the healthy condition
- 28. HRV Knows You
- 29. AcoMo built in-house OS for products and releases the basic part as an open source effort (invisible) Medical devices make sense in our life. :: home-care :: advance warning :: security
- 30. Booting Process Power On PC Embedded BIOS Power On X-Loader Get Bootloader Get Bootloader GRUB U-Boot Get Kernel Kernel Embedded hardware: TI OMAP3730 SoC Get Kernel Kernel
- 31. Embedded vs. PC • Hardware specification is not the major difference! – The functionality is. • PCs are a highly modular platform. Most components are in sockets or slots that permits easy replacement. • Embedded Systems tend to solder their components directly to the PCB as they don’t need to be replaced.
- 34. Embedded vs. PC D i ff e r e n t P C I - E s t a n d a r d s V1.0/v2.0/v3.0 D i ff e r e n t l a n e c o u n t s x1/x2/x4/x8/x16 Also Legacy PCI support
- 35. Embedded vs. PC USB 2.0 USB 3.0 Intel PCH Gigabit Ethernet 7.1 Audio Codec S-ATA 3 & 6Gbps IDE & Floppy
- 36. Embedded vs. PC TI OMAP 3730 Processor 512MB DDR@200MHz PowerVR SGX530 Graphics All soldered directly to the board. Not intended for replacements.
- 37. Booting Process ROM Code U-Boot IPL Startup Kernel X-Loader U-Boot Linux Kernel • On-Chip boot ROM code generally causes the CPU to perform minimal initialization of peripheral such as NAND Flash and instructs it to begin reading code from there into memory and executing it. • This code can be a standard embedded bootloader such as U-Boot, or it can be an IPL. • U-Boot loads the “IPL” image into memory, and begins executing it. • The “IPL” is an “Initial Program Loader” which is responsible for initializing basic hardware and passing control to “Startup” code, and subsequently the Kernel. Embedded hardware: TI OMAP3730 SoC
- 38. IPL • • • • Begin in assembly, performs initialization for HLL Initialize CPU/(some) Peripheral Clocks Initialize basic I/O (serial) Minimal pin multiplexing for required peripherals (i.e. SDHC hardware) • Read in and decompresse “IFS” image (ramdisk + kernel) • Include basic (FAT) fi lesystem drivers for SDHC reading • Passes control to “Startup” • Can start “minidrivers” for device interaction before OS/Kernel even begins booting
- 39. Startup • Startup begin in C language, initialize most peripherals, and sets up important kernel structures • Kernel expects a “syspage” structure to exist at a pre-defi ned location in memory. This structures provides important information about the host system. • Enable CPU SMP operation (multiple-cores) • Often re-do initialization done by IPL (such as serial I/O) to enable more advanced functionality • Inform minidrivers of new environment before passing control to kernel.
- 40. System Information • Indicate CPU type (e.g. ARM) and vital information (e.g. number of cores), and other supported features such as NEON extensions. • Provide access to hardware-specifi c function callouts made available to the system before the Kernel was running • Provide information about the memory environment in which the kernel is running • Information about bus devices, IRQs • Information about connected peripherals and device trees for /dev population
- 41. Cheap ARM Boards check "Introduction to Raspberry Pi" by Computer Science Club, University of Cyprus Student Clubs
- 42. Development flow using Open Source Technologies
- 43. Baking Pi – Operating System Development • Operating Systems Development! Course by Alex Chadwick. Version 1.0c (July 2013). http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/projects/raspberrypi/tutorials/os/ • Divided into several basic “blocks".
- 44. JTAG • Initially devised for testing printed circuit boards with its boundary scanning functionality JTAG is now used extensively for debugging, programming CPLDS and initialising flash memory. • Can be useful to recover bricked devices or write new firmware to NAND on restricted devices. But the IGEP is un-brickable • Tools like OpenOCD and GDB ARM have successfully been used on OMAP530 devices like Beagleboard.
- 45. Conclusion • BYOD (Build Your Own Device) and BYOD (Build Your Own Operating System) are feasible and getting easier with open source technologies • Domain specific applications always expect innovations from various sources including the customized kernel and userland • System trial with very low cost
- 46. Reference • “Dingo: Taming Device Drivers”, Leonid Ryzhyk, Peter Chubb, Ihor Kuz, Gernot Heiser, UNSW/NICTA/Open Kernel Labs (2009) • "Hardware and Device Drivers", Björn Döbel, TU Dresden (2012) • "Configuration Coverage in the Analysis of Large-Scale System Software", Reinhard Tartler, Daniel Lohmann, Christian Dietrich, Christoph Egger, Julio Sincero, Friedrich-Alexander University (2011) • “AIRAC: A Static Analyzer for Detecting All Buffer Overrun Errors in C Programs", Kwangkeun Yi, Seoul National University (2005) • “CCured: Taming C Pointers”, George Necula, Scott McPeak, Wes Weimer, Berkeley (2002)










![Anecdote: Linux e1000 NVRAM bug
• [Aug 8, 2008] Bug report: e1000 PCI-X network cards
rendered broken by Linux 2.6.27-rc
– overwritten NVRAM on card
• [Oct 1, 2008] Intel releases quickfix
– map NVRAM somewhere else
• [Oct 15, 2008] Reason found:
– dynamic ftrace framework tries to patch __init code, but .init
sections are unmapped after running init code
– NVRAM got mapped to same location
– scary cmpxchg() behavior on I/O memory
• [Nov 2, 2008] dynamic ftrace reworked for Linux
2.6.28-rc3
FTrace & NIC driver!
instrumentation vs. device driver](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arm-osdev-140123183132-phpapp02/85/Develop-Your-Own-Operating-Systems-using-Cheap-ARM-Boards-10-320.jpg)
![Linux Device Driver bugs
[Dingo: Taming device drivers, 2009]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arm-osdev-140123183132-phpapp02/85/Develop-Your-Own-Operating-Systems-using-Cheap-ARM-Boards-11-320.jpg)