Software and os ch5
- 1. Abdul Wajid Khan Yousafzai 1
- 2. Logical Component of a Computer We can not touch These are in form of instructions that tell the computer that what to do It can not executed without hardware. If any problem in software then it will reinstall. 2
- 3. Software may be in the form of System Software Application Software 3
- 4. It controls a computer’s internal function System software manages the fundamental operations of your computer Operating system Utilities Library Programming Languages It also control mouse ,printer, Monitors Examples Operating System Language Software 4
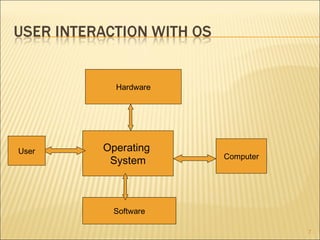
- 5. Is collection of System software An interface between applications and hardware Hardware needs a manager to tell it what to do when to do it how to do it The (OS) controls all input output Processing Uses It manages the data and the memory and appearance Make the computer system convenient to use Execute user programs and make solving user problems easier. 5
- 6. Efficiency Ability to evolve They provide the way for application software to communicate with hardware Transfer data Permit effective development, testing, and introduction of new system functions without interfering with service Communication with hardware Allows computer system resources to be used in an efficient manner They manage the transfer of data to and from the various peripherals System Security They manage system security. Many operating systems allocate certain rights to user 6
- 8. Window 98 Window 2000 Window XP Window Vista Linux Unix 8
- 9. User interface is what you see when you turn on the computer It consists of the cursors, prompts, icons and menus etc Which allow you to get something done using your computer Ideally the user interface should be as easy to use as possible User interface may be Command driven interface Menu driven interface Graphical user interface 9
- 10. With a command driven interface, you type in an instruction, which is usually abbreviated, in order to get something done. Are not easy to use A set of commands used to interact with computer is called command language It requires exact spelling and punctuation Advantage: Commands for different software application are rarely the same so user can be faster to use and have learnt all the commands 10
- 11. The user enter data and instruction by using menus Easy to use because the user has not remember the syntax of commands User can make a selection by using either a mouse or a keyboard Drop down list Present options Both Microsoft Windows and Apple Macintosh programs are menu driven 11
- 12. Is a visual environment that is used by the user to communicate with computer It uses windows ,icons, menus and other graphical objects to issue commands. Easy to use Easy to learn Attractive WIMP: stands for windows, and pointing devices which describes the features of GUI 12
- 13. More immediate access store and secondary store More powerful processor and graphical card Slower then executing Greater no of operations is required 13
- 14. Consistency Positioning of items on the screen Use of colour Use of sound Availability of help 14
- 15. A type of system software that is used to solve particular problem. Designed to make life easier for computer users. Utility programs perform thousands of task Renaming files Listing file on a disk Deleting files Copying files Sending files to a printer Storing data Backing up files 15
- 16. File Viewer Is used to view and manage files in computer system. Window Explorer File Compressor: Is used to shrink the size of files Winzip and WinRAR Diagnostic Utilities: is used to detect problem in hardware and software AntiVirus Disk Defragmenter Backup utility Data Recover y Utility Task Manager utility Disk Cleanup Personal Firewall Spyware Remover 16
- 17. Application sof tware enables you to perform specific computer tasks, such as document production, spreadsheet calculations, and database management Any program that processes data for a user Users prepare these Packaged software Custom Software Integrated software Bespoke Software Shareware Free Ware Public Domain Software 17
- 18. Single program Kind of a Jack-of-all-trades Shares a common set of commands Commands are common throughout Moving data from one program to another is easy Which combine features from all below products Multiple functionality Word processor, spreadsheet, DBMS, Presentation graphics and communication software Advantages Lower cost Simpler Capabilities not as extensive Disadvantages: Tend to be strong in one area and weak in others 18
- 19. It is particular user or organization. The program are well tested Is available for different types of users Documentation are very good Examples: Word processing software such as word and word perfect Spread sheet software such as Lotus 1-2-3 and Excel Data base software such as Access 19
- 20. Is developed to meet the requirement of particular company or industry. If packaged software does not fulfill the requirement of an organization, it has to develop a custom software by hiring a programmer. The cost of custom software is higher. 20
- 21. The instructions that tell the computer what to do is called program Programmer: Who writes or design the program in any language. Computer can understand only the binary code 21
- 22. Humans can use different languages to communicate The instructions are written in a languages which are easy to understand Programming languages may be in the form of High level Languages Low Level Languages 22
- 23. Are languages that are easy for the computer to understand but more difficult for the programmer Each instruction usually translates into one machine code instruction 23
- 25. Is the language that directly understood by the machine It consists of series of a 0s and 1s It is a machine specific it mean that one computer’s machine code will not be understand by other computer type It needs no translation so that way it is very fast A lot of games or simulation programs are written in machine code for this reason 25
- 26. It is easier for the programmer to use and to debug Once a program has been written in assembly language it needs translating into machine code by software called assembler Is a low level language which allows the programmer to use Mnemonics and symbolic address Mnemonics: Is a word or set of letters which can be used to represent a function code and which is easy to remember Example: LDA use for Load Accumulation JMP for jump instruction and ADD are mnemonics Symbolic Address: Is a name inverted by the programmer to identify a location Loop ,value and prnt are symbolic addresses 26
- 27. Is developed with the programmer in mind rather than the computer High level language instructions are similar to English which mean programming is more easier. Once a program has been written it can be used on different computers with little alteration It can be translated into machine code by a compiler and then run 27
- 28. Simple instruction similar to English make high level language easy to understand It is easy to correct errors and test programs Programs written in high level language can be used on different makes of computer 28
- 29. COBOL: common business oriented language Purpose: easily understand language for commercial data processing application Features: look like English Statement Good facilities for file handling 29
- 30. Beginners all purpose symbolic instruction code Purpose: Teaching language for interactive work Features: Every line has to be numbered Easy for beginners to learn Many different versions 30
- 31. Formula translation Purpose : For scientific use. Usually batch work Features: Lacks of statements which makes program structure clear Designed to be used with cards as input and a line printer as a output 31
- 32. Purpose : An educational language that encourage logical thinking Features : New instructions can be added and can be defined Facilities to process lists 32
- 33. Purpose : To allow clear structuring of data and program Features: All variables are declared before they can be used. Encourages clear structure and stepwise refinement New procedures ,functions and data types can be defined and added in 33
- 34. A language especially suited for writing software used to search for things on the internet. HTML Hypertext markup language A language used for the development of websites 34
- 35. Source code Is written in high language or assembly language Easy to understand Easy to modify Contain fewer statements It contain .exe extension Object code Is written in machine language through compiler difficult to understand Difficult to modify More statement than source code It contain .obj extension 35
- 36. Are part of the system software and are used to convert the programs commands into machine code There are three types of translation program Compiler Interpreters Assemblers 36
- 37. Is software that converts the whole of a program written in a high level language into machine code in one go. There are no mistakes in the program the complete program is converted to machine code If a program needs to be altered at a later date the original source code is altered and program recompiled 37
- 38. Each instructions in turn, converts it to machine code and then caries it out It run one line at a time The computer recognizes each instruction 38
- 39. Compiler Converts a program into a machine code as a whole Creates object code file Converts high level programs that can be executed in many times Execution is fast Displays syntax errors after compiling the whole program Interpreter Converts a program into machine code statement by statement Object file is not created Converts high level programs each time it is executed Program execution is slow Displays the syntax error on each statement of program 39
- 40. Is a program which translates a program written in as assembly language into are in machine code The main functions of an assembler are to : Translate an assembly language source program into a machine code object program Work out where to store the object program and its data Detects errors in the source program and say what they are Link the program to any other programs or routines it uses Print a listing of the source and object programs 40