Introduction To Cloud Computing
- 1. Introduction to Cloud Computing 2008-08 Liming Liu [email_address]
- 2. Content What is cloud computing Cloud computing discriminate Cloud computing technology Cloud computing products and market
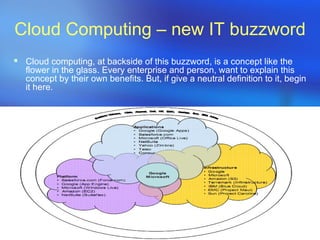
- 3. Cloud Computing – new IT buzzword Cloud computing, at backside of this buzzword, is a concept like the flower in the glass. Every enterprise and person, want to explain this concept by their own benefits. But, if give a neutral definition to it, begin it here.
- 4. Cloud computing definition Cloud computing is a resource delivery and usage model, it means get resource (Hardware, software)via network. The network of providing resource is called ‘Cloud’. The hardware resource in the ‘Cloud’ seems scalable infinitely and can be used whenever.
- 5. Cloud computing and technology New advances in processors, virtualization technology, distributed storage, broadband Internet access , automated management and fast, inexpensive server s have all combined to make cloud computing a compelling paradigm.This vast process power is usually got with a distributed, large-scale server cluster and server virtualization software.
- 6. Cloud computing impact As a result, cloud computing has the potential to upend the software industry entirely, as applications are purchased, licensed and run over the network instead of a user's desktop. This shift will put data center s and their administrators at the center of the distributed network, as processing power, electricity, bandwidth and storage are all managed remotely. It affects not only business models, but the underlying architecture of how we develop, deploy, run and deliver applications.
- 7. Content What is cloud computing Cloud computing discriminate Cloud computing technology Cloud computing products and market
- 8. Cloud computing’s brother buzzwords Cloud computing is becoming one of the next industry buzz words. And it has more or less relation with these words: grid computing, utility computing, virtualization, server cluster, Dedicated server, Colocation. Cloud computing infrastructure usually use virtualization technology, and is built based on a server cluster, have nature relation to grid computing and utility computing, and is use to compete with Dedicated server and Colocation.
- 9. Utility computing Utility computing is a business model of providing computing resource , user get and use the computing resource from service provider and pay for practically used resource. To say it simply, it is a price model based on resource usage quantity. The main benefit of utility computing is better economics. Corporate data centers are notoriously underutilized, with resources such as servers often idle 85 percent of the time. This is due to overprovisioning — buying more hardware than is needed on average in order to handle peaks (such as the opening of the Wall Street trading day or the holiday shopping season), to handle expected future loads and to prepare for unanticipated surges in demand. Utility computing allows companies to only pay for the computing resources they need, when they need them.
- 10. Comparison of Utility Computing and Cloud Computing Utility computing is a business model, it is a type of price model to deliver application infrastructure resource. Cloud computing is a computing model, relates to the way we design, build, deploy and run applications that operate in a sharing resources and boasting the ability to dynamically grow, shrink and self-heal. Utility computing is often need a cloud computing infrastructure, but not must need. Sameness, above the cloud computing, we can adopt utility computing, and, we can adopt other price model. Monitor Meter Billing Pay Utility computing Cloud computing
- 11. Distributed Computing Distributed computing deals with hardware and software systems containing more than one processing element or storage element, concurrent processes, or multiple programs, running under a loosely or tightly controlled regime .In distributed computing , a program is split up into parts that run simultaneously on multiple computers communicating over a network. Distributed computing is a form of parallel computing , but parallel computing is most commonly used to describe program parts running simultaneously on multiple processors in the same computer. Both types of processing require dividing a program into parts that can run simultaneously, but distributed programs often must deal with heterogeneous environments, network links of varying latencies, and unpredictable failures in the network or the computers.
- 12. Grid computing Grid computing is a term for either of two broad subcategories of distributed computing : 1 Online computation or storage offered as a service supported by a pool of distributed computing resources, also known as utility computing , on-demand computing, or cloud computing . Data grids provide controlled sharing and management of large amounts of distributed data, often used in combination with computational grids. 2 The creation of a "virtual supercomputer" composed of a network of loosely-coupled computers, acting in concert to perform very large tasks. This technology has been applied to computationally-intensive scientific, mathematical, and academic problems through volunteer computing , and it is used in commercial enterprises for such diverse applications as drug discovery , economic forecasting , seismic analysis , and back-office data processing in support of e-commerce and web services .
- 13. Difference between Cloudcomputing and grid computing Grid computing emphasizes on resource sharing, every grid node can apply for resource from other nodes, and every node should contribute resource to the grid. The focus of grid computing is on the ability of moving a workload to the location of theneeded computing resources, which are mostly remote and are readily available for use.Grids also require applications to conform to the grid software interfaces. Cloud computing emphasize on proprietary, every user out of the cloud can get it’s own private resource from the cloud, and the cloud resource are provided by the specific service provider, the user need not contribute its resource. In a cloud environment, computing resouces, such as servers, can be dynamically shaped or carved out from its underlying hardware infrastructure and made available to a workload. In addition, while a cloud does support grid, a cloud can also support nongrid environments,such as a three-tier Web architecture running traditional or Web 2.0 applications. Grid computing emphasizes on computing sensitive task, and is difficult to automated scale. Cloud computing emphasizes on transactional application, a great amount of separate request, and can scale automatically or semiautomatically.
- 14. Computer cluster A computer cluster is a group of coupled computers that work together closely so that in many respects they can be viewed as though they are a single computer. The components of a cluster are commonly, but not always, connected to each other through fast local area networks . Clusters are usually deployed to improve performance and/or availability over that provided by a single computer, while typically being much more cost-effective than single computers of comparable speed or availability. [1] Grids tend to be more loosely coupled , heterogeneous, and geographically dispersed, grid computers do not fully trust each other.
- 15. Virtualization Virtualization is a broad term that refers to the abstraction of computer resources. Virtualization hides the physical characteristics of computing resources from their users, be they applications , or end users . [1] This includes making a single physical resource (such as a server , an operating system , an application, or storage device ) appear to function as multiple virtual resources; it can also include making multiple physical resources (such as storage devices or servers) appear as a single virtual resource. [2] Virtualization technology is a aggregative term of technical means and methods to implement virtualization. It can be divided to many types based on objects: storage virtualization, computing virtualization, network virtualization. Computing virtualization include : OS level virtualization, application level virtualization, hyper visor. Hypervisor include: host vm and guest vm.
- 16. Cloud computing break out Compared to its brother buzzwords, cloud computing is just beginning. Trends in usage of the terms from Google searches shows Cloud Computing is a relatively new term introduced in the past year. There has also been a decline in general interest of Grid, Utility and Distributed computing. Cloud Computing and Virtualization are the next hot hosting platforms; the Dedicated server term is slowly starting to lose ground vs. Virtualization and Cloud Computing.
- 17. Content What is cloud computing Cloud computing discriminate Cloud computing technology Cloud computing products and market
- 18. What cloud computing means to service provider? Fast Provision Reduce servers scale Increase resource utilization rate Improve management efficiency Lower maintenance cost Location of infrastructure in areas with lower costs of real estate and electricity Provide business continuity service Improve management efficiency Improve service levels Complex architecture Change of business model and faith
- 19. What cloud computing means to suers? Lower client workload Lower Total Cost Ownership Separation of infrastructure maintenance duties from domain-specific application development Separation of application code from physical resources Not have to purchase assets for one-time or infrequent intensive computing tasks Expand resource on-demand Make the application have high availability Quickly deploy application Pay per use
- 20. Cloud computing infrastructure features Self-healing Multi-tenancy Virtualized Linearly Scalable Resource Monitor and measure Resource registration and discovery
- 21. Cloud computing infrastructure architecture The physical hardware layer is virtualized to provide a flexible adaptive platform to improve resource utilization. The keys to new enterprise data center infrastructure services are the next two layers, the virtualization environment and management layer. The combination of these two layers ensure that resources in a data center are efficiently managed and can be provisioned, deployed, and configured rapidly.
- 22. Difficulties for cloud computing Continuous high availability Cosistency Interoperability and standarlization Scalability of all components Data secrecy Legal and political problem of data store and translation across regions Performance issue Difficulty customizing Organizational obstacle
- 23. Potencial issues in cloud computing Privileged user access. Regulatory compliance. Data location. Data segregation. Recovery. Investigative support. Long-term viability.
- 24. Content What is cloud computing Cloud computing discriminate Cloud computing technology Cloud computing products and market
- 25. 10 examples of entpereises using the clouds The NY Times Amazon EC2 Nasdaq Amazon S3 Major League Baseball Joyent ESPN Rightscale using Amazon EC2 Hasbro Amazon EC2 British Telecom 3Tera Taylor Woodrow Google Apps CSS Amazon EC2 Activision Amazon EC2 Business Objects (A SAP Company) Rightscale using Amazon EC2
- 26. Cloud computing market Hardware provider Cloud technology enabler Infrastructure as a service Platform as a service Software as a service Everything is a service
- 27. Cloud computing infrastructure tech&solution provider 3Tera - AppLogic grid OS used as cloud computing platform by service providers and enterprises Appistry - Cloud computing middleware - Enables easily scalable cloud computing in the enterprise. Cassatt - Cassatt Active Response platform enables administrators to set policies to power physical and virtual servers safely on and off and pool their computing resources. CloudHan - Cloud tech and infrastructure consultant, in China. CloudScale Networks - Cloud enabler. Currently in private ALPHA only Enomaly Inc - Service Provider & Cloud Enabler - Developer of the Enomalism Elastic Computing Platform & Elastic Drive Q-layer - provides software for data centers that enables cloud computing, support VSAN, VLAN, VPDC, currently support VMware ESX. Skytap - IaaS service optimized for QA, Training, Demo, and Ops Testing. Supports VMware, Xen hypervisors & Windows, Linux & Solaris OS guests.
- 28. Cloud computing infrastructure provider Agathon Group - Cloud provider. Services include highly available VPS, virtual private datacenters and ready-to-use LAMP stacks. Self-service ordering. Custom development and managed services available. Amazon Web Services - Amazon EC2/S3 (Hardware-a-a-S & Cloud Storage) CohesiveFT - CohesiveFT Elastic Server On-Demand ElasticHosts - UK-based instant, on-demand servers in the cloud Flexiscale - Another instant provisioner of web servers with some advanced features like auto-scaling coming soon. GoGrid - instant, on-demand servers offering "control in the cloud". Deploy Windows/Linux servers via web-interface in minutes GridLayer - Cloud Provider. A service by Layered Technologies that delivers Virtual Private Datacenters and virtual private servers from grids of commodity servers LayeredTechnologies - Cloud Provider. provider of on-demand hosting and cloud and utility computing solutions through its brand GridLayer Mosso - Rackspace's cloud hosting service Newservers - Instant provisioning of web servers either Windows or Linux
- 29. Cloud computing Paas provider Bungee Connect - Provides end to end tools and systems required to develop, deploy and host web applications (Platform as a Service) Coherence - Oracle Coherence Data Grid for EC2 and other cloud platforms Force.com - Salesforce.com's application development platform (PaaS) GigaSpaces - middleware for the cloud, "cloudware" Google AppEngine - (PaaS)Now support python Heroku - Ruby on Rails in their Cloud Qrimp - An AJAX based PaaS RightScale - RightScale provides a platform and expertise that enable companies to create scalable web applications running on Amazon’s Web Services that are reliable, easy to manage, and cost less
- 30. Service provider based on Cloud computing CAM Solutions - SaaS Provider. Cloud Event Management, Autonomics and Monitoring-as-a-Service(TM) CloudStatus - CloudEnabler. Real-time performance trending of cloud infrastructure (currently AWS). Kaavo 's IMOD is an easy to use online application. Cloud Computing Made Easy. Microsoft Mesh Nasstar - SaaS provider. Business grade Hosted Desktop service, UK market leaders. Nirvanix - Cloud Storage TrustSaaS - uptime monitoring and alerting service ('SaaS Weather Report') for Software as a Service (SaaS) run by an independent third party
- 31. Cloud computing open source projects Infrastructure management projects : Enomalism, convirt, redhat genome, hyperVM, lxlabs, LN, OpenNEbula, reservoir-fp7, scalr,eucalyptus,ganeti,gplhost , ovirt Useful open source projects to build cloud platform : Kenso, hyperic, virt-P2V 。
- 32. Thanks Liming Liu [email_address]
![Introduction to Cloud Computing 2008-08 Liming Liu [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-cloud-computing-1231468672808509-1/85/Introduction-To-Cloud-Computing-1-320.jpg)











![Computer cluster A computer cluster is a group of coupled computers that work together closely so that in many respects they can be viewed as though they are a single computer. The components of a cluster are commonly, but not always, connected to each other through fast local area networks . Clusters are usually deployed to improve performance and/or availability over that provided by a single computer, while typically being much more cost-effective than single computers of comparable speed or availability. [1] Grids tend to be more loosely coupled , heterogeneous, and geographically dispersed, grid computers do not fully trust each other.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-cloud-computing-1231468672808509-1/85/Introduction-To-Cloud-Computing-14-320.jpg)
![Virtualization Virtualization is a broad term that refers to the abstraction of computer resources. Virtualization hides the physical characteristics of computing resources from their users, be they applications , or end users . [1] This includes making a single physical resource (such as a server , an operating system , an application, or storage device ) appear to function as multiple virtual resources; it can also include making multiple physical resources (such as storage devices or servers) appear as a single virtual resource. [2] Virtualization technology is a aggregative term of technical means and methods to implement virtualization. It can be divided to many types based on objects: storage virtualization, computing virtualization, network virtualization. Computing virtualization include : OS level virtualization, application level virtualization, hyper visor. Hypervisor include: host vm and guest vm.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-cloud-computing-1231468672808509-1/85/Introduction-To-Cloud-Computing-15-320.jpg)
















![Thanks Liming Liu [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-cloud-computing-1231468672808509-1/85/Introduction-To-Cloud-Computing-32-320.jpg)