RavenDB
- 1. Document databases in practice Nicola Baldi http://it.linkedin.com/in/nicolabaldi Luigi Berrettini http://it.linkedin.com/in/luigiberrettini
- 2. Overview 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice 2
- 3. Unbounded result sets problem Unbounded number of requests problem 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice - Overview 3
- 4. They favor denormalization over composition and joins Relations are different than in RDBMSs They are schema-less, but attention should be paid in designing documents 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice - Overview 4
- 5. « a conceptual model should be drawn with little or no regard for the software that might implement it » (Martin Fowler, UML Distilled) A domain model should be independent from implementation details like persistence In RavenDB this is somewhat true 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice - Overview 5
- 6. RDBMS are schema-full • tuples = sets of key-value pairs ⇒ flat structure • more complex data structures are stored as relations Document databases are schema-less • object graphs stored as docs ⇒ no flat structure • each document is treated as a single entity RavenDB suggested approach is to follow the aggregate pattern from the DDD book 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice - Overview 6
- 7. ENTITY Some objects are not defined primarily by their attributes They represent a thread of identity that runs through time and often across distinct representations Mistaken identity can lead to data corruption 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice - Overview 7
- 8. VALUE OBJECT When you care only about the attributes of an element of the model, classify it as a value object Make it express the meaning of the attributes it conveys and give it related functionality Treat the value object as immutable Don't give it any identity and avoid the design complexities necessary to maintain entities 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice - Overview 8
- 9. AGGREGATE Invariants are consistency rules that must be maintained whenever data changes They’ll involve relationships within an aggregate (relations & foreign keys: order / orderlines) Invariants applied within an aggregate will be enforced with the completion of each transaction 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice - Overview 9
- 10. Cluster entities and value objects into aggregates and define boundaries around each Choose one entity to be the root of each aggregate and control all access to the objects inside the boundary through the root Allow external objects to hold references to the root only Transient references to internal members can be passed out for use within a single operation only 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice - Overview 10
- 11. Because the root controls access, it cannot be blindsided by changes to the internals This arrangement makes it practical to enforce all invariants for objects in the aggregate and for the aggregate as a whole in any state change 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice - Overview 11
- 12. Nested child document 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice - Overview 12
- 13. Document referenced by ID 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice - Overview 13
- 14. Denormalized reference we clone properties that we care about when displaying or processing a containing document avoids many cross document lookups and results in only the necessary data being transmitted over the network it makes other scenarios more difficult: if we add frequently changing data, keeping details in synch could become very demanding on the server use only for rarely changing data or for data that can be dereferenced by out-of-sync data 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice - Overview 14
- 15. 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice - Overview 15
- 16. Order contains denormalized data from Customer and Product Full data are saved elsewhere 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice - Overview 16
- 17. 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice - Overview 17
- 18. Querying 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice 18
- 19. DocumentStore • used to connect to a RavenDB data store • thread-safe • one instance per database per application Session • used to perform operations on the database • not thread-safe • implements the Unit of Work pattern in a single session, a single document (identified by its key) always resolves to the same instance change tracking 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice – Querying 19
- 20. 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice – Querying 20
- 21. Sequential GUID key • when document key is not relevant (e.g. log entries) • entity Id = sequential GUID (sorts well for indexing) • Id property missing / not set ⇒ server generates a key Identity key • entity Id = prefix + next available integer Id for it • Id property set to a prefix = value ending with slash • new DocumentStore ⇒ server sends a range of HiLo keys Assign a key yourself • for documents which already have native id (e.g. users) 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice – Querying 21
- 22. 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice – Querying 22
- 23. soft-limit = 128 no Take() replaced by Take(128) hard-limit = 1024 if x > 1024 Take(x) returns 1024 documents 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice – Querying 23
- 24. RavenDB can skip over some results internally ⇒ TotalResults value invalidated For proper paging use SkippedResults: Skip(currentPage * pageSize + SkippedResults) Assuming a page size of 10… 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice – Querying 24
- 25. 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice – Querying 25
- 26. 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice – Querying 26
- 27. RavenDB supports Count and Distinct SelectMany, GroupBy and Join are not supported The let keyword is not supported For such operations an index is needed 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice – Querying 27
- 28. All queries use an index to return results Dynamic = created automatically by the server Static = created explicitly by the user 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice – Querying 28
- 29. no matching static index to query ⇒ RavenDB automatically creates a dynamic index on the fly (on first user query) based on requests coming in, RavenDB can decide to promote a temporary index to a permanent one 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice – Querying 29
- 30. permanent expose much more functionality low latency: on first run dynamic indexes have performance issues map / reduce 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice – Querying 30
- 31. 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice – Querying 31
- 32. 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice – Querying 32
- 33. 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice – Querying 33
- 34. Advanced topics 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice 34
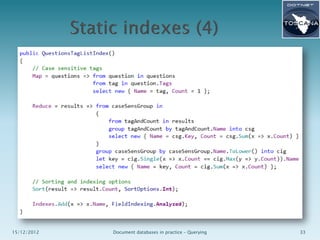
- 35. an index is made of documents document • • • • 15/12/2012 atomic unit of indexing and searching flat ⇒ recursion and joins must be denormalized flexible schema made of fields Document databases in practice – Advanced topics 35
- 36. field • a name-value pair with associated info • can be indexed if you're going to search on it ⇒ tokenization by analysis • can be stored in order to preserve original untokenized value within document example of physical index structure {“__document_id”: “docs/1”, “tag”: “NoSQL”} 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice – Advanced topics 36
- 37. 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice - Overview 37
- 38. 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice – Advanced topics 38
- 39. 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice – Advanced topics 39
- 40. One to one 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice – Advanced topics 40
- 41. One to many ⇒ SELECT N+1 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice – Advanced topics 41
- 42. Value type 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice – Advanced topics 42
- 43. indexing: thread executed on creation or update server responds quickly BUT you may query stale indexes (better stale than offline) 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice – Advanced topics 43
- 44. 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice – Advanced topics 44
- 45. documentStore.Conventions.DefaultQueryingConsistency ConsistencyOptions.QueryYourWrites same behavior of WaitForNonStaleResultsAsOfLastWrite ConsistencyOptions.MonotonicRead you never go back in time and read older data than what you have already seen 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice – Advanced topics 45
- 46. 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice - Overview 46
- 47. 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice - Overview 47
- 48. 15/12/2012 Document databases in practice - Overview 48