Mongo DB
- 2. The Right database to fit your data {“author”:”kirankumar”}
- 3. The Right database to fit your Development
- 4. The Right database for Scale and Performance
- 7. NoSQL Defining Characteristics – Scaling out on commodity hardware – Aggregate structure – Schema-less attitude – Impedance Mismatch : Relational model in-memory data structures – Big Data : Massive data being stored and transacted – Reduced Data Management and Tuning Requirements – Eventually consistent / BASE (not ACID)
- 8. NoSQL databases are little different than conventional databases (in terms of storage, reterival, performance, scalability, security, accuracy. They are widely used in web applications (like storing website cache so that results can be fetched on search, for example google). Conventional databases involves storing rows (tables) and then multiple tables might be joined to fetch results for required query. In NoSQL solution data might be stored based on columns or key/value pair. Performance is better in NoSQL databases (again depends how it’s used and setup). To improve performance of conventional databases hardware or database optimization will be required. Understanding NO SQL
- 9. • Mongo DB is an open source project. • On Github • Licensed under the AGPL • Started and Sponsored by Mongo DB Inc( Formely Know as 10gen) Open source
- 11. History of the Database • 1960’s – Hierarchical and Network type (IMS and CODASYL) • 1970’s – Beginnings of theory behind relational model. Codd • 1980’s – Rise of the relational model. SQL. E/R Model (Chen) • 1990’s – Access/Excel and MySQL. ODMS began to appear • 2000;’s – Two forces; large enterprise and open source. Google and Amazon. CAP Theorem (more on that to come…) • 2010’s – Immergence of NoSQL as an industry player and viable alternative
- 14. Why MongoDB • Intrinsic support for agile development • Super low latency access to your data • Very little CPU overhead • No Additional caching layer required • Built in Replication and Horizontal Scaling support {“author”:”kirankumar”}
- 15. ● A document is the basic unit of data for MongoDB, roughly equivalent to a row in arelational database management system (but much more expressive). ● Similarly, a collection can be thought of as the schema-free equivalent of a table. ● A single instance of MongoDB can host multiple independent databases, each of which can have its own collections and permissions. ● MongoDB comes with a simple but powerful JavaScript shell, which is useful for the administration of MongoDB instances and data manipulation. Overview on Mongo DB
- 16. 10gen is the company behind MongoDB. Set the direction & contribute code to MongoDB Foster community & ecosystem Provide MongoDB management services Provide commercial services Founded in 2007 • Dwight Merriman, Eliot Horowitz • Doubleclick, Oracle, Marklogic, HP $73M+ in Funding • Flybridge, Sequoia, NEA, Union Square Worldwide Expanding Team • 140+ employees • NY, Palo Alto, London, Dublin, Sydney {“author”:”kirankumar”}
- 17. Terminology RDBMS Mongo Table, View Collection Row(s) JSON Document Index Index Join Embedded Document Partition Shard Partition Key Shard Key
- 18. MongoDB is Easy to Use { title: ‘MongoDB’, contributors: [ { name: ‘Eliot Horowitz’, email: ‘[email protected]’ }, { name: ‘Dwight Merriman’, email: ‘[email protected]’ } ], model: { relational: false, awesome: true } }
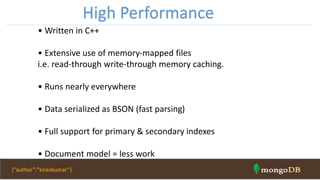
- 19. • Written in C++ • Extensive use of memory-mapped files i.e. read-through write-through memory caching. • Runs nearly everywhere • Data serialized as BSON (fast parsing) • Full support for primary & secondary indexes • Document model = less work High Performance {“author”:”kirankumar”}
- 20. Performance
- 22. Communication
- 23. Communication
- 24. Replica set communication breaks down {“author”:”kirankumar”}
- 26. Primary Election
- 28. Document • At its simplest form, Mongo is a document oriented database • MongoDB stores all data in documents, which are JSON-style data structures composed of field-and-value pairs. • MongoDB stores documents on disk in the BSON serialization format. BSON is a binary representation of JSON documents. BSON contains more data types than does JSON. • ** For in-depth BSON information, see bsonspec.org. NOSQL Intro & MongoDB 28{“author”:”kirankumar”}
- 29. What does a Document Look Like • { • "_id" : "52a602280f2e642811ce8478", • "ratingCode" : "PG13", • "country" : "USA", • "entityType" : "Rating” • } NOSQL Intro & MongoDB 29
- 30. Rules for a document • Documents have the following rules: • The maximum BSON document size is 16 megabytes. • The field name _id is reserved for use as a primary key; its value must be unique in the collection. • The field names cannot start with the $ character. • The field names cannot contain the . character. NOSQL Intro & MongoDB 30
- 31. BSON • JSON has powerful, but limited set of datatypes • Mongo extends datypes with Date, Int types, Id, … • MongoDB stores data in BSON • BSON is a binary representation of JSON • Optimized for performance and navigational abilities • Also compression • See bsonspec.org
- 33. Mongo Install • Windows • http://docs.mongodb.org/manual/tutorial/install-mongodb-on-windows/ • MAC • http://docs.mongodb.org/manual/tutorial/install-mongodb-on-os-x/ • Create Data Directory , Defaults • C:datadb • /data/db/ (make sure have permissions) • Or can set using -dbpath • C:mongodbbinmongod.exe --dbpath d:testmongodbdata NOSQL Intro & MongoDB 33{“author”:”kirankumar”}
- 34. Start IT! • Database • mongod • • Shell • mongo • show dbs • show collections • db.stats() NOSQL Intro & MongoDB 34{“author”:”kirankumar”}
- 35. Basic Operations • 1_simpleinsert.txt • Insert • Find • Find all • Find One • Find with criteria • Indexes • Explain() NOSQL Intro & MongoDB 35{“author”:”kirankumar”}
- 36. More Mongo Shell • 2_arrays_sort.txt • Embedded documents • Limit, Sort • Using regex in query • Removing documents • Drop collection NOSQL Intro & MongoDB 36
- 37. Import / Export • 3_imp_exp.txt • Mongo provides tools for getting data in and out of the database • Data Can Be Exported to json files • Json files can then be Imported NOSQL Intro & MongoDB 37{“author”:”kirankumar”}
- 38. Import / Export • 3_imp_exp.txt • Mongo provides tools for getting data in and out of the database • Data Can Be Exported to json files • Json files can then be Imported NOSQL Intro & MongoDB 38{“author”:”kirankumar”}
- 39. Conditional Operators • 4_cond_ops.txt • $lt • $gt • $gte • $lte • $or • Also $not, $exists, $type, $in • (for $type refer to http://docs.mongodb.org/manual/reference/operator/query/type/#_S_typ e ) NOSQL Intro & MongoDB 39{“author”:”kirankumar”}
- 40. Admin Commands • 5_admin.txt • how dbs • show collections • db.stats() • db.posts.stats() • db.posts.drop() • db.system.indexes.find() NOSQL Intro & MongoDB 40{“author”:”kirankumar”}
- 41. Data MODELING • Remember with NoSql redundancy is not evil • Applications insure consistency, not the DB • Application join data, not defined in the DB • Datamodel is schema-less • Datamodel is built to support queries usually NOSQL Intro & MongoDB 41{“author”:”kirankumar”}
- 42. Questions to ask • Your basic units of data (what would be a document)? • How are these units grouped / related? • How does Mongo let you query this data, what are the options? • Finally, maybe most importantly, what are your applications access patterns? • Reads vs. writes • Queries • Updates • Deletions • How structured is it NOSQL Intro & MongoDB 42{“author”:”kirankumar”}
- 43. Data Model - Normalized • Normalized • Similar to relational model. • One collection per entity type • Little or no redundancy • Allows clean updates, familiar to many SQL users, easier to understand NOSQL Intro & MongoDB 43{“author”:”kirankumar”}
- 44. Other considerations For Data Modeling • Many or few collections • Many Collections • As seen in normalized • Clean and little redundancy • May not provide best performance • May require frequent updates to application if new types added • Multiple Collections • Middle ground, partially normalized • Not many collections • One large generic collection • Contains many types • Use type field NOSQL Intro & MongoDB 44{“author”:”kirankumar”}
- 45. Consideration Continued • Document Growth – will relocate if exceeds allocated size • Atomicity • Atomic at document level • Consideration for insertions, remove and multi-document updates • Sharding – collections distributed across mongod instances, uses a shard key • Indexes – index fields often queries, indexes affect write performance slightly • Consider using TTL to automatically expire documents NOSQL Intro & MongoDB 45{“author”:”kirankumar”}
- 47. Text Search • Now production-ready • Integrated with query engine • Integrated with aggregation framework • Multi-language document support {“author”:”kirankumar”}
- 48. Features • Language-specific tokenization and stemming • Stop words • Relevance ranking • Field boosting
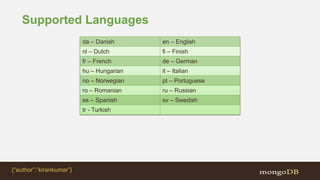
- 49. Supported Languages da – Danish en – English nl – Dutch fi – Finish fr – French de – German hu – Hungarian it – Italian no – Norwegian pt – Portuguese ro – Romanian ru – Russian es – Spanish sv – Swedish tr - Turkish {“author”:”kirankumar”}
- 55. Query System Improvements • Index Intersection • Aggregation Framework • New Update Operators
- 56. Index Intersection • Simpler ad-hoc queries • Existing indexes can be combined to optimize a query – Less Index Maintenance – Smaller Working Set – Lower Write Overhead – MoreAdaptive – Able to control potential intersections using QueryShape
- 58. New Update Operators • $mul • $min/$max • $bit • $currentDate • New modifiers for $push
- 59. Security
- 60. Security • Authentication with LDAP (Enterprise only) • x.509 Certificates • User defined roles • Collection level security • Auditing (Enterprise only) • Windows Kerberos Support
- 61. State of Security in MongoDB 2.6 • Authentication – Who are you? – X.509 authentication and Kerberos • Authorization – What can you do? – User Defined Roles, Collection-levelAccess Control • Auditing – What have you done? – DDL, User Manipulation,Authorization failure
- 62. Roles and Collection-level Security {“author”:”kirankumar”}
- 63. Auditing • Schema actions • Replica Set actions • Authentication &Authorization actions • Other actions {“author”:”kirankumar”}
- 64. Auditing – Dropping a collection {“author”:”kirankumar”}
- 65. Auditing – Shutting down the server {“author”:”kirankumar”}
- 66. •Cost It's free, open source. Can has more scale? Just add hardware. Licensing costs need not apply (can run on Linux) . •Schema-less If you need to support a flexible schema, MongoDB's document storage is a big plus. It doesn't mean you don't need to think about schema at all, it just means you can very easily model data of this nature and cope with changes without headaches. •Quick start & fast learning Mongodb was quick and easy. There was no entry barrier. I can't fault how quick and easy it was to get up and running with the basics. Hacking around to pick up the more advanced stuff was also a pretty painless exercise too. Using the C# driver has been a largely very positive and intuitive experience. •Replica sets Configuring is simple, making scaling reads and failover pretty effortless. Want more redundancy or scaling of reads? Fire up another machine, add to the set and away you go. Mongo DB Pros
- 67. •Auto Sharding Again, configuring is simple. You do need to give very careful consideration to this up front when deciding on what keys you want to shard on. Once you've done that, sharding "just does it's stuff". •Community It has a good community behind it and that IMHO is very important. I don't like sitting in a cupboard on my own with the lights off. I like being a part of a bigger community - to learn from, work through issues with and to contribute back to. •Rapidly evolving MongoDB is rapidly changing and it's good to see bugs are being tracked and fixed in good time. There is also a fast flowing feature enhancement pipeline too, so you typically don't have to wait for a long time to get something. •Choose your consistency You can choose to have data replicated to a configurable number of replicas before returning if you wish to have stronger level of consistency. Depends on what value you put on certain bits of data, but the choice is yours. So you can trade off performance for consistency. Mongo DB Pros
- 68. • Data size in MongoDB is typically higher due to e.g. each document has field names stored it • less flexibity with querying (e.g. no JOINs) • no support for transactions - certain atomic operations are supported, at a single document level • at the moment Map/Reduce (e.g. to do aggregations/data analysis) is OK, but not blisteringly fast. So if that's required, something like Hadoop may need to be added into the mix • less up to date information available/fast evolving product Mongo DB cons
- 69. Design decisions with Mongo • Agile incremental releases • Unstructured data from multiple suppliers • GridFS : Stores large binary objects • Spring Data Services • Embedding and linking documents • Easy replication set up for AWS
- 70. Books MongoDB: The Definitive Guide, 2nd Edition By: Kristina Chodorow Publisher: O'Reilly Media, Inc. Pub. Date: May 23, 2013 Print ISBN-13: 978-1-4493-4468-9 Pages in Print Edition: 432 MongoDB in Action By: Kyle Banker Publisher: Manning Publications Pub. Date: December 16, 2011 Print ISBN-10: 1-935182-87-0 Print ISBN-13: 978-1-935182-87-0 Pages in Print Edition: 312 The Definitive Guide to MongoDB: The NoSQL Database for Cloud and Desktop Computing By Eelco Plugge; Peter Membrey; Tim Hawkins Apress, September 2010 ISBN: 9781430230519 327 pages NOSQL Intro & MongoDB 70{“author”:”kirankumar”}
- 71. Books Cont. MongoDB Applied Design Patterns By: Rick Copeland Publisher: O'Reilly Media, Inc. Pub. Date: March 18, 2013 Print ISBN-13: 978-1-4493-4004-9 Pages in Print Edition: 176 MongoDB for Web Development (rough cut!) By: Mitch Pirtle Publisher: Addison-Wesley Professional Last Updated: 14-JUN-2013 Pub. Date: March 11, 2015 (Estimated) Print ISBN-10: 0-321-70533-5 Print ISBN-13: 978-0-321-70533-4 Pages in Print Edition: 360 Instant MongoDB By: Amol Nayak; Publisher: Packt Publishing Pub. Date: July 26, 2013 Print ISBN-13: 978-1-78216-970-3 Pages in Print Edition: 72 NOSQL Intro & MongoDB 71{“author”:”kirankumar”}
- 72. Important Sites • http://www.mongodb.org/ • https://mongolab.com/welcome/ • https://education.mongodb.com/ • http://blog.mongodb.org/ • http://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/mongodb • http://bitnami.com/stack/mean NOSQL Intro & MongoDB 72
- 75. For more details {“Linked In” : “in.linkedin.com/pub/kiran-kumar-matam/2b/239/91b/”} {“catchme on”: [ {“name” : “kirankumar”, “website” : [ “techincal”:”www.javaquestionbank.net”, “personal” :www.matamkirankumar.com ], “twitter : ” @matamkiran11” } ] }
- 76. Thank you


















![MongoDB is Easy to Use
{
title: ‘MongoDB’,
contributors: [
{ name: ‘Eliot Horowitz’,
email: ‘eliot@10gen.com’ },
{ name: ‘Dwight Merriman’,
email: ‘dwight@10gen.com’ }
],
model: {
relational: false,
awesome: true
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongokkppt-150115085706-conversion-gate02/85/Mongo-DB-18-320.jpg)






















































![For more details
{“Linked In” : “in.linkedin.com/pub/kiran-kumar-matam/2b/239/91b/”}
{“catchme on”:
[
{“name” : “kirankumar”,
“website” : [
“techincal”:”www.javaquestionbank.net”,
“personal” :www.matamkirankumar.com ],
“twitter : ” @matamkiran11”
}
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongokkppt-150115085706-conversion-gate02/85/Mongo-DB-75-320.jpg)
