NOSQL- Presentation on NoSQL
- 1. Presentation on NoSQL “Towards the end of RDBMS ?” By: Ramakant Soni Asst. Professor, Dept. of Computer Science, BKBIET, Pilani
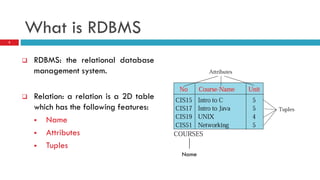
- 2. What is RDBMS RDBMS: the relational database management system. Relation: a relation is a 2D table which has the following features: Name Attributes Tuples Name 2
- 3. Issues with RDBMS- Scalability Issues with scaling up when the dataset is just too big e.g. Big Data. Not designed to be distributed. Looking at multi-node database solutions. Known as ‘horizontal scaling’. Different approaches include: Master-slave Sharding 3
- 4. Scaling RDBMS Master-Slave All writes are written to the master. All reads are performed against the replicated slave databases. Critical reads may be incorrect as writes may not have been propagated down. Large data sets can pose problems as master needs to duplicate data to slaves. Sharding Scales well for both reads and writes. Not transparent, application needs to be partition-aware. Can no longer have relationships or joins across partitions. Loss of referential integrity across shards. 4
- 5. What is NoSQL Stands for Not Only SQL. Term was redefined by Eric Evans after Carlo Strozzi. Class of non-relational data storage systems. Do not require a fixed table schema nor do they use the concept of joins. Relaxation for one or more of the ACID properties (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) using CAP theorem. 5
- 6. Need of NoSQL Explosion of social media sites (Facebook, Twitter, Google etc.) with large data needs. (Sharding is a problem) Rise of cloud-based solutions such as Amazon S3 (simple storage solution). Just as moving to dynamically-typed languages (Ruby/Groovy), a shift to dynamically-typed data with frequent schema changes. Expansion of Open-source community. NoSQL solution is more acceptable to a client now than a year ago. 6
- 7. NoSQL Types NoSQL database are classified into four types: • Key Value pair based • Column based • Document based • Graph based 7
- 8. Key Value Pair Based • Designed for processing dictionary. Dictionaries contain a collection of records having fields containing data. • Records are stored and retrieved using a key that uniquely identifies the record, and is used to quickly find the data within the database. Example: CouchDB, Oracle NoSQL Database, Riak etc. We use it for storing session information, user profiles, preferences, shopping cart data. We would avoid it when we need to query data having relationships between entities. 8
- 9. Column based It store data as Column families containing rows that have many columns associated with a row key. Each row can have different columns. Column families are groups of related data that is accessed together. Example: Cassandra, HBase, Hypertable, and Amazon DynamoDB. We use it for content management systems, blogging platforms, log aggregation. We would avoid it for systems that are in early development, changing query patterns. 9
- 10. Document Based The database stores and retrieves documents. It stores documents in the value part of the key-value store. Self- describing, hierarchical tree data structures consisting of maps, collections, and scalar values. Example: Lotus Notes, MongoDB, Couch DB, Orient DB, Raven DB. We use it for content management systems, blogging platforms, web analytics, real-time analytics, e- commerce applications. We would avoid it for systems that need complex transactions spanning multiple operations or queries against varying aggregate structures. 10
- 11. Graph Based Store entities and relationships between these entities as nodes and edges of a graph respectively. Entities have properties. Traversing the relationships is very fast as relationship between nodes is not calculated at query time but is actually persisted as a relationship. Example: Neo4J, Infinite Graph, OrientDB, FlockDB. It is well suited for connected data, such as social networks, spatial data, routing information for goods and supply. 11
- 12. CAP Theorem According to Eric Brewer a distributed system has 3 properties : Consistency Availability Partitions We can have at most two of these three properties for any shared-data system To scale out, we have to partition. It leaves a choice between consistency and availability. ( In almost all cases, we would choose availability over consistency) Everyone who builds big applications builds them on CAP : Google, Yahoo, Facebook, Amazon, eBay, etc. 12
- 13. Advantages of NoSQL Cheap and easy to implement (open source) Data are replicated to multiple nodes (therefore identical and fault- tolerant) and can be partitioned When data is written, the latest version is on at least one node and then replicated to other nodes No single point of failure Easy to distribute Don't require a schema 13
- 14. What is not provided by NoSQL Joins Group by ACID transactions SQL Integration with applications that are based on SQL 14
- 15. Where to use NoSQL NoSQL Data storage systems makes sense for applications that process very large semi-structured data –like Log Analysis, Social Networking Feeds, Time-based data. To improve programmer productivity by using a database that better matches an application's needs. To improve data access performance via some combination of handling larger data volumes, reducing latency, and improving throughput. 15
- 16. Conclusion All the choices provided by the rise of NoSQL databases does not mean the demise of RDBMS databases as Relational databases are a powerful tool. We are entering an era of Polyglot persistence, a technique that uses different data storage technologies to handle varying data storage needs. It can apply across an enterprise or within an individual application. 16
- 17. References 1. “NoSQL Databases: An Overview”. Pramod Sadalage, thoughtworks.com(2014) 2. “Data management in cloud environments: NoSQL and NewSQL data stores”. Grolinger, K.; Higashino, W. A.; Tiwari, A.; Capretz, M. A. M. (2013). JoCCASA, Springer. 3. “Making the Shift from Relational to NoSQL”. Couchbase.com(2014). 4. “NoSQL - Death to Relational Databases”. Scofield, Ben (2010). 17