Software Project Management for 'Weather Forecasting using Data mining'
- 1. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Weather Forecasting Using Data Mining Final Project 05/04/2016 SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management 1
- 2. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Contents Sr. No. Artifact Slide Number 01 Business case 03 02 Vision 46 03 Architecture 63 04 Work Breakdown structure 81 05 Software Development Plan 99 06 Summary 2
- 3. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Weather Forecasting using Data Mining Business Case 03/30/2016 SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management 3
- 4. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Overview Background Project overview Architecture Cost Schedule Financial benefit 4
- 5. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Background The Problem Weather forecasting is a vital application in meteorology and has been one of the most scientifically and technologically challenging problem around the world. Primary users for the system are general public, aviation, fire and marine. Aviation forecasters use them in order to keep an eye on surface observations for wind shear, restrictions to visibility that could affect takeoffs and landings.[4] 5
- 6. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Background Forecasters support fire weather programs by checking for relative humidity because it can have critical impact on behaviors of fire. Every member of population uses weather data on regular basis, thinking of how weather can affect your travel, activity and business decision the list of users become longer[4] Similar service providers are – National Weather Services(NWS), popular sites like Weather Underground, forecast.io, Weather spark and Google 6
- 7. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Project Overview In data mining we use analysis tools to discover patterns and relationships in data, that maybe used to make valid prediction In this proposed software we investigate use of data mining in forecasting maximum temperature, rainfall, evaporation and wind speed. 7
- 8. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Project team based Project Manager Architect Business Analyst Designer Tester Requirement specialist 8
- 9. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar What we plan to do In this proposed software, we plan to use the data mining techniques in forecasting weather. This can be carried out with help of Artificial Neural Network, Decision Tree Algorithm and meteorological data collected in specific time. We plan to follow Royce’s project lifecycle, and the software development plan and work breakdown structure explains the activities we have scheduled. Primarily, the elaboration phase will focus on getting the prototype approved from stakeholders. 9
- 10. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar High Level Architecture For weather prediction software, we plan to use both algorithm using both Artificial Neural Network(ANN) and Decision Trees(DT). The data mining technique which is going to be used will require historical data which is done under Data Collection component of this process. For data sets we will be using current weather services APIs like Weather.com, forecast.io, Accuweather. 10
- 11. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar High Level Architecture Image Source: Click here [1] 11
- 12. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Data mining Architecture Image Source: Click here [2] 12
- 13. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Major Components Data Collection: As explained earlier we would be feeding historical data to the system, this could be from specific region Data Cleaning: Under this component the data glitches like the missing data, duplicated data is found and bad data is weed out Data selection: Under this stage, relevant data related to analysis is retrieved and classified under 10 attributes as shown in table below 13
- 14. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Attributes of data set[Image Source [2]] 14
- 15. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Major Components Data Transformation: Under this stage the selected data will be transformed to accepted form for data mining(Commas Separated Values) Data mining : Under this stage, the algorithms are used to analyze meteorological datasets which further results in interesting patterns which are then studied 15
- 16. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar COTS Historical climate data from various sources for specific region which can be bought from meteorological centers or airport stations 16
- 17. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Estimating Cost We shall be estimating cost using use case points, estimating use case points System Requirements: o Enumerated Functional Requirements: The system should allow administrator to add historical weather data The system should be able to recognize patterns in temperature, humidity and wind with use of historical data 17
- 18. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Estimating Cost System should periodically apply prediction algorithms or models on obtained data and store results to central database System shall obtain and display confidence value for each prediction given to user System shall support registering new user by providing email, so system can send daily weather updates to registered users System shall allow users to check weather for one week ahead 18
- 19. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Estimating Cost System should be able to alert its registered users by sending storm warnings in emergencies Non-functional requirements: System shall allow for users to get prediction for weather within almost two mouse clicks System should ensure that features that do not require a user to be logged in are not hidden to unregistered users 19
- 20. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Estimating Cost System should be able to run with core functionality intact from Smartphone or tablet System should be able to show interactive animations to users regarding current and future climatic conditions System should allow language preference to users System should provide graphs and maps of climate conditions 20
- 21. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Estimating Cost Actors and User goals: • Registered User • Visitor • Database • Historical data provider • Graph plotter • Administrator 21
- 22. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Estimating Costs Use cases: 1. For Administrator: i. Report(Feed) historical weather data ii. Report status iii. Remove data iv. Logout 22
- 23. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Estimating Costs 2. For Registered user: i. Track weather ii. Search for future predictions iii. Get hourly/timely weather updates in email 3. For Graph plotter: i. Plot sketches of weather predictions on map 23
- 24. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Estimating Costs 4. Visitor: i. Check weather status ii. Register for timely updates 24
- 25. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Estimating Costs Effort Estimation: Unadjusted Actor Weight Standards: Actor Type Example Weight Simple Another system through an API 1 Average Another system through a protocol A person through a text based user interface 2 Complex A person through a graphical user interface 3 25
- 26. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Estimating Costs Actor Description Complexity Weight Registered User A registered user Complex 3 Visitor A unregistered user Complex 3 Database Records of weather information, user data and system data Average 2 Historical weather data provider Provides historical data from different source Average 2 Graph plotter Provides visuals from raw data Simple 1 Administrator Special case Complex 326
- 27. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Estimating Costs UAW = 3 x Complex + 2 x Average + 1 x Simple = 3 x 3 + 2 x 2 + 1 x 1 = 9 + 4 + 1 = 14 Unadjusted use case weight (UUCW): In Kerner’s original formula, each use case is assigned a number of points based on number of transactions within the use case 27
- 28. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Estimating Costs Unadjusted Use case weights standards: Use case complexity Number of transactions Weights Simple 3 or fewer 5 Average 4 to 7 10 Complex More than 7 15 28
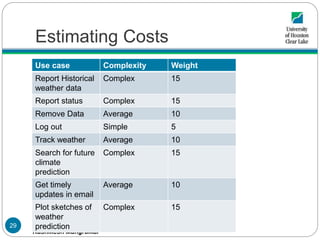
- 29. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Estimating Costs Use case Complexity Weight Report Historical weather data Complex 15 Report status Complex 15 Remove Data Average 10 Log out Simple 5 Track weather Average 10 Search for future climate prediction Complex 15 Get timely updates in email Average 10 Plot sketches of weather prediction Complex 15 29
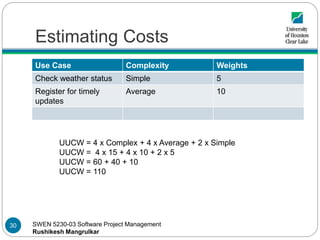
- 30. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Estimating Costs Use Case Complexity Weights Check weather status Simple 5 Register for timely updates Average 10 UUCW = 4 x Complex + 4 x Average + 2 x Simple UUCW = 4 x 15 + 4 x 10 + 2 x 5 UUCW = 60 + 40 + 10 UUCW = 110 30
- 31. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Adjustment for Technical Complexity: Factor Complexity Weight Calculated Factor Distributed System 2 3 6 Performance objectives 2 3 6 End user efficiency 1 2 2 Complex processing 1 4 4 Reusable Code 1 2 2 Easy to install 0.5 3 1.5 Easy to use 0.5 5 2.5 Portable 2 2 4 Easy to change 1 1 1 31
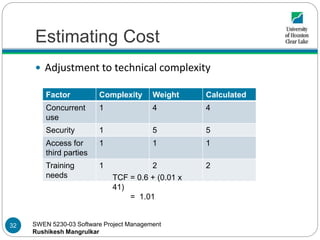
- 32. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Estimating Cost Adjustment to technical complexity Factor Complexity Weight Calculated Concurrent use 1 4 4 Security 1 5 5 Access for third parties 1 1 1 Training needs 1 2 2 TCF = 0.6 + (0.01 x 41) = 1.01 32
- 33. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Environmental Complexity Factor Factor Weight Assessm ent Impact E1 Familiarity with development process 1.5 3 4.5 E2 Application Experience 0.5 4 2 E3 Object oriented experience 1 4 4 E4 Lead analyst capability 0.5 4 2 E5 Motivation 1 5 5 E6 Stable requirements 2 1 2 E7 Part time staff -1 0 0 E8 Difficult programming language -1 2 -2 33
- 34. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Environmental Complexity Factor ECF = 1.4 + (-0.03 x EFactor) = 1.4 + (-0.03 x 17.5) = 0.875 34
- 35. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Estimate Cost and Schedule Unadjusted use case points (UUCP) = UAW + UUCW = 110 + 14 = 124 Use case points (UCP) = 124 x TCF x ECF = 124 x 1.01 x 0.875 = 109.383 or 109 Use Case Points Duration = Use Case Points * ( 20 - 28) hours per week = 2180 to 3052 hours 35
- 36. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Estimate Cost and Schedule Explaining 20 – 28 hours estimate: According to approach proposed by Schneider and Winters (1998), they suggest counting number of environmental factors in E1 through E6 that are 3, and those in E7 and E8 that are below 3. Hence if the total is 2 or less, assume 20 hours per use case point, and for total 3 or 4 assume 28 hours per use case point. Any total larger than 4 indicates that there are two many environmental factors stacked against the project.[4, Page 8] Since our environmental factors total falls in ‘two or less’ category, we assume 20 hours per use case point. Therefore, 109 use cases * 20 hours per use case point: 2180 hours (person hours) 36
- 37. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Estimate Cost and Schedule Accurate cost estimates are critical to both developers and customers. They can be used to request for proposal, contract negotiation and scheduling. We got 2180 hours (For 1 person). We estimate having 3 persons working per iteration and assume each iteration lasts two weeks: We also estimate that each developer will spend about 30 hours per week on project tasks. The rest of their time will be sucked up by corporate overhead—answering email, attending meetings, and so on[5] 37
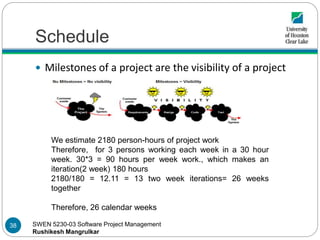
- 38. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Schedule Milestones of a project are the visibility of a project We estimate 2180 person-hours of project work Therefore, for 3 persons working each week in a 30 hour week. 30*3 = 90 hours per week work., which makes an iteration(2 week) 180 hours 2180/180 = 12.11 = 13 two week iterations= 26 weeks together Therefore, 26 calendar weeks 38
- 39. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Estimate Cost and Schedule For 2180 hours, 2180 * $100 = $218000, also we need to consider 30% overhead cost 30/100 * 218000 = $65400 218000 + 654000 = $283400 Therefore, total cost of the project is : $283400 39
- 40. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Schedule Phase Start End Associated Milestones Inception Phase Week 1 Week 6 Lifecycle objective milestone Elaboration Phase Week 7 Week 15 Lifecycle architecture milestone Construction Phase Week 16 Week 22 Initial operational capability milestone Transition Phase Week 23 Week 26 Product release milestone 40
- 41. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Financial Benefit Accurate weather data is demanded by significant amount of users, for nearly every facet of our population, the weather data has critical role in decision making. Major buyers: A. Aviation forecasters B. Marine Industry C. Daily commuting users 41
- 42. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Financial Benefit Some studies have examined value of short term weather predictions: i. Saving to oil drilling companies in Gulf of Mexico from avoiding unnecessary drill rig evacuations[1] ii. Improved fueling decisions at Australian airports resulting from better forecast, could save companies $6 – 7 million per year[1] iii. Better hurricane forecast for Atlantic coast over past 100 years have resulted in major reductions in yearly deaths in hurricane activity[1] 42
- 43. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Summary All sectors whether private or public get affected to sudden weather changes, having at least near to accurate prediction of weather can generate huge impact and reduce losses. With the help of this software we can work towards achieving this goal We have prepared a business case which plans the cost estimated using the use cases laid out on basis of functional requirements and also estimate the schedule of the project. We also have designed a high level architecture and plan to proceed with vision artifact after getting approval for the business case 43
- 44. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar References [1] https://www.gwu.edu/~spi/assets/docs/Socio- EconomicBenefitsFinalREPORT2.pdf [2]For cost estimation using use case: http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~jhm/Readings/Cohn%20- %20Estimating%20with%20Use%20Case%20Points_v2%2012-24-50- 761.pdf [3]http://sceweb.sce.uhcl.edu/helm/rationalunifiedprocess/examples/cs ports/ex_sdp.htm [4]http://www.srh.noaa.gov/srh/dad/coop/USEWX.pdf [5] http://www.methodsandtools.com/archive/archive.php?id=25p3 44
- 45. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar References Image References: 1. http://www.slideshare.net/NitHik1/data-mining2- 43891941 2. http://www.zentut.com/data-mining/data-mining- architecture/ 45
- 46. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Weather Forecasting using Data Mining Vision 04/06/2016 SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management 46
- 47. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Overview Stakeholder and User Descriptions Product Overview Product Features Constraints 47
- 48. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Stakeholder & User Descriptions Market demographics Daily changing weather plays important part in everyone’s life. Primary users for the system are general public, aviation, fire and marine Aviation forecasters use them in order to keep an eye on surface observations for wind shear, restrictions to visibility that could affect takeoffs and landings Many users have been relying over different website for reliable weather service, and most of them get data from the pro – National Weather Service, branch of National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Every member of population uses weather data on regular basis, thinking of how weather can affect your travel, activity and business decision, the list of users become longer 48
- 49. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Stakeholder & User Descriptions Market demographics NWS has been providing weather reports on county by county basis which on its site which is free, ad – free and quick loading The other sites which followed the popularity were Weather Underground, Forecast.io, Weather Spark, Intellicast and not to forget the Google, as its easily available, but its forecast however is provided by Weather.com.[1] The users are anticipated to be consumers who already use cell phones on a regular basis for personal and/or business use According to report[4], the weather apps are the most downloaded app after gaming apps, they have generated the highest total revenue from paid downloads. It’s really a must-have app for every smart phone user — we want to know whether we’re about to walk into a tornado or not 49
- 50. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Market Demographics: Tim Spangler, director of the COMET atmospheric sciences training program, estimates the broad U.S. weather and climate industry at more than $5 billion, including some 250 commercial weather companies that generate roughly $2 billion [5] 50
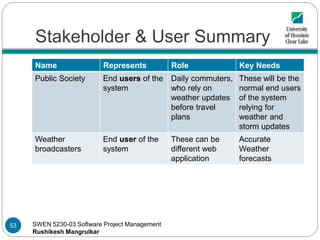
- 51. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Stakeholder & User Summary Name Represents Role Key Needs Private Weather Services Weather data providers A single weather service cannot succeed on basis of its collected data, but requires contribution from different services The system should accept this historical weather data which shall be helpful for developing patterns State and Local governme nt agencies Weather data providers As we plan weather prediction on county basis, the local agencies should also be involved in data contribution The system should accept local as well as global weather data which will be helpful in better prediction 51
- 52. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Stakeholder & User Summary Name Description Key Needs Weather Researchers End users of the system These stakeholders would be studying the predictions provided by our system hence we also can refer them as a stakeholder Requirement Engineers This stakeholder works with customers and other stakeholder to translate needs into requirements Specifies domain, categories requirements into functional and non functional. Refines requirements as needed Software Architect This stakeholder is the lead in development of prediction system The Architect will be required to be responsible for architecture of system, guides design and implementation Project Managers This stakeholder is the lead in development of prediction system The manager will be required to plan, manage, coordinate interactions and keep the team focused 52
- 53. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Stakeholder & User Summary Name Represents Role Key Needs Public Society End users of the system Daily commuters, who rely on weather updates before travel plans These will be the normal end users of the system relying for weather and storm updates Weather broadcasters End user of the system These can be different web application Accurate Weather forecasts 53
- 54. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Product Overview Perspectiv e The diagram explains an high level perspective of the product we plan to develop. The end user will input the current temperature and humidity into the system using mobile/desktop device. The system will have data set feed from the database which was entered by the Admin. The system then runs prediction algorithm in order to forecast the temperature and wind also will notify the end user with these values.54
- 55. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Product Overview The vision document applies to Weather forecast using data mining application which will be developed as a web application. The application will provide way to predict weather based on old weather data feed into system. User will enter temperature, wind and humidity and system will predict weather from previous data in database. Since the system will predicting based on the real old data fed earlier, the prediction can be reliable. 55
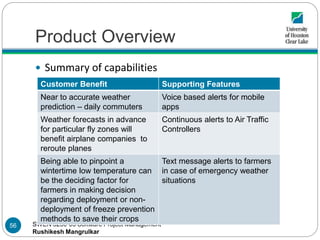
- 56. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Product Overview Summary of capabilities Customer Benefit Supporting Features Near to accurate weather prediction – daily commuters Voice based alerts for mobile apps Weather forecasts in advance for particular fly zones will benefit airplane companies to reroute planes Continuous alerts to Air Traffic Controllers Being able to pinpoint a wintertime low temperature can be the deciding factor for farmers in making decision regarding deployment or non- deployment of freeze prevention methods to save their crops Text message alerts to farmers in case of emergency weather situations 56
- 57. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Product Overview Assumption and Dependencies: i. In using the onscreen keyboard, it is assumed that the user is literate and can type ii. The default language for the application shall be US English. It is assumed that users who cannot speak and write in English will not be using the text to speech features(third party mobile app) in the system, at least initially. iii. The prediction would be dependent on the old weather data provided, and may not give accurate results every time iv. The device used by end user mobile or desktop is required to be connected to the internet in order to access the weather data 57
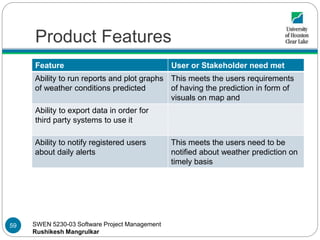
- 58. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Product Features Feature User or Stakeholder Need Met Ability to allow administrator to feed historical data This meets the stakeholders need to make use of the historical weather data Ability to hold user contact information in order to send alerts This meets the users need to be notified about weather prediction on provided contact information Ability to recognize pattern in temperature, humidity and wind from old data This meets the stakeholders needs to apply algorithms and recognize patterns Ability to apply prediction algorithms and store results to database This meets stakeholders need of preserving data 58
- 59. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Product Features Feature User or Stakeholder need met Ability to run reports and plot graphs of weather conditions predicted This meets the users requirements of having the prediction in form of visuals on map and Ability to export data in order for third party systems to use it Ability to notify registered users about daily alerts This meets the users need to be notified about weather prediction on timely basis 59
- 60. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Constraints Usability: i. Ability to read maps, as the weather pattern would be plotted over maps ii. Must be able to understand units of temperature(F or C), wind and humidity Performance I. Accuracy of result depends on accuracy of previous weather data fed into system II. Algorithm calculation may take time, hence delay for data to load 60
- 61. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Summary Our vision of project is develop near to accurate weather prediction system based on historical data. We listed the number of stakeholders and users who are the direct beneficiary of the weather prediction results. Our every listed feature focuses on satisfying the present need of weather forecast, as we march towards our goal we seem to suffer certain constraints which we hope to overcome. 61
- 62. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar References [1] http://lifehacker.com/5897973/five-best-weather- web-sites [2] http://www.trishmarie.com/vision.pdf [3] http://www.livingontherealworld.org/?p=1317 [4] http://techcrunch.com/2011/09/12/report-android- market-nearing-6-billion-downloads-weather-apps- are-makin-it-rain/ [5] http://www.cnbc.com/id/43672839 62
- 63. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Weather Forecasting using Data Mining Architecture April 12 2016 SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management 63
- 64. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Overview Architecture goals Use case view Logical view Process view Deployment view Implementation view 64
- 65. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Architecture Goals The system should allow administrator to add historical weather data The system should be able to recognize patterns in temperature, humidity and wind with use of historical data System should periodically apply prediction algorithms or models on obtained data and store results to central database System shall obtain and display confidence value for each prediction given to user 65
- 66. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Architecture Goals System shall support registering new user by providing email, so system can send daily weather updates to registered users System shall allow users to check weather for one week ahead System should be able to alert its registered users by sending storm warnings in emergencies System should have 99.99% uptime and should recover and be running immediately after disaster An uptime guarantee would be a good indication of our applications commitment to keeping our application up and running 66
- 67. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar High Level Use Case View 67
- 68. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar High Level Use Case This is an high level use case diagram which explains the overall high level functional requirements in our system The user, admin and database are the primary actors interacting with the system The user first registers himself/herself in the system with email id for notifications, and may also enroll its phone number for instant alerts The Admin is responsible for continuously feeding historical weather data into the system from the database The system holds prediction algorithms which shall study patterns in the data and provide future predictions of weather to the user 68
- 69. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Use Case View – Machine side 69
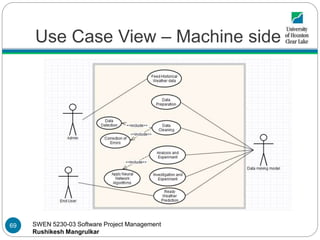
- 70. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Use case view – Machine side The machine side use case view provides overview of major functional requirements on the machine side development Most of the use cases are the stages involved in data mining The Admin feeds the historical weather data into the system, then under the data preparation, we conduct data staging, where data is prepared and kept ready to mine. The data staging area sits between data source and data targets. Further, data is cleaned and redundant data is removed. The cleaned data is now processed by data prediction algorithms Algorithms study the data for patterns developed in data sets, and the ready weather prediction is provided to the end user 70
- 71. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Logical View(Class Diagram) 71
- 72. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Logical View (Class diagram) The ‘Logical View class diagram’ provides the necessary classes working in our system and their relationships. An User can be a ‘registered user’ or a ‘visitor’ to our website, hence their respective classes handle their personal information attributes. An registered user holds an user account, hence user account is a class which handles registered user account information A user checks the weather information hence, weather information is also a class which will hold the weather data to be shown to the end user The weather information would be pulled from the database which also is a class 72
- 73. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar High Level Process View [1] 73
- 74. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar High Level Process View The ‘High Level process view’ diagram is flow of process in our system as the diagram explains The weather data is collected from different weather stations and collected at the data centers The data experts at the data centers analyze the data and feed into the data prediction model The prediction reports are generated and the forecast is shown using graphical representation on maps 74
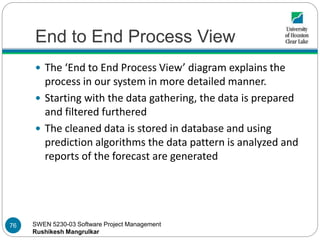
- 75. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar End to End Process View [3] 75
- 76. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar End to End Process View The ‘End to End Process View’ diagram explains the process in our system in more detailed manner. Starting with the data gathering, the data is prepared and filtered furthered The cleaned data is stored in database and using prediction algorithms the data pattern is analyzed and reports of the forecast are generated 76
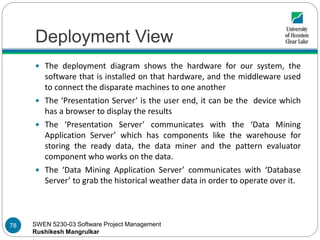
- 77. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Deployment View [2] 77
- 78. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Deployment View The deployment diagram shows the hardware for our system, the software that is installed on that hardware, and the middleware used to connect the disparate machines to one another The ‘Presentation Server’ is the user end, it can be the device which has a browser to display the results The ‘Presentation Server’ communicates with the ‘Data Mining Application Server’ which has components like the warehouse for storing the ready data, the data miner and the pattern evaluator component who works on the data. The ‘Data Mining Application Server’ communicates with ‘Database Server’ to grab the historical weather data in order to operate over it. 78
- 79. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Summary A well designed architecture is a major milestone in success of software project and hence we make an effort to architect the design view, logical view, process view and deployment view. The design view have completed using use case diagram, which describes an high level and a machine perspective use case. The deployment view at the end describes the hardware and software layout expected when product is ready. 79
- 80. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Image References 1. http://www.ctwatch.org/quarterly/print.php%3Fp=1 03.html 2. http://agilemodeling.com/artifacts/deploymentDiag ram.htm 3. http://www.slideshare.net/jafaeldon/data-centric- hpc-for-numerical-weather-forecasting 80
- 81. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Weather Forecasting Using Data Mining Work Breakdown Structure April 20, 2016 SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management 81
- 82. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar WBS According to paper ‘Planning successful data mining projects‘ by IBM, there are four critical data mining success factors for successful planning for data mining projects – the right application, right people, right data and right tools, accordingly we have build this Work breakdown structure. [1] 82
- 83. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar WBS The above diagram shows overall layout of Work Breakdown Structure for our project ‘Weather Forecasting using Data mining‘ All the phases the project must pass through for successful execution have been included, and every entity further breaks into manageable work packages. 83
- 84. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar WBS (Requirement Gathering) a. Our first major deliverable of the project is ‘Requirements Gathering’, the major component deliverables under this are gathering requirements from stakeholders and documenting them using use case scenarios and planning the activity flow using diagrams. 84
- 85. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar WBS(Planning) The project is a data mining project and hence our major focus here will also be on collecting data sets for carrying mining over it. The next major deliverable here is ‘Planning’, once the requirements for building the project have been gathered, we now plan to create a plan with strategic end in mind, for which we have to plan use of essential resources, the right data, right people, clear vision and plan data resources for future as well. Estimating project schedule and project milestones will be essential for monitoring the progress of our project. 85
- 86. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar WBS(Planning) 86
- 87. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar WBS(Planning) Responsibility of the data expert would be to discover what relevant data is available to meet our strategic business goal and to help us identify the right data by answering questions such as: “What do the codes in this field mean?” and “Can there be more than one record per weather parameter in this table?” Consider how much data knowledge is available and evaluate any risks caused by its absence or scarcity. Under building the right team deliverable, we primarily focus on hiring or training a Data Miner and Data Expert as our project revolves more around working on right data. A Data miner is the one who understands the questions that can be answered using data mining and how to answer them while a Data Expert is the one who understands existing IT capabilities and signs off on data mining integration with those systems[1] 87
- 88. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar WBS(Design) 88
- 89. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar WBS(Design) Next major deliverable is ‘Design’: a. This deliverable holds most important component deliverables which provides a blueprint of the system which will be developed b. Architecture will hold information regarding the correct software development lifecycle picked and the flow of activities expected within its various phases c. This involves creating structural models like class diagrams which covers the major classes and its associations in system and can be beneficial for developers who can directly convert them to actual classes in program also the deliverable component includes behavioral models like activity diagrams which explains flow of information among various components in the system d. The design deliverable also includes creating a prototype of the expected software and getting it approved in stakeholders meeting so that desired changes can be implemented immediately in prototype and same be documented for product development 89
- 90. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar WBS(Execution) 90
- 91. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar WBS(Execution) The next major deliverable is ‘Execution’ where the we actual development is planned to happen The requirements collected until now are verified and validated and the development is initiated, development is initiated in two stages: A. Client side development: i. Build interface for users to check weather information by input of current temperatures ii. Build maps which show weather results iii. Build graphs which provide easy analysis of future weather predictions B. Server side development i. Build interface for administrator to enter historical weather data sets ii. Run prediction algorithms iii. Continuously update system with new weather data from different weather sources via APIs 91
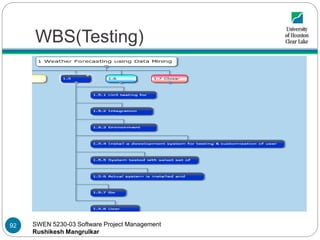
- 92. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar WBS(Testing) 92
- 93. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar WBS(Testing) The testing phase starts unit testing of code packages followed by testing of whole after units are integrated. The environment testing is carried out where system is tested for entered data against production data and in different environments The next testing deliverable includes work packages for assessing the developed product under various user scenarios The system undergoes testing with selected set of users, they can be registered and non registered users The use of system is documented called user manual for end users, also required training is provided 93
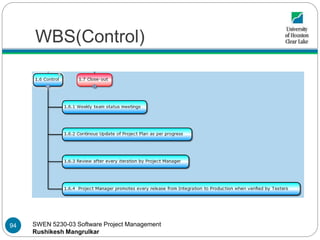
- 94. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar WBS(Control) 94
- 95. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar WBS(Close-out) 95
- 96. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar WBS(Control and Close-out) The control deliverable is the project monitoring entity which will hold work packages for status meetings and continuous update to project plans as the plans keep changing and the project keeps progressing Every iteration release is monitored by Project manager After approval is received from tester the releases at development/integrations stage are promoted to production by project manager The close-out is the summarization of the project, which includes documenting the software, gain formal acceptance of software created from the sake holders 96
- 97. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar WBS(Control and Close-out) When all the releases over the production are approved by the tester over production, the manager promotes and the system is deployed to the users end 97
- 98. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Summary 98 We have designed the work breakdown structure, and laid out major components of our project at level 1 and further include the small work packages under every component at different levels.
- 99. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar References [1]. Planning successful data mining projects http://www.besmart.company/wp- content/uploads/2014/12/Planning.pdf 99
- 100. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Weather Forecasting Using Data Mining Software Development Plan April 27, 2016 SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management 100
- 101. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Overview Scope Overview & objectives Assumptions and Constraints Deliverables Project Organization Staffing Control & Performance Milestones 101
- 102. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Scope In this project we plan to investigate use of data mining in forecasting temperature, rainfall, evaporation and wind speed using historical weather data This Software Development Plan describes the overall plan to be used in our project, including deliverables of the product. The details of the staffing will be described in the staffing table. The plans as outlined in this document are based upon the product requirements as defined in the Vision Document[3]. 102
- 103. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Overview and Objectives This project will implement a customized for Weather forecast. This will deliver notification of weather report to registered users cellular phones or electronic mail while unregistered users can check the weather updates on the landing page of the website. The users will be required to enter today’s weather information in order to receive future forecast using data mining. 103
- 104. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Assumptions and Constraints Staffing: We do not have a release/delivery manager and those duties are preformed by project manager, which is a staffing constraint. Additional open source contributors are welcome, but are not assumed. Budget: Personally financed Schedule: Development efforts are constrained by "day-jobs". 104
- 105. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Deliverables Business Case: The business case will be delivered by the project manager to the stakeholders of the project during the week 01 Inception phase Vision Artifact: The vision artifact is delivered by project manager to stakeholders during week 02-03 Requirements Gathering: The requirements gathered with the use cases and user stories will be delivered to the project manager from requirements specialist during week 03 – 04 Software Development Plan: This is the final draft of the development plan before the actual development starts and is delivered by project manager to stakeholders during week 05 -06. 105
- 106. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Deliverables Supplementary Specifications: The Supplementary Specifications shall capture the system requirements that are not readily captured in the use cases of the use-case model and which shall include legal and regulatory requirements and should be delivered by the business analyst and requirements specialist to developers during week 03 – 04. Developers will use the Supplementary Specifications as a reference when defining responsibilities, operations, and attributes on classes, and when adjusting classes to the implementation environment[1] Creative Design Briefs: The designer will deliver the design briefs to stakeholders and after getting approved from them the developers should start development over same under consent of project manager during week 07 - 08.106
- 107. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Deliverables User Interface Prototype: The user interface prototype is designed by developer and delivered to stakeholders during week 09- 10 for approval meeting before initiating with development in project Historical Weather Data Gathered: The system uses data sets of weather report of past few years which are delivered by local and state government agencies monitoring weather during week 05-07 and build patterns of changing weather and with help of algorithms predict the future weather prediction. Data Model Design: Since the system’s efficiency primarily revolves around the use of data, it is very necessary to have a clear and efficient data model design. The data model design will be delivered by the database developer to project manager, and get it approved before week 15 107
- 108. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Deliverables Model Database : After the design for database is ready, the database model is delivered by database developer to himself/herself during week 15 and the historical weather data is fed into database by database developer. Design Software Architecture Document: The software architecture document is delivered by the software architect to project manager during week 12. Under which, the right SDLC lifecycle is chosen which fits the system planned to build. 108
- 109. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Deliverables Test Package : These are the test cases designed by the testing developers to themselves during end of week 23 and delivered in order to test thoroughly the developed system. Change Requests: The system after undergoing through testing might need changes which are now delivered by testers to developers post week 23. Test Summary: The system might undergo numerous changes recommended by testers and after the changes are delivered, documentation of the completed changes are made which is delivered by testers to project manager end of testing phase and delivered during end of week 24 109
- 110. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Deliverables Implementation Subsystem: The development of the system starts and is delivered by the front end developers and database developers to project manager and end of week 21. User Documentation: As the project progress and the system evolves, the features are delivered by the project manager to the ready to ship software package with inputs from the team and the complete is user documentation is delivered at end of the project that can be week 25 - 26. 110
- 111. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Project Organization We plan to follow more of Project based organization structure than a Functional based organization structure as traditionally followed in larger organizations. Project Manager Requirements Specialist Business Analyst Architect Designer Front end developer Database developer Data Expert Data Miner Tester We plan to have integration and development environment as same with use of SVN(Subversion) 111
- 112. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Project Organization In the project organization shown graphically in the earlier slide, has project manager as the leader who leads the project and monitors the other teammates performance, schedule and the team directly reports to the manager The ‘Data Expert’ and ‘Data Miner’ are exclusively needed for this project as we need expert to gather and study data before feeding to our system. Further, the data miner is responsible for studying patterns in data. They both will be part of the database team, but not necessarily reporting to database developer112
- 113. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Staffing Role Responsi bility Skills Required Number of staff required Duration Project Manager Lead Team, Report status Project Managem ent 1 Complete duration Requirem ents Specialists Requirem ents gathering Research and Analysis 1 Week 1 – Week 7 Business Analyst Requirem ents validations Presentati on, Communic ation and Critical Analysis 1 Complete duration Web Create Web 1 Week 30 – I n c e p t i o n E la b o r at io n 113
- 114. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Staffing Roles Responsibili ties Skills Required No. Of Staff Required Duration Data Expert Understand existing IT capabilities and sign off on data mining integration with systems Data Extracting and Data Loading 1 Week 30 – Week 50 Data Miner Build algorithm to understand pattern of data fed by Data Expert Data Analysis 1 Week 30 – Week 50 114
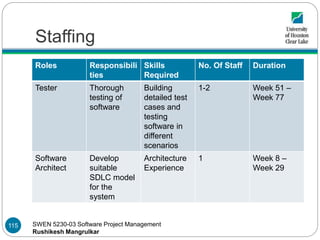
- 115. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Staffing Roles Responsibili ties Skills Required No. Of Staff Duration Tester Thorough testing of software Building detailed test cases and testing software in different scenarios 1-2 Week 51 – Week 77 Software Architect Develop suitable SDLC model for the system Architecture Experience 1 Week 8 – Week 29 115
- 116. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Control and Performance Schedule & Budget control plan: Project status reports will be issued weekly and will include Milestone Tracking detail to ensure that the project stays on track. Changes in the schedule will be escalated to the project manager, who will then decide whether to alter scope in order to preserve target completion dates.[1] Quality Control Plan: Formal reviews will be executed for each design and implementation subsystem post every iteration in presence of manager. This will ensure that the objects under review meet the specified requirements.[1] Close-out plan: At the end of the project, a Lessons Learned meeting will be held to capture new techniques, tools, or methods. Project deliverables will be archived to the Knowledge Management repository for future reference.[1] 116
- 117. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Control and Performance Monitoring Performance: We have laid out certain Key Performance Indicators(KPIs) which will help us in measuring how the project is performing. KPIs are not objectives but the readings that enable a manager to assess performance towards the achievement of objectives.[2] Typical KPIs we use will be schedule and budget compliance, number of scope changes, number of issues and defects, and stakeholder satisfaction. Projects must end and completion time is regularly firmly connected to the business targets that drove the project's introduction. Following to a financial plan in dollars and/or asset time is a key pointer since it gives us a feeling of whether we are executing as we have anticipated that would perform. Much of the time, project financers and customers are cost conscious. They need to know the amount they will spend on the venture and they need to know it before the undertaking is over. 117
- 118. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Milestones Phase Start Date Start End End Date Associat ed Milestone s Inception Phase July 01 2016 Week 1 Week 6 August 12 2016 Lifecycle objective milestone Elaboratio n Phase August 15 2016 Week 7 Week 15 October 10 2016 Lifecycle architectu re milestone 118
- 119. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Milestones Phase Start Date Start Week End Week End Date Associate d Milestone Constructi on Phase October 11 2016 Week 16 Week 22 December 06 2016 Initial operationa l capability milestone Transition Phase December 07 2016 Week 23 Week 26 December 28 2016 Product release milestone 119
- 120. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar References [1]http://sce.uhcl.edu/helm/RationalUnifiedProcess/pro cess/artifact/ar_sspec.htm [2]http://www.projecttimes.com/georgepitagorsky/mea suring-in-progress-project-performance.html [3]https://kenai.com/projects/cps/pages/SoftwareDevel opmentPlan#Scope 120
- 121. SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management Rushikesh Mangrulkar Summary We have worked with all software artifacts, and did encounter a lack of abstraction; but have attempted to deal with all details of the artifacts. Examples assuming all small work packages that would be needed to complete and adding them in WBS In this project, we are investigating approaches to generate reasonable summaries of software artifacts. The goal is to raise the level of abstraction and improve the productivity for software developers. With an estimated plans earlier discussed for schedule, staffing and cost estimation using use cases, we have sufficient information to proceed with our ‘Weather Forecasting Using Data Mining’ project. 121




![SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management
Rushikesh Mangrulkar
Background
The Problem
Weather forecasting is a vital application in
meteorology and has been one of the most
scientifically and technologically challenging problem
around the world.
Primary users for the system are general public,
aviation, fire and marine.
Aviation forecasters use them in order to keep an eye
on surface observations for wind shear, restrictions to
visibility that could affect takeoffs and landings.[4]
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/studid1315331finalrushikeshmangrulkar-161012142245/85/Software-Project-Management-for-Weather-Forecasting-using-Data-mining-5-320.jpg)
![SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management
Rushikesh Mangrulkar
Background
Forecasters support fire weather programs by
checking for relative humidity because it can have
critical impact on behaviors of fire. Every member of
population uses weather data on regular basis,
thinking of how weather can affect your travel,
activity and business decision the list of users become
longer[4]
Similar service providers are – National Weather
Services(NWS), popular sites like Weather
Underground, forecast.io, Weather spark and Google
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/studid1315331finalrushikeshmangrulkar-161012142245/85/Software-Project-Management-for-Weather-Forecasting-using-Data-mining-6-320.jpg)




![SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management
Rushikesh Mangrulkar
High Level Architecture
Image Source: Click here [1]
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/studid1315331finalrushikeshmangrulkar-161012142245/85/Software-Project-Management-for-Weather-Forecasting-using-Data-mining-11-320.jpg)
![SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management
Rushikesh Mangrulkar
Data mining Architecture
Image Source: Click here [2]
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/studid1315331finalrushikeshmangrulkar-161012142245/85/Software-Project-Management-for-Weather-Forecasting-using-Data-mining-12-320.jpg)

![SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management
Rushikesh Mangrulkar
Attributes of data
set[Image Source
[2]]
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/studid1315331finalrushikeshmangrulkar-161012142245/85/Software-Project-Management-for-Weather-Forecasting-using-Data-mining-14-320.jpg)


















![SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management
Rushikesh Mangrulkar
Estimate Cost and Schedule
Explaining 20 – 28 hours estimate:
According to approach proposed by Schneider and Winters (1998),
they suggest counting number of environmental factors in E1 through
E6 that are 3, and those in E7 and E8 that are below 3. Hence if the
total is 2 or less, assume 20 hours per use case point, and for total 3 or
4 assume 28 hours per use case point. Any total larger than 4 indicates
that there are two many environmental factors stacked against the
project.[4, Page 8]
Since our environmental factors total falls in ‘two or less’ category,
we assume 20 hours per use case point.
Therefore, 109 use cases * 20 hours per use case point: 2180 hours
(person hours)
36](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/studid1315331finalrushikeshmangrulkar-161012142245/85/Software-Project-Management-for-Weather-Forecasting-using-Data-mining-36-320.jpg)
![SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management
Rushikesh Mangrulkar
Estimate Cost and Schedule
Accurate cost estimates are critical to both developers and customers.
They can be used to request for proposal, contract negotiation and
scheduling.
We got 2180 hours (For 1 person). We estimate having 3 persons
working per iteration and assume each iteration lasts two weeks:
We also estimate that each developer will spend about 30 hours per
week on project tasks. The rest of their time will be sucked up by
corporate overhead—answering email, attending meetings, and so
on[5]
37](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/studid1315331finalrushikeshmangrulkar-161012142245/85/Software-Project-Management-for-Weather-Forecasting-using-Data-mining-37-320.jpg)



![SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management
Rushikesh Mangrulkar
Financial Benefit
Some studies have examined value of short term
weather predictions:
i. Saving to oil drilling companies in Gulf of Mexico
from avoiding unnecessary drill rig evacuations[1]
ii. Improved fueling decisions at Australian airports
resulting from better forecast, could save
companies $6 – 7 million per year[1]
iii. Better hurricane forecast for Atlantic coast over past
100 years have resulted in major reductions in
yearly deaths in hurricane activity[1]
42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/studid1315331finalrushikeshmangrulkar-161012142245/85/Software-Project-Management-for-Weather-Forecasting-using-Data-mining-42-320.jpg)

![SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management
Rushikesh Mangrulkar
References
[1] https://www.gwu.edu/~spi/assets/docs/Socio-
EconomicBenefitsFinalREPORT2.pdf
[2]For cost estimation using use case:
http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~jhm/Readings/Cohn%20-
%20Estimating%20with%20Use%20Case%20Points_v2%2012-24-50-
761.pdf
[3]http://sceweb.sce.uhcl.edu/helm/rationalunifiedprocess/examples/cs
ports/ex_sdp.htm
[4]http://www.srh.noaa.gov/srh/dad/coop/USEWX.pdf
[5] http://www.methodsandtools.com/archive/archive.php?id=25p3
44](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/studid1315331finalrushikeshmangrulkar-161012142245/85/Software-Project-Management-for-Weather-Forecasting-using-Data-mining-44-320.jpg)




![SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management
Rushikesh Mangrulkar
Stakeholder & User Descriptions
Market demographics
NWS has been providing weather reports on county by county basis which
on its site which is free, ad – free and quick loading
The other sites which followed the popularity were Weather
Underground, Forecast.io, Weather Spark, Intellicast and not to forget the
Google, as its easily available, but its forecast however is provided by
Weather.com.[1]
The users are anticipated to be consumers who already use cell phones on
a regular basis for personal and/or business use
According to report[4], the weather apps are the most downloaded app
after gaming apps, they have generated the highest total revenue from
paid downloads. It’s really a must-have app for every smart phone user —
we want to know whether we’re about to walk into a tornado or not
49](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/studid1315331finalrushikeshmangrulkar-161012142245/85/Software-Project-Management-for-Weather-Forecasting-using-Data-mining-49-320.jpg)
![SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management
Rushikesh Mangrulkar
Market Demographics:
Tim Spangler, director of the COMET atmospheric
sciences training program, estimates the broad U.S.
weather and climate industry at more than $5 billion,
including some 250 commercial weather companies
that generate roughly $2 billion [5]
50](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/studid1315331finalrushikeshmangrulkar-161012142245/85/Software-Project-Management-for-Weather-Forecasting-using-Data-mining-50-320.jpg)








![SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management
Rushikesh Mangrulkar
References
[1] http://lifehacker.com/5897973/five-best-weather-
web-sites
[2] http://www.trishmarie.com/vision.pdf
[3] http://www.livingontherealworld.org/?p=1317
[4] http://techcrunch.com/2011/09/12/report-android-
market-nearing-6-billion-downloads-weather-apps-
are-makin-it-rain/
[5] http://www.cnbc.com/id/43672839
62](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/studid1315331finalrushikeshmangrulkar-161012142245/85/Software-Project-Management-for-Weather-Forecasting-using-Data-mining-62-320.jpg)









![SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management
Rushikesh Mangrulkar
High Level Process View
[1]
73](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/studid1315331finalrushikeshmangrulkar-161012142245/85/Software-Project-Management-for-Weather-Forecasting-using-Data-mining-73-320.jpg)

![SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management
Rushikesh Mangrulkar
End to End Process View
[3]
75](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/studid1315331finalrushikeshmangrulkar-161012142245/85/Software-Project-Management-for-Weather-Forecasting-using-Data-mining-75-320.jpg)
![SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management
Rushikesh Mangrulkar
Deployment View
[2]
77](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/studid1315331finalrushikeshmangrulkar-161012142245/85/Software-Project-Management-for-Weather-Forecasting-using-Data-mining-77-320.jpg)



![SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management
Rushikesh Mangrulkar
WBS
According to paper ‘Planning successful data mining
projects‘ by IBM, there are four critical data mining
success factors for successful planning for data mining
projects – the right application, right people, right
data and right tools, accordingly we have build this
Work breakdown structure. [1]
82](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/studid1315331finalrushikeshmangrulkar-161012142245/85/Software-Project-Management-for-Weather-Forecasting-using-Data-mining-82-320.jpg)




![SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management
Rushikesh Mangrulkar
WBS(Planning)
Responsibility of the data expert would be to discover what
relevant data is available to meet our strategic business goal and
to help us identify the right data by answering questions such as:
“What do the codes in this field mean?” and “Can there be more
than one record per weather parameter in this table?” Consider
how much data knowledge is available and evaluate any risks
caused by its absence or scarcity.
Under building the right team deliverable, we primarily focus on
hiring or training a Data Miner and Data Expert as our project
revolves more around working on right data. A Data miner is the
one who understands the questions that can be answered using
data mining and how to answer them while a Data Expert is the
one who understands existing IT capabilities and signs off on
data mining integration with those systems[1]
87](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/studid1315331finalrushikeshmangrulkar-161012142245/85/Software-Project-Management-for-Weather-Forecasting-using-Data-mining-87-320.jpg)









![SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management
Rushikesh Mangrulkar
References
[1]. Planning successful data mining projects
http://www.besmart.company/wp-
content/uploads/2014/12/Planning.pdf
99](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/studid1315331finalrushikeshmangrulkar-161012142245/85/Software-Project-Management-for-Weather-Forecasting-using-Data-mining-99-320.jpg)


![SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management
Rushikesh Mangrulkar
Scope
In this project we plan to investigate use of data mining in
forecasting temperature, rainfall, evaporation and wind
speed using historical weather data
This Software Development Plan describes the overall plan
to be used in our project, including deliverables of the
product. The details of the staffing will be described in the
staffing table.
The plans as outlined in this document are based upon the
product requirements as defined in the Vision
Document[3].
102](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/studid1315331finalrushikeshmangrulkar-161012142245/85/Software-Project-Management-for-Weather-Forecasting-using-Data-mining-102-320.jpg)



![SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management
Rushikesh Mangrulkar
Deliverables
Supplementary Specifications: The Supplementary
Specifications shall capture the system requirements that are
not readily captured in the use cases of the use-case model and
which shall include legal and regulatory requirements and should
be delivered by the business analyst and requirements
specialist to developers during week 03 – 04. Developers will
use the Supplementary Specifications as a reference when
defining responsibilities, operations, and attributes on classes,
and when adjusting classes to the implementation
environment[1]
Creative Design Briefs:
The designer will deliver the design briefs to stakeholders
and after getting approved from them the developers should
start development over same under consent of project manager
during week 07 - 08.106](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/studid1315331finalrushikeshmangrulkar-161012142245/85/Software-Project-Management-for-Weather-Forecasting-using-Data-mining-106-320.jpg)








![SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management
Rushikesh Mangrulkar
Control and Performance
Schedule & Budget control plan: Project status reports will be
issued weekly and will include Milestone Tracking detail to
ensure that the project stays on track. Changes in the schedule
will be escalated to the project manager, who will then decide
whether to alter scope in order to preserve target completion
dates.[1]
Quality Control Plan: Formal reviews will be executed for each
design and implementation subsystem post every iteration in
presence of manager. This will ensure that the objects under
review meet the specified requirements.[1]
Close-out plan: At the end of the project, a Lessons Learned
meeting will be held to capture new techniques, tools, or
methods. Project deliverables will be archived to the Knowledge
Management repository for future reference.[1]
116](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/studid1315331finalrushikeshmangrulkar-161012142245/85/Software-Project-Management-for-Weather-Forecasting-using-Data-mining-116-320.jpg)
![SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management
Rushikesh Mangrulkar
Control and Performance
Monitoring Performance: We have laid out certain Key
Performance Indicators(KPIs) which will help us in measuring
how the project is performing. KPIs are not objectives but the
readings that enable a manager to assess performance towards
the achievement of objectives.[2]
Typical KPIs we use will be schedule and budget compliance,
number of scope changes, number of issues and defects,
and stakeholder satisfaction.
Projects must end and completion time is regularly firmly
connected to the business targets that drove the project's
introduction. Following to a financial plan in dollars and/or asset
time is a key pointer since it gives us a feeling of whether we are
executing as we have anticipated that would perform. Much of
the time, project financers and customers are cost conscious.
They need to know the amount they will spend on the venture
and they need to know it before the undertaking is over.
117](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/studid1315331finalrushikeshmangrulkar-161012142245/85/Software-Project-Management-for-Weather-Forecasting-using-Data-mining-117-320.jpg)


![SWEN 5230-03 Software Project Management
Rushikesh Mangrulkar
References
[1]http://sce.uhcl.edu/helm/RationalUnifiedProcess/pro
cess/artifact/ar_sspec.htm
[2]http://www.projecttimes.com/georgepitagorsky/mea
suring-in-progress-project-performance.html
[3]https://kenai.com/projects/cps/pages/SoftwareDevel
opmentPlan#Scope
120](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/studid1315331finalrushikeshmangrulkar-161012142245/85/Software-Project-Management-for-Weather-Forecasting-using-Data-mining-120-320.jpg)
