04 - Networking Technologies.ppt
- 2. 2 What’s Technology Whereas the topology of a network is the shape of the network, the technology is the method of putting information onto the network and controlling it based on the physical components that are used and how they operate within the network. The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) developed a set of standards called the 802 project (the 80th year and the second month). These are Ethernet Token Passing Wireless FDDI
- 3. 3 Ethernet Ethernet is by far the most common technology in use today. The Internet operates using Ethernet technology. defined as 802.3 by the IEEE. Ethernet speeds include 3Mbps, 10Mbps, 100Mbps, and 1000Mbps. Ethernet uses an access method known as Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD).
- 4. 4 CSMA/CD On a network that uses CSMA/CD, when a system wants to send data to another system, it first checks to see whether the network media is free. It must do this because each piece of network media used in a LAN can carry only one signal at a time. If the sending node detects that the media is free, it transmits, and the data is sent to the destination. It seems simple. Unfortunately, in networking, things do not always go as a planned. The problem arises when two systems attempt to transmit at exactly the same time. Collision detection works by detecting fragments of the transmission on the network media that result when two systems try to talk at the same time. The two systems wait for a randomly calculated amount of time before attempting to transmit again. This amount of time is a matter of milliseconds known as the backoff. When the backoff period has elapsed, the system attempts to transmit again. If the system doesn't succeed on the second attempt, it keeps retrying until it gives up and reports an error.
- 5. 5 The upside of CSMA/CD is that it has relatively low overhead, meaning that not much is involved in the workings of the system. The downside is that as more systems are added to the network, more collisions occur, and the network becomes slower. Despite its problems, CSMA/CD is an efficient system. As a result, rather than replace it with some other technology, workarounds have been created that reduce the likelihood of collisions. One such strategy is the use of network switches that create multiple collision domains and therefore reduce the impact of collisions on performance.
- 6. 6 Pros and Cons Advantages It has low overhead. Utilizes all available bandwidth when possible. Disadvantages Collisions degrade network performance. Priorities cannot be assigned to certain nodes. Performance degrades exponentially as devices are added.
- 7. 7 CSMA/CA The carrier-sense multiple access with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA) access method uses signal avoidance rather than detection. On CSMA/CA networks, each computer signals its intent to transmit data signals before any data is actually sent. When a networked system detects a potential collision, it waits before sending out the transmission allowing systems to avoid transmission collisions. The CSMA/CA access method uses a random backoff time and waits before trying to send data on the network. When the backoff time expires, the system will again "listen" to verify a clear channel on which to transmit. If the media is still busy, another backoff interval is initiated that is less than the first. The process continues until the wait time reaches zero, and the media is clear. The CSMA/CA access method uses a "listen before talking" strategy.
- 8. 8
- 9. 9 Token Passing IEEE 802.5 standard On a token-passing network, a special packet called a token is passed among the systems on the network. The network has only one token, and a system can send data only when it has possession of the token. When the data arrives, the receiving computer sends a verification message to the sending computer. The sender then creates a new token, and the process begins again. Standards dictate how long a system can have control over the token.
- 10. 10
- 11. 11 Pros and Cons Adv lack of collisions. Even under heavy load conditions, the speed of a token-passing system does not degrade in the same way as a contention-based method such as CSMA/CD. Disadv The creation and passing of the token generate overhead on the network, which reduces the maximum speed. The software and hardware requirements of token-passing network technologies are more complex and therefore more costly.
- 12. 12 MSAU The physical layout of a ring network is altogether different from logical topology. Ring networks are most commonly implemented in a star configuration. In a Token Ring network, a multistation access unit (MSAU) is equivalent to a hub or switch on an Ethernet network is implemented. The MSAU performs the token circulation internally.
- 13. 13
- 14. 14
- 15. 15 Wireless IEEE 802.11 standard The 802.11 standard has two common levels: 802.11b and 802.11g. The 802.11b standard offers speeds up to 11Mbps, and the 802.11g standard increases the speed to 54Mbps. Both use an CSMA/CA. The media that 802.11 wireless networks use is the 2.4GHz radio wave band.
- 16. 16
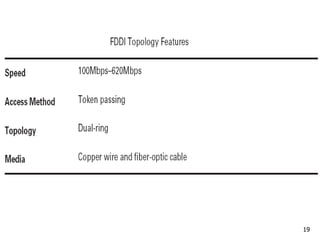
- 17. 17 FDDI Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) uses a token- passing access method and a dual-ring topology. The media used by FDDI is typically fiber-optic cable, but it can also use STP or UTP cable. FDDI communicates at a speed of 100 Mbps on copper wire, but can communicate much faster on fiber-optic cable. To avoid a single break in the ring that could disrupt network connectivity, FDDI uses a dual-ring configuration. If one computer or cable is damaged, the other ring will form a single ring topology.
- 18. 18
- 19. 19
- 20. 20 Characteristics of Cable Standards 10Base2 speeds of 10Mbps Baseband signaling total segment length of 185 (close to 200) meters using thin coaxial (thinnet) cable. 10Base5 speeds of 10Mbps Baseband signaling total segment length of 500 meters using thick coaxial (thicknet) cable.
- 21. 21 10BASE-T The “10” represents the maximum speed of 10Mbps; “BASE” represents a baseband type of transmission in which only one signal can be on the wire at any given time; “T” indicates that a twisted-pair cable was used. The maximum length of any network segment using 10BASE-T is 100 meters. 10BASE-FL 10BASE-FL uses a fiber-optic cable to transmit the signal rather than the copper twisted-pair cable. The speed of 10BASE-FL was still 10Mbps, but the maximum transmission length could be up to 20 kilometers! Many of these networks are still in use today where speed is not a concern but maximum distance is a factor.
- 22. 22 Fast Ethernet Fast Ethernet is the most commonly used network design. It includes 100BaseTX speed up to 100Mbps implemented with CAT5 UTP cable 100 meter distance limitations 100BaseFX speed up to 100Mbps uses fiber-optic cable 412 meters for multimode fiber, 10,000 meters single-mode fiber. uses SC or ST fiber connectors.
- 23. 23
- 24. 24 Gigabit Ethernet Has the basic 1000BaseX and 1000BaseT standards 1000BaseX refers collectively to three distinct standards: 1000BaseLX, 1000BaseSX, and 1000BaseCX. 1000BaseSX and 1000BaseLX are laser standards used over fiber. LX refers to long wavelength laser, and SX refers to short wavelength laser. Both the SX and LX wave lasers can be supported over two types of multimode fiber-optic cable Only LX wave lasers support the use of single-mode fiber. 1000BaseCX uses shielded copper wire. Segment lengths in 1000BaseCX are severely restricted; the maximum cable distance is 25 meters. Because of the restricted cable lengths, 1000BaseCX networks are not widely implemented.
- 25. 25 1000BaseT, sometimes referred to as 1000BaseTX, is another Gigabit Ethernet standard, over Category 5e/6 UTP cable. The standard allows for full-duplex transmission using the four pairs of twisted cable. To reach speeds of 1000Mbps over copper, a data transmission speed of 250Mbps is achieved over each pair of twisted-pair cable.
- 26. 26 10 Gigabit Ethernet The newest and fastest cable standard is the 10G standard. Designed primarily as a WAN and MAN connectivity medium. The 10G standard allows a maximum transmission speed of 10Gbps in a star topology. The 10G standard is currently subdivided into three standards: 10GBASE-SR, 10GBASE-LR, and 10BASE-ER. All of these 10G standards use fiber-optic cable. The major difference between the standards is the maximum transmission distance.
- 27. 27
- 28. 28 Review Recognize the terminology used when identifying cable standards Describe the characteristics of the 100BASE-TX standard. Know the characteristics of the three 10G standards. Describe the characteristics of the 1000BASE-SX standard.