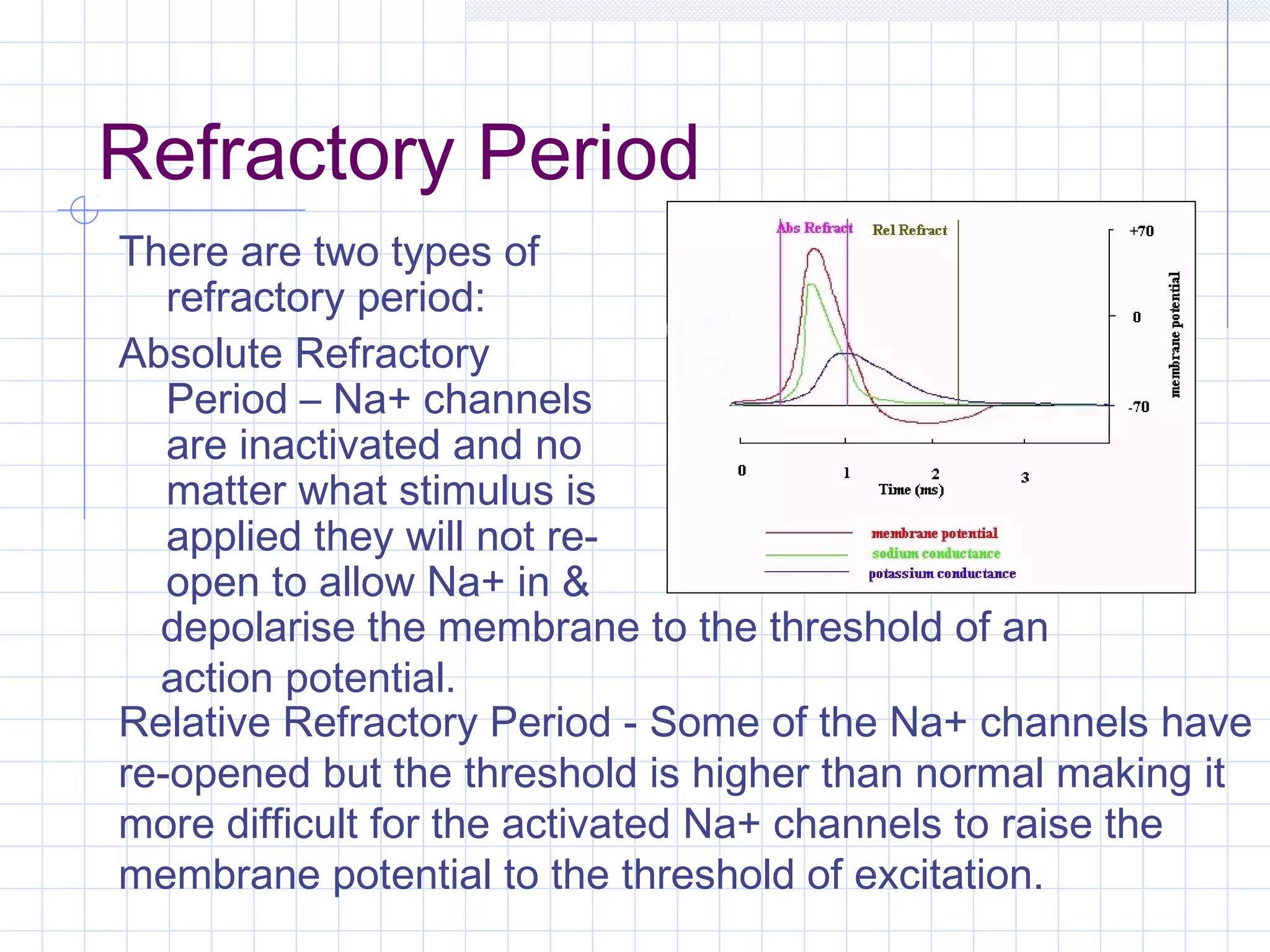
Neurons conduct electrical signals through three main parts - the cell body, dendrites, and axon. The axon transmits signals to other neurons through an electrical impulse known as an action potential. At rest, the inside of the neuron maintains a negative charge compared to the outside through active transport of ions. When stimulated, the neuron's membrane becomes permeable to sodium ions, causing the inside to depolarize and generate an action potential if the threshold is reached. This signal then propagates rapidly along the axon before the neuron enters a refractory period.