1 introduction to compiler
- 1. COMPILER INTRODUCTION 4TH STAGE Lecturer: Hanan Kamal International University of Erbil College of Science Computer Science Department
- 2. Outlines • Overview and History • What Do Compilers Do? • The Structure of a Compiler • The Syntax and Semantics of Programming Languages 2
- 3. Overview and History (1) • Cause • Software for early computers was written in assembly language • The benefits of reusing software on different CPUs started to become significantly greater than the cost of writing a compiler • The first real compiler • FORTRAN compilers of the late 1950s 3
- 4. Overview and History (2) • Compiler technology • is more broadly applicable and has been employed in rather unexpected areas. • Text-formatting languages • Command languages of OS • Query languages of Database systems 4
- 5. What Do Compilers Do (1) • A compiler acts as a translator, transforming human-oriented programming languages into computer-oriented machine languages. Programming Language (Source) Compiler Machine Language (Target) 5
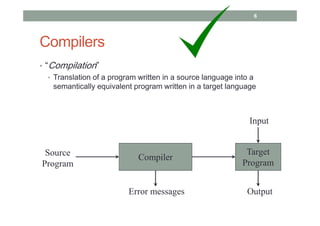
- 6. Compilers • “Compilation” • Translation of a program written in a source language into a semantically equivalent program written in a target language Compiler Error messages Source Program Target Program Input Output 6
- 7. Interpreters • “Interpretation” • Performing the operations implied by the source program Interpreter Source Program Input Output Error messages 7
- 8. What Do Compilers Do (2) • Compilers may generate three types of code: • Pure Machine Code • Machine instruction set without assuming the existence of any operating system or library. • Mostly being OS or embedded applications. • Augmented Machine Code • Code with OS routines and runtime support routines. • More often • Virtual Machine Code • Virtual instructions, can be run on any architecture with a virtual machine interpreter or a just-in-time compiler • Ex. Java 8
- 9. What Do Compilers Do (3) • Another way that compilers differ from one another is in the format of the target machine code they generate: • Assembly or other source format • Relocatable binary • Relative address • A linkage step is required • Absolute binary • Absolute address • Can be executed directly 9
- 10. • Any compiler must perform two major tasks • Analysis of the source program • Synthesis of a machine-language program The Structure of a Compiler (1) Compiler Analysis Synthesis 10
- 11. The Structure of a Compiler (2) Scanner Parser Semantic Routines Code Generator Optimizer Source Program Tokens Syntactic Structure Symbol and Attribute Tables (Used by all Phases of The Compiler) (Character Stream) Intermediate Representation Target machine code 11
- 12. The Structure of a Compiler (3) Scanner Parser Semantic Routines Code Generator Optimizer Source Program Tokens Syntactic Structure Symbol and Attribute Tables (Used by all Phases of The Compiler) Scanner The scanner begins the analysis of the source program by reading the input, character by character, and grouping characters into individual words and symbols (tokens) RE ( Regular expression ) NFA ( Non-deterministic Finite Automata ) DFA ( Deterministic Finite Automata ) LEX (Character Stream) Intermediate Representation Target machine code 12
- 13. The Structure of a Compiler (4) Scanner Parser Semantic Routines Code Generator Optimizer Source Program Tokens Syntactic Structure Symbol and Attribute Tables (Used by all Phases of The Compiler) Parser Given a formal syntax specification (typically as a context- free grammar [CFG] ), the parse reads tokens and groups them into units as specified by the productions of the CFG being used. As syntactic structure is recognized, the parser either calls corresponding semantic routines directly or builds a syntax tree. CFG ( Context-Free Grammar ) BNF ( Backus-Naur Form ) GAA ( Grammar Analysis Algorithms ) LL, LR, SLR, LALR Parsers YACC (Character Stream) Intermediate Representation Target machine code 13
- 14. The Structure of a Compiler (5) Scanner Parser Semantic Routines Code Generator Optimizer Source Program (Character Stream) Tokens Syntactic Structure Intermediate Representation Symbol and Attribute Tables (Used by all Phases of The Compiler) Semantic Routines Perform two functions Check the static semantics of each construct Do the actual translation The heart of a compiler Syntax Directed Translation Semantic Processing Techniques IR (Intermediate Representation) Target machine code 14
- 15. The Structure of a Compiler (6) Scanner Parser Semantic Routines Code Generator Optimizer Source Program Tokens Syntactic Structure Symbol and Attribute Tables (Used by all Phases of The Compiler) Optimizer The IR code generated by the semantic routines is analyzed and transformed into functionally equivalent but improved IR code This phase can be very complex and slow Peephole optimization loop optimization, register allocation, code scheduling Register and Temporary Management Peephole Optimization (Character Stream) Intermediate Representation Target machine code 15
- 16. The Structure of a Compiler (7) Source Program (Character Stream) Scanner Tokens Parser Syntactic Structure Semantic Routines Intermediate Representation Optimizer Code Generator Code Generator Interpretive Code Generation Generating Code from Tree/Dag Grammar-Based Code Generator Target machine code 16
- 17. Preprocessors, Compilers, Assemblers, and Linkers Preprocessor Compiler Assembler Linker Skeletal Source Program Source Program Target Assembly Program Relocatable Object Code Absolute Machine Code Libraries and Relocatable Object Files Try for example: gcc -S myprog.c javap Class 17
- 18. Analysis of Source Programs lexical analyzer syntax analyzer semantic analyzer source program tokens parse trees parse trees 18
- 21. Semantic Analysis type checking type conversion 21
- 22. Symbol Table • There is a record for each identifier • The attributes include name, type, location, etc. 22
- 23. Synthesis of Object Code intermediate code generator code optimizer code generator parse tree & symbol table intermediate code optimized intermediate code target program 23
- 28. The Syntax and Semantics of Programming Language • A programming language must include the specification of syntax (structure) and semantics (meaning). • Syntax typically means the context-free syntax because of the almost universal use of context- free-grammar (CFGs) • Ex. • a = b + c is syntactically legal • b + c = a is illegal 28
- 29. The Syntax and Semantics of Programming Language • The semantics of a programming language are commonly divided into two classes: • Static semantics • Semantics rules that can be checked at compiled time. • Ex. The type and number of a function’s arguments • Runtime semantics • Semantics rules that can be checked only at run time 29
- 30. Compiler 30
- 31. Thanks for your attention Questions??? 31











![The Structure of a Compiler (4)
Scanner Parser
Semantic
Routines
Code
Generator
Optimizer
Source
Program Tokens Syntactic
Structure
Symbol and
Attribute
Tables
(Used by all
Phases of
The Compiler)
Parser
Given a formal syntax specification (typically as a context-
free grammar [CFG] ), the parse reads tokens and groups
them into units as specified by the productions of the CFG
being used.
As syntactic structure is recognized, the parser either calls
corresponding semantic routines directly or builds a
syntax tree.
CFG ( Context-Free Grammar )
BNF ( Backus-Naur Form )
GAA ( Grammar Analysis Algorithms )
LL, LR, SLR, LALR Parsers
YACC
(Character
Stream)
Intermediate
Representation
Target machine code
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-introductiontocompiler-210607002616/85/1-introduction-to-compiler-13-320.jpg)

















