2 08 client-server architecture
- 1. Client-Server Architecture King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals SWE 316: Software Design & Architecture Semester: 072
- 2. Objectives To understand client-server architecture 2-tier 3-tier SWE 316 (072) Client-Server Architecture 2
- 3. Client-Server Architecture The application is modelled as a set of services that are provided by servers and a set of clients that use these services. Clients know of servers but servers need not know of clients. Clients and servers are logical processes. SWE 316 (072) Client-Server Architecture 3
- 4. Application Layers Presentation layer Concerned with presenting the results of a computation to system users and with collecting user inputs. Application processing layer Concerned with providing application specific functionality e.g., in a banking system, banking functions such as open account, close account, etc. Data management layer Concerned with managing the system databases. SWE 316 (072) Client-Server Architecture 4
- 5. Application Layers (Cont’d) SWE 316 (072) Client-Server Architecture 5
- 6. Types of Client-Server Architectures Two-tier The three application layers are mapped onto two computer systems – the client and the server. Client can be Thin client; or Fat client Three-tier The three application layers are mapped onto three logically separate processes that executes on different processors. SWE 316 (072) Client-Server Architecture 6
- 7. Thin and Fat Clients Thin-client model In a thin-client model, all of the application processing and data management is carried out on the server. The client is simply responsible for running the presentation software. Fat-client model In this model, the server is only responsible for data management. The software on the client implements the application logic and the interactions with the system user. SWE 316 (072) Client-Server Architecture 7
- 8. Thin and Fat Clients (Cont’d) SWE 316 (072) Client-Server Architecture 8
- 9. Thin-Client Model Used when legacy systems are migrated to client server architectures. The legacy system acts as a server in its own right with a graphical interface implemented on a client. A major disadvantage is that it places a heavy processing load on both the server and the network. SWE 316 (072) Client-Server Architecture 9
- 10. Fat-Client Model More processing is delegated to the client as the application processing is locally executed. Most suitable for new C/S systems where the capabilities of the client system are known in advance. More complex than a thin client model especially for management. New versions of the application have to be installed on all clients. SWE 316 (072) Client-Server Architecture 10
- 11. A Client-Server ATM System SWE 316 (072) Client-Server Architecture 11
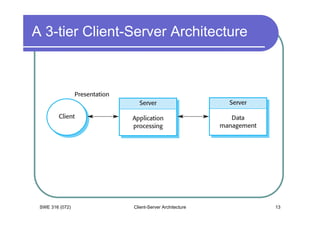
- 12. Three-Tier Architecture Each of the application layers may execute on a separate processor. Allows for better performance than a thin-client model and is simpler to manage than a fat-client model. A more scalable architecture - as demands increase, extra servers can be added. SWE 316 (072) Client-Server Architecture 12
- 13. A 3-tier Client-Server Architecture SWE 316 (072) Client-Server Architecture 13
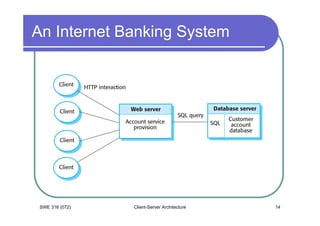
- 14. An Internet Banking System SWE 316 (072) Client-Server Architecture 14
- 15. Use of Client-Server Architectures Architecture Applications Two-tier C/S Legacy system applications where separating application processing and architecture with data management is impractical. thin clients Computationally-intensive applications such as compilers with little or no data management. Data-intensive applications (browsing and querying) with little or no application processing. Two-tier C/S Applications where application processing is provided by off-the-shelf architecture with software (e.g. Microsoft Excel) on the client. fat clients Applications where computationally-intensive processing of data (e.g. data visualisation) is required. Applications with relatively stable end-user functionality used in an environment with well-established system management. Three-tier or Large scale applications with hundreds or thousand s of clients multi-tier C/S Applications where both the data and the application are volatile. architecture Applications where data from multiple sources are integrated. SWE 316 (072) Client-Server Architecture 15
- 16. Summary Tow basic client-server architecture 2-tier Thin client: all of the application processing and data management is carried out on the server Fat clients: run some or all of the application logic. 3-tier Allows for better performance than a thin-client approach and is simpler to manage than a fat-client approach. SWE 316 (072) Client-Server Architecture 16