6.3 c-Functions.ppt
- 1. Vijesh Nair Vijesh Nair Assistant Professor Dept. of Computer Engineering
- 2. Vijesh Nair Introduction What is function? How functions will work? How to declare a function in C language? What are the different types of functions are there in C language? Example programs.
- 4. Vijesh Nair Modular Programming Break a large problem into smaller pieces Smaller pieces sometimes called ‘modules’ or ‘subroutines’ or ‘procedures’ or functions Divide and Conquer
- 5. Vijesh Nair Why Modular Programming? Helps in managing the complexity of the program - Smaller blocks of code - Easier to read Encourages re-use of code Within a particular program or across different programs Allows independent development of code Provides a layer of ‘abstraction’
- 6. Vijesh Nair What is function? Function is a set of instructions to carry out a particular task. The Function after processing returns a single value. In other word, we say a Function is a group of statements that can perform any particular task. Function in programming is a segment that groups a number of program statements to perform specific task
- 7. Vijesh Nair Every C program has at least one function, which is main(). We have already used functions like…..
- 8. Vijesh Nair Every function in C must have two things… A function declaration tells the compiler about a function's name, return type, and parameters. A function definition provides the actual body of the function.
- 9. Vijesh Nair A function declaration tells the compiler about a function's name, return type, and parameters. A function declaration must be done within main function or before main function.
- 10. Vijesh Nair A function definition must be done before main function or after main function. A function definition provides the actual body of the function.
- 11. Vijesh Nair Types of functions? Predefined Userdefined
- 12. Vijesh Nair Predefined functions Actually all predefined functions in C Language are defined inside in any one of the header files. If the functionality of a function is defined by the compiler those functions are called predefined functions. The functionality of the predefined function is fixed, users cannot change or redefine it.
- 13. Vijesh Nair Predefined functions Predefined functions are also called as System Defined functions or Library functions. NOTE
- 14. Vijesh Nair User-defined functions User-defined functions are small programs that you can write to perform an operation. If the functionality of a function is defined by the user those functions are called user-defined functions. Users are free to define their own code for the user-defined functions. Every user-defined function must have the following….
- 15. Vijesh Nair Declaring User-defined functions Syntax Example We also call it as Function Prototype NOTE
- 16. Vijesh Nair Definition of User-defined functions Syntax Example
- 17. Vijesh Nair Calling User-defined functions Syntax Example
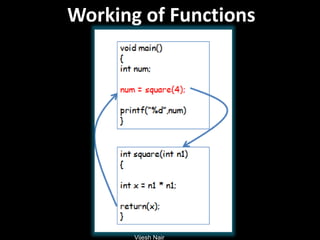
- 18. Vijesh Nair Working of Functions
- 19. Vijesh Nair Example Program void main() { int a, b, c; void addition(int , int); printf(“We are in main…..n”); printf(“Enter any two numbers: ”); scanf(“%d%d”, &a, &b); addition(a, b); printf(“We are again in main…..”); } void addition(int x, int y) { printf(“SUM = %dn”, x+y); }
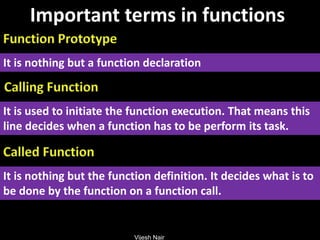
- 20. Vijesh Nair Important terms in functions It is nothing but a function declaration It is used to initiate the function execution. That means this line decides when a function has to be perform its task. It is nothing but the function definition. It decides what is to be done by the function on a function call.
- 21. Vijesh Nair Example Program void main() { int a, b, c; void addition(int , int); printf(“We are in main…..n”); printf(“Enter any two numbers: ”); scanf(“%d%d”, &a, &b); addition(a, b); printf(“We are again in main…..”); } void addition(int x, int y) { printf(“SUM = %dn”, x+y); } Prototype Calling Called
- 22. Vijesh Nair Parameters & Return Value Parameters are the data values which are passed from calling function to called function Return value is the data value which passed from called function to calling function For a function we can have any number of parameters For a function we can have only one return value In a function the total number of parameters and the order of the parameters must be same in all function prototype, function calling and function definition
- 23. Vijesh Nair Parameters & Return Value To return a value from called function to calling function we use ‘return’ statement
- 24. Vijesh Nair Parameter types In C programming language there are two types of parameters
- 25. Vijesh Nair These are the parameters used at the time of function calling Whenever we pass actual parameters copy of its value is sent to the called function but not entire variable
- 26. Vijesh Nair These are the parameters used at called function as receivers of the actual parameters The order of the actual parameters and their datatypes should exactly match with the order and datatypes of the formal parameters
- 27. Vijesh Nair Function types Based on the parameters and return value, functions are classified into FOUR types
- 28. Vijesh Nair Without Parameters and without Return value In this type, there is no data transfer between calling and called functions Simple control transfer from calling function to called function, executes called function body and comes back to the calling function. Everything is performed within the called function like reading data, processing data and displaying result. This type of functions are used to print some message, line….
- 29. Vijesh Nair Example Program: void main() { void add(); printf(“We are in main….n”); add(); printf(“We are again in main….n”); } void add() { int a,b,c; printf(Enter any two numbers: ); scanf(“%d%d”, &a, &b); c = a + b; printf(“Result = %d”, c); }
- 30. Vijesh Nair void main( ) { void add( ); printf(“We are in main….n”); add( ); printf(“We are again in main….n”); } void add( ) { int a,b,c; printf(Enter any two numbers: ); scanf(“%d%d”, &a, &b); c = a + b; printf(“Result = %d”, c); } Control No input Control No return value
- 31. Vijesh Nair With Parameters and without Return value In this type, there is data transfer from calling to called function, but not from called to calling function. Simple control transfer from calling function to called function along with some data (parameters), executes called function body and comes back to the calling function without any data. This type of functions are depend on the calling function. Generated result is utilized by called function and nothing will be sent back to the calling function.
- 32. Vijesh Nair Example Program: void main() { void add( int, int ); printf(“We are in main….n”); add( 10, 20); printf(“We are again in main….n”); } void add(int a, int b) { int c; c = a + b; printf(“Result = %d”, c); }
- 33. Vijesh Nair void main( ) { void add( int, int ); printf(“We are in main….n”); add( 10, 20 ); printf(“We are again in main….n”); } void add( int a, int b) { int c; c = a + b; printf(“Result = %d”, c); } Control 10 & 20 as input Control No return value
- 34. Vijesh Nair Without Parameters and with Return value In this type, there is no data transfer from calling to called function, but from called to calling function one data is sent. Simple control transfer from calling function to called function, executes called function body and a data value is sent back to the calling function from called function. This type of functions are called function is independent. It reads data, process data and result is sent back to the calling function.
- 35. Vijesh Nair Example Program: void main() { int c; int add( ); printf(“We are in main….n”); c = add( ); printf(“Result = %dn”, c); } int add( ) { int a, b; printf(“Enter any two numbers:”); scanf(“%d%d”, &a, &b); return (a + b); }
- 36. Vijesh Nair void main( ) { int c; int add( ); printf(“We are in main….n”); c = add( ); printf(“Result = %dn”, c); } void add( ) { int a,b; printf(Enter any two numbers: ); scanf(“%d%d”, &a, &b); return (a + b); } Control No input Control 30 as return value input values for a & b are 10 & 20 respectively
- 37. Vijesh Nair With Parameters and with Return value In this type, there is data transfer from calling to called function, and from called to calling function one data is sent back. Control transfer from calling function to called function along with data, executes called function body and a data value is sent back to the calling function from called function. In this type of functions are called & calling functions both dependent on each other.
- 38. Vijesh Nair Example Program: void main() { int c; int add( int, int ); printf(“We are in main….n”); c = add( 10, 20 ); printf(“Result = %dn”, c); } int add( int a, int b) { return (a + b); }
- 39. Vijesh Nair void main( ) { int c; int add( int, int ); printf(“We are in main….n”); c = add( 10, 20 ); printf(“Result = %dn”, c); } void add( int a, int b) { return (a + b); } Control 10 & 20 as input Control 30 as return value
- 40. Vijesh Nair Different ways to make a function call There are THREE ways of making function call…
- 41. Vijesh Nair 1. From main function We have already seen making a function call from main function. When we make a function call from main, the control transfers to called function, executes it, again comes back to the main function.
- 42. Vijesh Nair 2. From another user-defined function We can also make a function call from another user-defined function.
- 43. Vijesh Nair void main() { function1(); } void function1() { function2(); } void function2() { body of the function; }
- 44. Vijesh Nair 3. From same function We can also make a function call from same function. That means function calls itself If a function calls itself, then it is called as “RECURSION”. When a function calls itself until the last call is invoked till that time the first call also remains open. At every time, a function invoked, the function returns the result of previous call.
- 45. Vijesh Nair void main( ) { printf(“This is example of Recursion!!!”); main( ); } Example Program: Output: This is example of Recursion!!! This is example of Recursion!!! This is example of Recursion!!! This is example of Recursion!!! …….
- 46. Vijesh Nair int factorial( int ); void main( ) { int fact, n; printf(“Enter any positive integer: ”); scanf(“%d”, &n); fact = factorial( n ); printf(“Factorial of %d is %d”, n, fact); } int factorial( int n ) { int temp; if( n == o) return 1; else temp = n * factorial( n-1 ); return temp; } Example Program:
- 47. Vijesh Nair int factorial( int ); void main( ) { int fact, n; printf(“Enter any positive integer: ”); scanf(“%d”, &n); fact = factorial( n ); printf(“Factorial of %d is %d”, n, fact); } int factorial( int n ) { int temp; if( n == o) return 1; else temp = n * factorial( n-1 ); return temp; }
- 48. Vijesh Nair int factorial( int n ) { int temp; if( n == o) return 1; else temp = n * factorial( n-1 ); return temp; } n = 3 n 3 temp int factorial( int n ) { int temp; if( n == o) return 1; else temp = n * factorial( n-1 ); return temp; } 3 * factorial(2) n = 2 n 2 temp int factorial( int n ) { int temp; if( n == o) return 1; else temp = n * factorial( n-1 ); return temp; } 2 * factorial(1) n = 1 int factorial( int n ) { int temp; if( n == o) return 1; else temp = n * factorial( n-1 ); return temp; 1 * factorial(0) n 1 0 n temp temp n = 0 1 1 1 1*1 = 1 2 2*1 = 2 2 3*2 = 6 6 6 Memory Allocation
- 49. Vijesh Nair