A gentle introduction to random and strategic networks
- 1. Random Networks & Strategic Networks Why and how networks form A gentle introduction
- 2. Who am I? Software engineer by day …curious all the time @1littleendian https://www.linkedin.com/in/junasalviati/
- 3. Random Networks How networks form?
- 4. Why random networks are important? in-school friendship network (http://icecreamhitearth.blogspot.com/) ER network with parameters n=50, p=0.3 Approximating “real” networks Try to explain “how” real networks form
- 5. Some Social Networks properties - Short average path length - High clustering - Characteristic degree distributions - Homophily - Link interdependence - Different measures for prestige and importance
- 6. Models - random formation (Erdős–Rényi) - rewiring (Watts-Strogatz) - preferential attachment (Barabasi-Albert) Erdős–Rényi Watts-Strogatz Barabasi-Albert
- 7. ER Model Given n nodes, links form with independent probability p. Observation (trivial): when p is high, we get more connections. n=20, p=0.03 n=20, p=0.08n=20, p=0.06
- 8. Modello ER - Thresholds Playing with n,p values, we observe some “threshold” phenomena... - links emerge - giant component emerge - connected component emerge ...and those thresholds and transition phases are well defined!
- 9. ER Model - Thresholds and phases Some links emerge but some nodes are pretty isolated. n = 50 p = 0.01
- 10. ER Model - Thresholds and phases 0.02 is threshold for cycles and giants components. We still observe isolated nodes and small links. n = 50 p = 0.02
- 11. Modello ER - Soglie 0.05 is the threshold for a well defined giant component. n = 50 p = 0.05
- 12. Modello ER - Soglie 0.08 is the threshold for the connected component to emerge. n = 50 p = 0.1
- 13. ER Model - Playground https://antigones.github.io/SimpleNets/erdosSteps.html
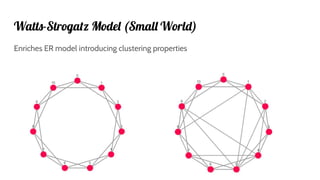
- 14. Watts-Strogatz Model (Small World) Enriches ER model introducing clustering properties
- 15. Watts-Strogatz Starts with a n nodes lattice, with a base wiring k (high clustering and high diameter)
- 16. Watts-Strogatz ...does a rewiring with β probability (and the diameter gets low)
- 17. Watts-Strogatz Model - Playground https://antigones.github.io/SimpleNets/wattsSteps.html
- 18. Barabasi-Albert Model No starting configuration defined in the paper…! We choose to start with a n nodes lattice...
- 19. Barabasi-Albert ...adding nodes following “preferential attachment” rule. A small set of nodes with many links (hub) Rich gets richer
- 21. Block models Probability of link formation depends on some property: ● Age ● Gender ● Nearness/Farness ● Cetus This model allows to see homophily (“those who are similar tends to connect”)
- 22. Exponential Random Graph (ERGMs) Allows to observe interdependence, analyzing network as a whole and not as a result of composition of dyadic relationship. For example: - network probability depends on the number of friends in common - network probability depends on the number of triangles 𝛽ₜL(g)+𝛽ₜL(g)
- 23. Exponential Random Graph (ERGMs) Passing to exponential (a trick!) we ensure positive probability and 0=<p<=1: Pr(G) ~exp[𝛽ₜL(g)+𝛽ₜT(g)-𝘤] Subtracting c, we ensure that the probabilities sums to 1. Every network model can be expressed in exponential with respect of some of its properties (Hammersly e Clifford)
- 24. Strategic Networks Why networks form?
- 25. Why strategic networks? Attempt to explain “why” social network tend to have some particular form. - agents can choose to form links or not - every agents has a utility and relationships imply a gain and a cost
- 26. Symmetric Connections model (Jackson-Wolinsky) Agents simultaneously declare the will to form a link or not: if they agree a link is formed.
- 27. Symmetric Connections model (Jackson-Wolinsky) Nash equilibrium: a configuration where nobody obtain a gain changing his/her own action. For a dyad, we have a Nash equilibrium: - when both agents announce each other and the link forms - when nobody announces nobody - because even if the other gives the announcement, the link will not form anyway! ...and this is a problem because we can’t make predictions, since every possible configuration is an equilibrium!
- 28. Pairwise stability (Jackson-Wolinsky) Network is pairwise stable: - no two agents both gain from adding a link (at least one “stricly”) - no one gain severing the link Both are Nash equilibria, only the latter is pairwise stable
- 29. Pareto efficiency and (strong) efficiency - Network is Pareto efficient when someone gains moving and someone else consequently suffer a loss. - we can have many Pareto efficient configurations. - Network is efficient if maximizes the sum of agent utilities. - we care about maximizing the whole network efficiency instead of that of the single agent. (utilitarianism) - with a utility transfer the network can obtain Pareto efficiency - Network stability is independent from those two properties so a stable configuration does not imply maximizing network or single agent utility!
- 30. Efficiency Efficient configuration varies depending on delta and cost. ● 𝙘 < 𝛅-𝛅², cost to form a link is very low so the complete network is efficient ● 𝛅-𝛅²<𝙘<𝛅+(n-2)*𝛅²/2, the cost is medium and the star network is efficient ● 𝛅+(n-2)*𝛅²/2<𝙘, the cost is high so the empty network is efficient Why stars? Because stars connect individuals at a minimum distances, minimizing indirect link delta loss.
- 32. Pairwise stability vs Efficiency Pairwise stable configuration varies depending on delta and cost. ● for a low cost 𝙘 < 𝛅-𝛅^2, complete network is pairwise stable ● for a medium/low cost 𝛅-𝛅^2< 𝙘 < 𝛅, star network is pairwise stable (but other networks can be pairwise stable too) ● for a medium/high cost 𝛅 < 𝙘 < 𝛅 + (n-2)𝛅^2/2, the cost does not justify bringing only one person in the network with the link so forming links tends to bring in more people to get indirect benefits to compensate cost. Additionally, every agent forms a link only with agents bringing other connection with them. This is actually the case where a star network is efficient but not pairwise stable. ● 𝛅 + (n-2)𝛅^2/2< 𝙘, the empty network is pairwise stable
- 33. Pairwise stability vs Efficiency For a low cost 𝙘 < 𝛅-𝛅^2, complete network is pairwise stable and efficient Pairwise stability Efficiency 𝛅 = 0.5 𝙘 = 0.2
- 34. Pairwise stability vs Efficiency For a medium cost 𝛅 > 𝙘 > 𝛅-𝛅^2, star network is pairwise stable and efficient Pairwise stability Efficiency 𝛅 = 0.5 𝙘 = 0.3
- 35. Pairwise stability vs Efficiency For a cost 𝙘 > 𝛅-𝛅^3, circle is pairwise stable, too. Pairwise stability 𝛅 = 0.5 𝙘 = 0.3
- 36. Pairwise stability vs Efficiency For a medium cost 𝙘 > 𝛅, star network is efficient but not pairwise stable. Pairwise stability Efficiency 𝛅 = 0.5 𝙘 = 0.7
- 37. Pairwise stability - Playground https://antigones.github.io/StrategicNets/pairwiseStableComplete.html
- 38. Links and reference https://www.coursera.org/learn/social-economic-networks Matthew O. Jackson, “Social and Economic Networks” (Princeton University Press) https://medium.com/@1littleendian/ https://github.com/antigones/SimpleNets https://github.com/antigones/StrategicNets https://antigones.github.io/SimpleNets/ https://antigones.github.io/StrategicNets/
- 39. Questions?
- 40. Thank you!






















![Exponential Random Graph (ERGMs)
Passing to exponential (a trick!) we ensure positive probability and 0=<p<=1:
Pr(G) ~exp[𝛽ₜL(g)+𝛽ₜT(g)-𝘤]
Subtracting c, we ensure that the probabilities sums to 1.
Every network model can be expressed in exponential with respect of some of its
properties (Hammersly e Clifford)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/en-agentleintroductiontorandomandstrategicnetworks-191004103909/85/A-gentle-introduction-to-random-and-strategic-networks-23-320.jpg)
















