A seven level cascaded multilevel dstatcom for compensation of reactive power and harmonics
- 1. International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 – 6480(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6499(Online) Volume 4, Issue 2, March – April (2013), © IAEME 106 A SEVEN LEVEL CASCADED MULTILEVEL DSTATCOM FOR COMPENSATION OF REACTIVE POWER AND HARMONICS USING PSCPWM AND LSCPWM TECHNIQUES D.MOHAN REDDY1 , T.GOWRIMANOHAR2 1 (Associate Professor,Department of EEE, Sri Vasavi Institute Of Engg & Technology,Machilipatnam, Krishna Dist, India) 2 (Associate Professor,Department of EEE, SVUniversity,Tirupati,Chittoor Dist, India) ABSTRACT The “multilevel converter” has drawn tremendous interest in the power industry. The general structure of the multilevel converter is to synthesize a sinusoidal voltage from several levels of voltages, Multilevel voltage source converters are emerging as a new breed of power converter options for high power applications, These converter topologies can generate high-quality voltage waveforms with power semiconductor switches operating at a frequency near the fundamental. Among the available multilevel converter topologies, the cascaded multilevel converter constitutes a promising alternative, providing a modular design that can be extended to allow a transformer less connection. This paper presents a three-phase, seven level cascaded multilevel voltage source inverter based DSTATCOM for power line conditioning to improve power quality in the distribution network. Finally a level shifted PWM (LSPWM) and phase shifted PWM (PSPWM) techniques are adopted to investigate the performance of CHB Inverter based DSTATCOM. The results are obtained through Mat lab / Simulink software package. Keywords: Cascaded H- Bridge Multilevel Inverter, DSTATCOM, Instantaneous power theory, Power quality.PWM. I. INTRODUCTION In recent years Electrical Power Quality had obtained more attention in power engineering. In present day’s power distribution systems is suffering from severe power quality problems. These power quality problems include high reactive power burden, harmonics currents, load unbalance, excessive neutral current etc. The measure of power INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (IJARET) ISSN 0976 - 6480 (Print) ISSN 0976 - 6499 (Online) Volume 4, Issue 2 March – April 2013, pp. 106-118 © IAEME: www.iaeme.com/ijaret.asp Journal Impact Factor (2013): 5.8376 (Calculated by GISI) www.jifactor.com IJARET © I A E M E
- 2. International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 – 6480(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6499(Online) Volume 4, Issue 2, March – April (2013), © IAEME 107 quality depends upon the needs of the equipment that is being supplied. What is good power quality for an electric motor may not be good enough for a personal computer. Usually the term power quality refers to maintaining a sinusoidal waveform of bus voltages at rated voltage and frequency [1]. The waveform of electric power at generation stage is purely sinusoidal and free from any distortion. Many of the Power conversion and consumption equipment are also designed to function under pure sinusoidal voltage waveforms. However, there are many devices that distort the waveform. These distortions may propagate all over the electrical network. In recent years, there has been an increased use of non-linear loads which has resulted in an increased fraction of non-sinusoidal currents and voltages in Electric Network. The wave shape phenomena associated with power quality may be characterized into synchronous and non synchronous phenomena. Synchronous phenomena refer to those in synchronism with A.C waveform at power frequency [2],[3]. A group of controllers together called Custom Power Devices (CPD), which include the DSTATCOM (distribution static compensator), The DSTATCOM, is a shunt-connected device, which takes care of the power quality problems in the currents It consists of a dc capacitor, three-phase inverter (IGBT, thyristor) module, ac filter, coupling transformer and a control strategy. The basic electronic block of the D-STATCOM is the voltage-sourced inverter that converts an input dc voltage into a three-phase output voltage at fundamental frequency. The D-STACOM employs an inverter to convert the DC link voltage Vdc on the capacitor to a voltage source of adjustable magnitude and phase. Therefore the D-STATCOM can be treated as a voltage-controlled source. The D-STATCOM can also be seen as a current-controlled source. The generalized instantaneous reactive power theory which is valid for sinusoidal or non-sinusoidal and balanced or unbalanced three-phase power systems with or without zero-sequence currents were later proposed [8]. The construction controller of the D-STATCOM is used to operate the inverter in such a way that the phase angle between the inverter voltage and the line voltage is dynamically adjusted so that the D- STATCOM generates or absorbs the desired VAR at the point of connection. The phase of the output voltage of the thyristor-based inverter, Vi, is controlled in the same way as the distribution system voltage, Vs. The DSTATCOM is based on the instantaneous real-power theory; it provides good compensation characteristics in steady state as well as transient states [11]. The instantaneous real-power theory generates the reference currents required to compensate the distorted line current harmonics and reactive power. It also tries to maintain the dc-bus voltage across the capacitor constant. Another important characteristic of this real-power theory is the simplicity of the calculations, which involves only algebraic calculation [12]. A multilevel inverter can reduce the device voltage and the output harmonics by increasing the number of output voltage levels. There are several types of multilevel inverters: cascaded H-bridge (CHB), neutral point clamped, flying capacitor [2-5]. In particular, among these topologies, CHB inverters are being widely used because of their modularity and simplicity. Various modulation methods can be applied to CHB inverters. CHB inverters can also increase the number of output voltage levels easily by increasing the number of H-bridges. This paper presents a DSTATCOM with a proportional integral controller based CHB multilevel (five level and seven level) inverter for the harmonics and reactive power mitigation of the nonlinear loads. This type of arrangements have been widely used for PQ applications due to increase in the number of voltage levels, low switching losses, low electromagnetic compatibility for hybrid filters and higher order harmonic elimination.
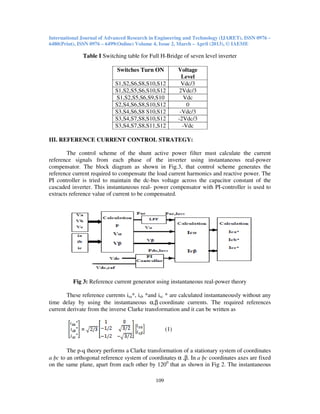
- 3. International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 – 6480(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6499(Online) Volume 4, Issue 2, March – April (2013), © IAEME 108 II.PROPOSED SYSTEM Fig 1: Schematic Diagram of DSTATCOM Instantaneous real-power theory based cascaded multilevel inverter based DSTATCOM is connected in the distribution network at the PCC through filter inductances and operates in a closed loop. The DSTATCOM system contains a cascaded inverter, RL-filters, a compensation controller (instantaneous real-power theory) and switching signal generator (proposed triangular- sampling current modulator) as shown in the Fig 1. The three-phase supply source connected with non-linear load and these nonlinear loads currents contains fundamental and harmonic components. If the active power filter provides the total reactive and harmonic power, is (t) will be in phase with the utility voltage and would be sinusoidal. At this time, the active filter must provide the compensation current therefore, active power filter estimates the fundamental components and compensating the harmonic current and reactive power. 2.1 Seven level CHB Inverter Fig. 2 Seven level CHB inverter Fig 2 Shows the seven level multilevel inverter and Table shows the switching states of the seven level inverter.
- 4. International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 – 6480(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6499(Online) Volume 4, Issue 2, March – April (2013), © IAEME 109 Table I Switching table for Full H-Bridge of seven level inverter Switches Turn ON Voltage Level S1,S2,S6,S8,S10,S12 Vdc/3 S1,S2,S5,S6,S10,S12 2Vdc/3 S1,S2,S5,S6,S9,S10 Vdc S2,S4,S6,S8,S10,S12 0 S3,S4,S6,S8 S10,S12 -Vdc/3 S3,S4,S7,S8,S10,S12 -2Vdc/3 S3,S4,S7,S8,S11,S12 -Vdc III. REFERENCE CURRENT CONTROL STRATEGY: The control scheme of the shunt active power filter must calculate the current reference signals from each phase of the inverter using instantaneous real-power compensator. The block diagram as shown in Fig.3, that control scheme generates the reference current required to compensate the load current harmonics and reactive power. The PI controller is tried to maintain the dc-bus voltage across the capacitor constant of the cascaded inverter. This instantaneous real- power compensator with PI-controller is used to extracts reference value of current to be compensated. Fig 3: Reference current generator using instantaneous real-power theory These reference currents isa*, isb *and isc * are calculated instantaneously without any time delay by using the instantaneous α,β coordinate currents. The required references current derivate from the inverse Clarke transformation and it can be written as (1) The p-q theory performs a Clarke transformation of a stationary system of coordinates a bc to an orthogonal reference system of coordinates α ,β. In a bc coordinates axes are fixed on the same plane, apart from each other by 1200 that as shown in Fig 2. The instantaneous
- 5. International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 – 6480(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6499(Online) Volume 4, Issue 2, March – April (2013), © IAEME 110 space vectors voltage and current Va , ia are set on the a-axis, Vb , ib are on the b axis, and Vc, ic are on the c axis. These space vectors are easily transformed into α ,β coordinates. The instantaneous source voltages vsa, vsb, vsc are transformed into the α ,β coordinate’s voltage Vα, Vβ by Clarke transformation as follows: (2) Similarly, the instantaneous source current isa, isb, isc also transformed into the α ,β coordinate’s current i α , i β by Clarke transformation that is given as: (3 a) Where α and β axes are the orthogonal coordinates. They Vα , iα are on the α-axis, and Vβ, iβ are on the β-axis. The reference currents isa*, isb * and isc * are compared with actual source current isa , isb and isc that facilitates generating cascaded multilevel inverter switching signals using the proposed triangular-sampling current modulator. The small amount of real-power is adjusted by changing the amplitude of fundamental component of reference currents and the objective of this algorithm is to compensate all undesirable components. When the power system voltages are balanced and sinusoidal, it leads to constant power at the dc bus capacitor and balanced sinusoidal currents at AC mains simultaneously. The orthogonal coordinates of voltage and current vα, iα are on the α-axis and vβ, iβ are on the β-axis. Let the instantaneous real-power calculated from the α-axis and β - axis of the current and voltage respectively. These are given by the conventional definition of real-power as : (3 b) 3.1. PWM Techniques for CHB Inverter The most popular PWM techniques used for CHB inverter are 1. Phase Shifted Carrier PWM (PSCPWM) 2. Level Shifted Carrier PWM (LSCPWM) V. MATLAB/SIMULINK MODELING AND SIMULATION RESULTS Here the simulation is carried out by three cases 1. Non-linear load Without DSTATCOM 2. Non-linear load with seven level PSCPWM cascaded multilevel DSTATCOM and 3. Non-linear load with seven level LSCPWM Cascaded multilevel DSTATCOM.
- 6. International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 – 6480(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6499(Online) Volume 4, Issue 2, March – April (2013), © IAEME 111 Case 1: Nonlinear load without DSTATCOM Fig 6 : Matlab/Simulink model of nonlinear load without DSTATCOM Fig-7 shows the three phase source voltages, three phase source currents and load currents respectively without DSTATCOM. It is clear that without DSTATCOM load current and source currents are same. Fig 7: Source voltage, Source current, Load current without DSTATCOM Case 2: Non-linear load with seven level PSCPWM cascaded multilevel DSTATCOM Fig.8 Seven-level PSCPWM output Fig 8 shows the seven level inverter output with Phase shifted Carrier pulse width modulation. From the Fig we can clearly observe the seven voltage levels.
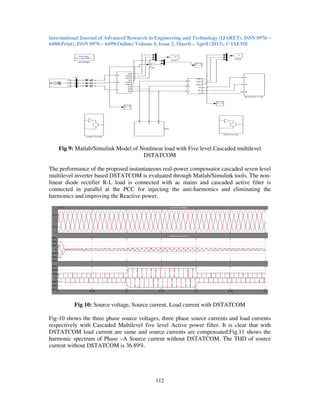
- 7. International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 – 6480(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6499(Online) Volume 4, Issue 2, March – April (2013), © IAEME 112 Fig 9: Matlab/Simulink Model of Nonlinear load with Five level Cascaded multilevel DSTATCOM The performance of the proposed instantaneous real-power compensator cascaded seven level multilevel inverter based DSTATCOM is evaluated through Matlab/Simulink tools. The non- linear diode rectifier R-L load is connected with ac mains and cascaded active filter is connected in parallel at the PCC for injecting the anti-harmonics and eliminating the harmonics and improving the Reactive power. Fig 10: Source voltage, Source current, Load current with DSTATCOM Fig-10 shows the three phase source voltages, three phase source currents and load currents respectively with Cascaded Multilevel five level Active power filter. It is clear that with DSTATCOM load current are same and source currents are compensated.Fig.11 shows the harmonic spectrum of Phase –A Source current without DSTATCOM. The THD of source current without DSTATCOM is 36.89%.
- 8. International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 – 6480(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6499(Online) Volume 4, Issue 2, March – April (2013), © IAEME 113 Fig.11 Harmonic spectrum of Phase-A Source current without DSTATCOM Fig. 12 Harmonic spectrum of Phase-A Source current with Seven level PSPWM - DSTATCOM Fig12 shows the harmonic spectrum of Phase –A Source current with cascaded Multilevel Seven level PSCPWM with DSTATCOM. The THD of source current with Seven level DSTATCOM is 4.37%. Fig 13 shows the power factor waveforms of the designed system without DSTATCOM. The waveform clearly shows that there is no unity power factor. Fig 13: Power Factor without DSTATCOM
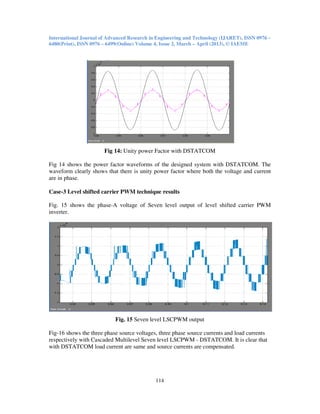
- 9. International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 – 6480(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6499(Online) Volume 4, Issue 2, March – April (2013), © IAEME 114 Fig 14: Unity power Factor with DSTATCOM Fig 14 shows the power factor waveforms of the designed system with DSTATCOM. The waveform clearly shows that there is unity power factor where both the voltage and current are in phase. Case-3 Level shifted carrier PWM technique results Fig. 15 shows the phase-A voltage of Seven level output of level shifted carrier PWM inverter. Fig. 15 Seven level LSCPWM output Fig-16 shows the three phase source voltages, three phase source currents and load currents respectively with Cascaded Multilevel Seven level LSCPWM - DSTATCOM. It is clear that with DSTATCOM load current are same and source currents are compensated.
- 10. International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 – 6480(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6499(Online) Volume 4, Issue 2, March – April (2013), © IAEME 115 Fig 16: Source voltage, Source current, Load current with Seven level LSPWM – DSTATCOM Fig 17. shows the harmonic spectrum of Phase –A Source current with cascaded Multilevel Seven level LSPWM - DSTATCOM. The THD of source current with seven level DSTATCOM is 4.37%. Fig. 17 Harmonic spectrum of Phase-A Source current with DSTATCOM
- 11. International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 – 6480(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6499(Online) Volume 4, Issue 2, March – April (2013), © IAEME 116 Table-II Comparison between the PSCPWM and LSCPWM schemes and System Specifications are Comparison PSPW M LSPWM S.No System Parameters Rating switching frequency Same for all devices Different 1 voltage 11kv,50Hz conduction period Same for all devices Different 2 Inductance 0.9e-3h Rotating of switching patterns Not required Required 3 Resistance 0.1ohm THD of Source Current 4.37% 2.82% 4 Load R=60,L=30e-3 5 Inverter Parameters DC Link voltage=14kv CONCLUSION A seven level cascaded multilevel voltage source inverter based DSTATCOM using instantaneous real-power controller is found to be an effective solution for power line conditioning. DSTATCOM with the proposed controller reduces harmonics and provides reactive power compensation due to non-linear load currents; as a result source current(s) become sinusoidal and unity power factor is also achieved under both transient and steady state conditions. The proposed instantaneous real-power controller uses reduced computation for reference current calculations compared to conventional approach. The cascaded inverter switching signals are generated using triangular-sampling current controller; it provides a dynamic performance under transient and steady state conditions. As evident from the simulation studies, dc bus capacitor voltage settles early and has minimal ripple because of the presence of PI-controller. The THD of the source current is investigated for both PSCPWM and LSCPWM for a seven level inverter based DSTATCOM. THD simulation results under non-linear loads are investigated and found that the LSCPWM results are better than PSCPWM. REFERENCES [1] Bhim Singh, Kamal Al-Haddad & Ambrish Chandra, “A New Control Approach to 3- phase Active Filter for Harmonics and Reactive Power Compensation”-IEEE Trans. on Power Systems, Vol. 46, NO. 5, pp.133 – 138, Oct-1999 [2] W. K. Chang, W. M. Grady, Austin, M. J. Samotyj “Meeting IEEE- 519 Harmonic Voltage and Voltage Distortion Constraints with an Active Power Line Conditioner”- IEEE Trans on Power Delivery, Vol.9, No.3, pp.1531-1537, 1994
- 12. International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 – 6480(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6499(Online) Volume 4, Issue 2, March – April (2013), © IAEME 117 [3] Hirofumi Akagi, “Trends in Active Power Line Conditioners”- IEEE Trans on Power Electronics, Vol.9, No.3, May-1994 [4] W.M.Grady, M.J.Samotyj, A.H.Noyola “Survey of Active Power Line Conditioning Methodologies” IEEE Trans on Power Delivery, Vol.5, No.3, pp.1536-1542, July-1990 [5] L. Gyugyi, E. C. Strycula, “Active AC Power Filters”- in Proc. IEEE/IAS Annu. Meeting, Vol.19-c, pp 529-535, 1976 [6] Hirofumi Akagi, Yoshihira Kanazawa, Akira Nabae “Instantaneous Reactive Power Compensators Comprising Switching Devices without Energy Storage Components”- IEEE Trans on Industry Appl, Vol.I1-20, No.3,pp.625-630, 1984 [7] E. H. Watanabe, R. M. Stephan, M. Aredes, “New Concepts of Instantaneous Active and Reactive Powers in Electrical Systems with Generic Loads”- IEEE Trans. Power Delivery, Vol.8, No.2, pp.697-703, 1993 [8] Fang Zheng Peng & Jih-Sheng Lai, “Generalized Instantaneous Reactive Power Theory for Three-Phase Power Systems”, IEEE Trans. on Inst. and Meast, Vol.45, No.1, pp.293-297, 1996 [9] Joao Afonso, Carlos Couto, Julio Martins “Active Filters with Control Based on the p-q Theory”- IEEE Industrial Elects Society Nletter-2000 [10] E. H. Watanabe, H. Akagi, M. Aredes “Instantaneous p-q Power Theory for Compensating Non sinusoidal Systems”- International School on Non sinlusoidal Currents and Compensation Lagow, Poland-2008 [11] Leszek S. Czarnecki “Instantaneous Reactive Power p-q Theory and Power Properties of Three-Phase Systems”- IEEE Trans on Power, VOL. 21, NO. 1, pp 362-367, 2006 [12] Karuppanan P and Kamala Kanta Mahapatra “Shunt Active Power Line Conditioners for Compensating Harmonics and Reactive Power”-Proceedings of the International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering (EEEIC), pp.277 – 280, May 2010 [13] Hirofumi Akagi, Akira Nabae and Satoshi Atoh “Control Strategy of Active Power Filters Using Multiple Voltage-Source PWM Converters” IEEE Trans on Industry Applications, Vol.IA-22, No.3, pp.460-465, May/June 1986 [14] Fang Zheng Peng, John W. McKeever, and Donald J. Adams “A Power Line Conditioner Using Cascade Multilevel Inverters for Distribution Systems” IEEE Trans on Industry Applications Vol.34, No.6, pp. 1293-98, Nov/Dec-1998 [15] S.-J.Huang and J.-C.Wu “Design and operation of cascaded active power filters for the reduction of harmonic distortions in a power System” IEE Proc.-Gener. Transm. Distrib.. Vol. 146, No. 2,pp. 193-199, March 1999. [16] G.Kumar and P.S.Raju, “Study of DSTATCOM in Improved Custom Power Park for Power Quality Improvement”, International Journal of Electrical Engineering & Technology (IJEET), Volume 2, Issue 2, 2011, pp. 12 - 20, ISSN Print : 0976-6545, ISSN Online: 0976- 6553. [17] Dr. Leena G, Bharti Thakur, Vinod Kumar and Aasha Chauhan, “Fuzzy Controller Based Current Harmonics Suppression using Shunt Active Filter with PWM Technique”, International Journal of Electrical Engineering & Technology (IJEET), Volume 4, Issue 1, 2013, pp. 162 - 170, ISSN Print : 0976-6545, ISSN Online: 0976-6553. [18] B.Kiran Kumar, Y.V.Sivareddy and M.Vijayakumar, “Comparative Analysis of Sine Triangle and Space Vector PWM for Cascaded Multilevel Inverters”, International Journal of Electrical Engineering & Technology (IJEET), Volume 4, Issue 2, 2013, pp. 155 - 164, ISSN Print : 0976-6545, ISSN Online: 0976-6553.
- 13. International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 – 6480(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6499(Online) Volume 4, Issue 2, March – April (2013), © IAEME 118 AUTHORS Mr. D. Mohan Reddy received the B.Tech. Degree in Electrical and Electronics Engineering from the JNT University, Hyderabad, India and he received the M.E Power Systems Engineering from Anna University Chennai and presently pursuing PhD from S.V.University,Tirupati,India. Presently he is working as an Associate Professor in the department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering in Sri Vasavi Institute of Engineering and Technology, Machilipatnam. His research areas of interests are power electronic converters, electrical drives and power quality. Dr T. Gowri Manohar received the B.Tech, M.Tech, and PhD Degrees in Electrical and Electronics Engineering from the S.V.University, Tirupati, India. Presently he is working as an Associate Professor in the department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering S.V.University, Tirupati, India. He is having 15 years of teaching experience and he was published 60 numbers of various international and national conferences & journals. He is a senior Member of IEEE and also he is a member in Indian Society for Technical Education. His research areas of interests are Modern restructured power systems, electrical drives and power quality and harmonics –issues & challenges.


![International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 –
6480(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6499(Online) Volume 4, Issue 2, March – April (2013), © IAEME
107
quality depends upon the needs of the equipment that is being supplied. What is good power
quality for an electric motor may not be good enough for a personal computer. Usually the
term power quality refers to maintaining a sinusoidal waveform of bus voltages at rated
voltage and frequency [1]. The waveform of electric power at generation stage is purely
sinusoidal and free from any distortion. Many of the Power conversion and consumption
equipment are also designed to function under pure sinusoidal voltage waveforms. However,
there are many devices that distort the waveform. These distortions may propagate all over
the electrical network. In recent years, there has been an increased use of non-linear loads
which has resulted in an increased fraction of non-sinusoidal currents and voltages in Electric
Network. The wave shape phenomena associated with power quality may be characterized
into synchronous and non synchronous phenomena. Synchronous phenomena refer to those in
synchronism with A.C waveform at power frequency [2],[3].
A group of controllers together called Custom Power Devices (CPD), which include
the DSTATCOM (distribution static compensator), The DSTATCOM, is a shunt-connected
device, which takes care of the power quality problems in the currents It consists of a dc
capacitor, three-phase inverter (IGBT, thyristor) module, ac filter, coupling transformer and a
control strategy. The basic electronic block of the D-STATCOM is the voltage-sourced
inverter that converts an input dc voltage into a three-phase output voltage at fundamental
frequency. The D-STACOM employs an inverter to convert the DC link voltage Vdc on the
capacitor to a voltage source of adjustable magnitude and phase. Therefore the D-STATCOM
can be treated as a voltage-controlled source. The D-STATCOM can also be seen as a
current-controlled source. The generalized instantaneous reactive power theory which is
valid for sinusoidal or non-sinusoidal and balanced or unbalanced three-phase power systems
with or without zero-sequence currents were later proposed [8]. The construction controller
of the D-STATCOM is used to operate the inverter in such a way that the phase angle
between the inverter voltage and the line voltage is dynamically adjusted so that the D-
STATCOM generates or absorbs the desired VAR at the point of connection. The phase of
the output voltage of the thyristor-based inverter, Vi, is controlled in the same way as the
distribution system voltage, Vs.
The DSTATCOM is based on the instantaneous real-power theory; it provides good
compensation characteristics in steady state as well as transient states [11]. The instantaneous
real-power theory generates the reference currents required to compensate the distorted line
current harmonics and reactive power. It also tries to maintain the dc-bus voltage across the
capacitor constant. Another important characteristic of this real-power theory is the simplicity
of the calculations, which involves only algebraic calculation [12].
A multilevel inverter can reduce the device voltage and the output harmonics by
increasing the number of output voltage levels. There are several types of multilevel
inverters: cascaded H-bridge (CHB), neutral point clamped, flying capacitor [2-5]. In
particular, among these topologies, CHB inverters are being widely used because of their
modularity and simplicity. Various modulation methods can be applied to CHB inverters.
CHB inverters can also increase the number of output voltage levels easily by increasing the
number of H-bridges. This paper presents a DSTATCOM with a proportional integral
controller based CHB multilevel (five level and seven level) inverter for the harmonics and
reactive power mitigation of the nonlinear loads. This type of arrangements have been widely
used for PQ applications due to increase in the number of voltage levels, low switching
losses, low electromagnetic compatibility for hybrid filters and higher order harmonic
elimination.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asevenlevelcascadedmultileveldstatcomforcompensationofreactivepowerandharmonics-130426000437-phpapp01/85/A-seven-level-cascaded-multilevel-dstatcom-for-compensation-of-reactive-power-and-harmonics-2-320.jpg)





![International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 –
6480(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6499(Online) Volume 4, Issue 2, March – April (2013), © IAEME
116
Table-II Comparison between the PSCPWM and LSCPWM schemes and System
Specifications are
Comparison PSPW
M
LSPWM S.No System Parameters Rating
switching
frequency
Same
for all
devices
Different 1 voltage 11kv,50Hz
conduction
period
Same
for all
devices
Different 2 Inductance 0.9e-3h
Rotating of
switching
patterns
Not
required
Required 3 Resistance 0.1ohm
THD of
Source
Current
4.37% 2.82% 4 Load R=60,L=30e-3
5 Inverter Parameters DC Link
voltage=14kv
CONCLUSION
A seven level cascaded multilevel voltage source inverter based DSTATCOM using
instantaneous real-power controller is found to be an effective solution for power line
conditioning. DSTATCOM with the proposed controller reduces harmonics and provides
reactive power compensation due to non-linear load currents; as a result source current(s)
become sinusoidal and unity power factor is also achieved under both transient and steady
state conditions. The proposed instantaneous real-power controller uses reduced computation
for reference current calculations compared to conventional approach. The cascaded inverter
switching signals are generated using triangular-sampling current controller; it provides a
dynamic performance under transient and steady state conditions. As evident from the
simulation studies, dc bus capacitor voltage settles early and has minimal ripple because of
the presence of PI-controller. The THD of the source current is investigated for both
PSCPWM and LSCPWM for a seven level inverter based DSTATCOM. THD simulation
results under non-linear loads are investigated and found that the LSCPWM results are better
than PSCPWM.
REFERENCES
[1] Bhim Singh, Kamal Al-Haddad & Ambrish Chandra, “A New Control Approach to 3-
phase Active Filter for Harmonics and Reactive Power Compensation”-IEEE Trans. on
Power Systems, Vol. 46, NO. 5, pp.133 – 138, Oct-1999
[2] W. K. Chang, W. M. Grady, Austin, M. J. Samotyj “Meeting IEEE- 519 Harmonic
Voltage and Voltage Distortion Constraints with an Active Power Line Conditioner”- IEEE
Trans on Power Delivery, Vol.9, No.3, pp.1531-1537, 1994](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asevenlevelcascadedmultileveldstatcomforcompensationofreactivepowerandharmonics-130426000437-phpapp01/85/A-seven-level-cascaded-multilevel-dstatcom-for-compensation-of-reactive-power-and-harmonics-11-320.jpg)
![International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 –
6480(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6499(Online) Volume 4, Issue 2, March – April (2013), © IAEME
117
[3] Hirofumi Akagi, “Trends in Active Power Line Conditioners”- IEEE Trans on Power
Electronics, Vol.9, No.3, May-1994
[4] W.M.Grady, M.J.Samotyj, A.H.Noyola “Survey of Active Power Line Conditioning
Methodologies” IEEE Trans on Power Delivery, Vol.5, No.3, pp.1536-1542, July-1990
[5] L. Gyugyi, E. C. Strycula, “Active AC Power Filters”- in Proc. IEEE/IAS Annu. Meeting,
Vol.19-c, pp 529-535, 1976
[6] Hirofumi Akagi, Yoshihira Kanazawa, Akira Nabae “Instantaneous Reactive Power
Compensators Comprising Switching Devices without Energy Storage Components”- IEEE
Trans on Industry Appl, Vol.I1-20, No.3,pp.625-630, 1984
[7] E. H. Watanabe, R. M. Stephan, M. Aredes, “New Concepts of Instantaneous Active and
Reactive Powers in Electrical Systems with Generic Loads”- IEEE Trans. Power Delivery,
Vol.8, No.2, pp.697-703, 1993
[8] Fang Zheng Peng & Jih-Sheng Lai, “Generalized Instantaneous Reactive Power Theory
for Three-Phase Power Systems”, IEEE Trans. on Inst. and Meast, Vol.45, No.1, pp.293-297,
1996
[9] Joao Afonso, Carlos Couto, Julio Martins “Active Filters with Control Based on the p-q
Theory”- IEEE Industrial Elects Society Nletter-2000
[10] E. H. Watanabe, H. Akagi, M. Aredes “Instantaneous p-q Power Theory for
Compensating Non sinusoidal Systems”- International School on Non sinlusoidal Currents
and Compensation Lagow, Poland-2008
[11] Leszek S. Czarnecki “Instantaneous Reactive Power p-q Theory and Power Properties of
Three-Phase Systems”- IEEE Trans on Power, VOL. 21, NO. 1, pp 362-367, 2006
[12] Karuppanan P and Kamala Kanta Mahapatra “Shunt Active Power Line Conditioners for
Compensating Harmonics and Reactive Power”-Proceedings of the International Conference
on Environment and Electrical Engineering (EEEIC), pp.277 – 280, May 2010
[13] Hirofumi Akagi, Akira Nabae and Satoshi Atoh “Control Strategy of Active Power
Filters Using Multiple Voltage-Source PWM Converters” IEEE Trans on Industry
Applications, Vol.IA-22, No.3, pp.460-465, May/June 1986
[14] Fang Zheng Peng, John W. McKeever, and Donald J. Adams “A Power Line
Conditioner Using Cascade Multilevel Inverters for Distribution Systems” IEEE Trans on
Industry Applications Vol.34, No.6, pp. 1293-98, Nov/Dec-1998
[15] S.-J.Huang and J.-C.Wu “Design and operation of cascaded active power filters for the
reduction of harmonic distortions in a power System” IEE Proc.-Gener. Transm. Distrib..
Vol. 146, No. 2,pp. 193-199, March 1999.
[16] G.Kumar and P.S.Raju, “Study of DSTATCOM in Improved Custom Power Park for
Power Quality Improvement”, International Journal of Electrical Engineering & Technology
(IJEET), Volume 2, Issue 2, 2011, pp. 12 - 20, ISSN Print : 0976-6545, ISSN Online: 0976-
6553.
[17] Dr. Leena G, Bharti Thakur, Vinod Kumar and Aasha Chauhan, “Fuzzy Controller
Based Current Harmonics Suppression using Shunt Active Filter with PWM Technique”,
International Journal of Electrical Engineering & Technology (IJEET), Volume 4, Issue 1,
2013, pp. 162 - 170, ISSN Print : 0976-6545, ISSN Online: 0976-6553.
[18] B.Kiran Kumar, Y.V.Sivareddy and M.Vijayakumar, “Comparative Analysis of Sine
Triangle and Space Vector PWM for Cascaded Multilevel Inverters”, International Journal of
Electrical Engineering & Technology (IJEET), Volume 4, Issue 2, 2013, pp. 155 - 164, ISSN
Print : 0976-6545, ISSN Online: 0976-6553.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asevenlevelcascadedmultileveldstatcomforcompensationofreactivepowerandharmonics-130426000437-phpapp01/85/A-seven-level-cascaded-multilevel-dstatcom-for-compensation-of-reactive-power-and-harmonics-12-320.jpg)
