"AI" for Blockchain Security (Case Study: Cosmos)
- 1. Nicolas Pinto Interchain Conversations, Berlin | June 2019 edition Buzzwords (a few more buzzwords here) buzzword
- 2. Nicolas Pinto Interchain Conversations, Berlin | June 2019 edition ”AI” for Cosmos Security Icarus: Deep (Learning) Explorations of the Cosmos SDK* *warning: very preliminary work
- 3. Goal • ”AI”-driven Security Audit for Blockchain Projects • Swim in buzzwords and equations* • Spark interest around a non-obvious topic • Present encouraging preliminary results • Bring two different cultures together • Get you involved!
- 4. Outcome
- 5. Outline 1. Intro: AI4BC / BC4AI 2. Methods: KISS 3. Results: ZBRA 4. Discussion: YOU
- 6. 1. Intro: ai4bc / bc4ai Buzzword Buzzword, Inc. (longer than usual)
- 8. What? • Applying “AI” / (Deep) Machine Learning to hunt for vulnerabilities in Blockchain projects. • Think of DeepBlue, Watson, AlphaGo, AlphaStar • But for Bugs! …
- 9. — Who? • Thomas France (CEO) • Nicolas Pinto (CTO) • Both interested in “AI/ML” and “BC”
- 10. — Who? • Thomas France (CEO): • Co-founder @ Bitcoin House in Paris • Co-founder @ Ledger • Angel investor & early contributor in crypto • Left Ledger in January 2019 to explore new projects around scalability, security and privacy
- 11. — Who? • Nicolas Pinto (CTO): • 2006-2010: Neuroscience/AI PhD @ MIT • 2009: Enthusiast @ Bitcoin • 2010-2012: Neuroscience/AI @ MIT/Harvard • 2012-2014: Co-founder @ Perceptio (Mobile Deep Learning) • 2014-2018: Ninja, Research Director @ Apple • 2018-now: Blockchain for AI <> AI for Blockchain
- 12. 13 years in 5 minutes
- 13. Back in 2006
- 14. Neuroscience DiCarlo Lab @ MIT Jim DiCarlo David Cox
- 15. The Approach Reverse and Forward Engineering Intelligence (Neuro)
- 16. The Approach Reverse and Forward Engineering the Brain Build Artificial System FORWARDREVERSE Study Natural System
- 17. Reverse Engineering TheVisual Cortex brain = 20 petaflops ?!
- 18. PeakGFLOP/s Computationalpower GPUs CPUs DIY GPU pr0n (since 2006) Sony Playstation 3s (since 2007) The blessing of GPUs 2006
- 20. Build your own! Sony Playstation 3s (since 2007) 2006
- 21. MIT (2008-2009) Harvard (2010-2012) Teaching our craft Sharing as early as possible, empowering others…
- 22. @end: 100s of GPUs (for free!) 2010-2012 @ MIT/Harvard
- 23. Pinto,Doukhan,DiCarlo,CoxPLoS2009 n e nd- en tes ates t es states, ap of is neigh- low, the becomes o the nd Rabi onal states ay lead to kely a nformation 009). tein expression p modium that were isolated from the patients; they identified about 100 proteins, some of which had not been found in laboratory cultures and could make promising drug or vac- cine targets. — HP Proteomics Clin. Appl. 3, 1314 (2009). N E U R O S C I E N C E The Next Top Model Consumers may be familiar with high-end graphic processing components in video game consoles, such as the PlayStation3, or as a con- sequence of outfitting personal computers ordered online with NVIDIA graphics cards; these advances in hardware have also attracted the attention of procurement officials in the military serv- ices. In the aca- demic realm, Pinto et al. have harnessed the power of clustered graphics processors to assess the relative performance of sion models of object recognition. arallel processing onJanuary4,2010 www.sciencemag.org Downloadedfrom C S owave Manipulation l lattices populated by neutral atoms are candidate for storing quantum infor- . Normally, internal degrees of freedom s the hyperfine state are used to create sic information unit, the qubit. However, also possess motional degrees of free- or example, the confinement of atoms in EDITORS’CHOICE Plasmodium in comparison to laboratory cul- tures revealed differences in gene expression profiles. Acharya et al. have analyzed the pro- tein expression profiles of two species of Plas- modium that were isolated from the blood of patients; they identified about 100 proteins, some of which had not been found in laboratory cultures and could make promising drug or vac- cine targets. — HP Proteomics Clin. Appl. 3, 1314 (2009). EDITED BY GILBERT CHIN AND JAKE YESTON full control of quantum transport, likely a necessity for processing quantum information in this system. — JS Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 233001 (2009). C E L L B I O LO G Y In the Wild Malaria is one of the most prevalent infectious diseases and kills around 900,000 people per year. It is caused by parasites of the genus Plas- modium, which are transmitted to humans by mosquitoes and enter red blood cells, causing fever and, if left untreated, death. Human pathogens of all kinds can develop resistance to the most effective drugs, such as artemisinin, so there is a constant need to identify new com- pounds. Animal models of malaria have proven problematic to establish, and most studies have used laboratory cultures of human blood cells to grow the parasites. While important insights into the life cycle and pathogenic action of Plas- modium have come from these in vitro studies, a recent study of clinically isolated samples of www.sciencemag.org SCIENCE VOL 327 1 JANUARY 2010 Pinto et al. h harnessed th of clustered processors to machine visi The availabi power at rea explore, in 1 regions of p ber of filters They genera were trained during an un then screene versus plane of orientatio The top-rank broadly acro toughest rec human faces sophisticate set of param with high ob vessel called the ductus arteriosus (DA) allows blood to bypass the nonfunctional fetal lungs by connecting the pulmonary artery, which supplies blood to the lungs, with the aorta, which supplies blood to the rest of the body. This vessel normally closes a day or two after birth, but in some new- borns, it remains open and can lead to life- threatening complications. Studying new- born mice, Echtler et al. make the surprising observation that platelets—cells noted for their role in blood clotting—were recruited to the lumen of the DA within 20 minutes after birth of the mice; when platelet pro- duction or function was disrupted, the DA failed to close completely, leading to abnor- mal patterns of blood flow. The recruited platelets play a dual role in DA closure—by forming a physical plug that seals the lumen of the constricted DA and by altering the behavior of other cell types involved in blood vessel remodeling. — PAK Nat. Med. 10.1038/nm.2060 (2009).
- 24. Did Google get inspired?
- 25. PERCEPTIO The world’s most advanced mobile-first deep learning startup* *also still the only one, as far as we know! ;-) 2012
- 26. Mobile first ! establishing trust, betting against the cloud…
- 27. A.I. you can trust protecting your privacy
- 28. More data, less power when running intelligence right next to the sensor
- 29. 2014
- 31. Is winter back? AlexNetNP’s PhD (Dec 2010) Perceptio (Aug 2012) Perceptio 2.0 ? (Mar 2018) Perceptio @ Apple (Nov 2014)
- 32. PERCEPTIO 2.0 Decentralized AI (bc4ai) 2018
- 33. Peter Thiel What do you disagree with that almost everyone else believes? *** ” “
- 34. Peter Thiel AI centralizes, Blockchain decentralizes…”“
- 35. Decentralized AI (bc4ai) • Move away from centralized & supervised AI • Are we in the Matrix? • Non-dystopian future: decentralized & unsupervised (autonomous) AI • Collective intelligence: • Scalable • Private • Secure (making smart contracts actually smart, but not only)
- 36. Too Early? • Decentralization (blockchain) technology may not be mature enough • Being too early is like being wrong… • You don’t want to be doing Neural Networks in the 80s…
- 38. Can we help… • … accelerate progress? • AI for Blockchain ;-) • Before bc4ai, let’s do ai4bc !
- 40. Help with scalability? (AI for Blockchain)
- 41. NIPS 2011 Scalability?we did something similar in the past… ai4gpu
- 42. Google (2018) Scalability?Google does it now…
- 43. • Parameters without closed-form solutions (e.g. block size :-) • Transaction throughput (i.e. tx / s) • Fee prediction (e.g. Bitcoin’s estimatesmartfee 2.0 ?) • Block construction (e.g. UTXO set selection) • Crypto implementation (e.g. ZKP) • etc. Optimize what?(for scalability)
- 44. Feedback(from many blockchain devs) Security First !
- 45. Security ?! • Scalability? not yet.. Security first! • Security is paramount for Blockchain • Any failure: huge reputational risk, if not killer
- 47. Why Cosmos ?! Because… • Cosmos community showed us the way… • Thanks in particular to: • Adrian Brink (TokenSummit’17), • Chris Goes (DevCon’18), • Jae Kwon (BUIDL’18) • Ethan Buchman (BPASE’19)
- 49. Why Cosmos ?! Because… • PBFT & IBC are sexy: • Blockchain of blockchains, • Internet of blockchains, • OS of blockchains? • Already used by many exciting projects: IRIS, LOOM, Binance DEX, Terra, etc. • Platform of choice for bc4ai ?!
- 50. Of course: Cosmos!! • Just launched! • We are big fans of the project: • Supporters/investors in ICO, All In Bits, CastleNode, Cryptium Labs, etc. • Game-of-Stakes “winner”: BouBouNode !
- 51. BouBouNode
- 52. Cosmos x Security • Talking about Game-of-Stakes… • Cosmos has taken security seriously since day one • Jae talked about a custom Ledger for Tendermint validators in 2015! • Implementation of best-in-class practices very early on • Security-driven development (slow like in hardware)
- 53. COSMOS CODE IS PUBLIC !
- 54. Cosmos x Security • Afraid? Many audits! Bounty program! • Active community of security researchers with a wide range of expertise, for example: • Certus.One: infrastructure • B-Harvest: economics
- 55. Cosmos x Security • Interchain Foundation very open to experimenting • Already pushing the boundaries of testing in blockchain… • Simulator available!
- 59. “AI” vs. IA • “AI” (today): • Skeptic: “AI = glorified guided random search (almost brute force)” • Centralized & disrupting/displacing jobs • IA (tomorrow): • IA = Intelligence Augmentation • Decentralized & empowering devs :)
- 60. Reality: Blue vs. White vs. Pajamas Collar
- 61. Icarus: Preliminary Ideas • Practical: • Deep Learning for Fuzzing Cosmos (buzzwords ;-) • Long shots: • Formal verification relaxation: bridge from dynamic to static verification ? • Source code analysis: “hotspot” prediction / classification
- 62. Bug “hotspot” prediction • Simulate dev/auditor • Generalizable?
- 63. Interviews: the cast • Tendermint family: Chris, Jae, Ethan, Zaki, Anton, Jessy, Alex • Validators: • Cryptium Labs: Adrian* • CastleNode: Gautier • Certus.One: Hendrik • B-Harvest: Hyung • Independent security consultants • Future collaborators (in blockchain, security, and AI spaces) etc.
- 64. Interviews: pain points • Simulator (random tests already in place) • Maths / Types (how numbers are handled) • Amino (serialization) • Jepsen (distributed system tests) • P2P / RPC • Fairness (e.g. block proposer) • Mempool (e.g. non-obvious mempool DDoS) • Trust boundaries • Crypto economics / financial distribution logics etc. little overlap!
- 65. Interviews: quotes • “It’s easier to find bugs from the data than from looking at the code” (Hyung @ B-Harvest) • “The simulator is only vaguely fuzzing at the moment, it’s more like a sophisticated integration test suite” • “Transactions are too clean in the simulator” (Hendrik @ Certus.One)
- 66. Interviews: “bug correlates” • (Deep) Learning needs gradients • Bugs are non differentiable ;-) • We need proxies/surrogates = "bug correlates” • Signals that tend to correlate with bugs, alone or in high-order / complex interactions • Which ones would you suggest? F(X) = Y ~ Z 0 1
- 67. Interviews: “bug correlates” • Resources usage: • Memory (e.g. leaks) • Go routines • File descriptors • Stack depth • Gas consumed (surrogate for complex operations) • Block time (e.g. w.r.t. blockchain size) • Long running chains • Complex cross-module interactions (i.e. hooks) etc.
- 68. Getting our feet wet We focused on: • Amino (fuzzer already in place) • Jepsen tests • Math / types • Simulator (integration tests) *
- 69. Simulator: flow sim params output stats848275874 random seed fast slow
- 72. Simulator: “AI” • Goal: focus compute power on more “interesting” runs (defined as “likely to produce a bug” ;) • Use machine learning for “interesting” classification • Like spam !
- 73. Simulator: “AI” sim params output sta75874 m seed fast slowfast yes no AI magic*
- 74. Linus Pauling (double Nobel Prize Winner) If you want to have good ideas you must have many ideas.” “ Most of them will be wrong, and what you have to learn is which ones to throw away. “ ”
- 77. 3. Results: preliminary (super fresh)
- 79. Brute Force Data Collection • KISS, DIY, duck-taped… • ML: training/validation/testing all intertwined • Not necessarily statistically correct, but it doesn’t matter here • All simulation runs are valid • Any jamming during data collection is valuable
- 80. SuperComputer • At first: my laptop + 2x 2€/month nodes ;-) • Then: 6x CX51 nodes on Hetzner (6x 30€/month) • 6x 8vCPUs / 32GB • 48 concurrent processes
- 81. #blocks count Insights most “die” early
- 83. TADAAAA ! • Dead lock in invariant checks • 0.5% of the FAIL runs are “time out” (24h !!!!) • i.e. you need 200 runs to get one! • after a while all CPUs get stuck BUG FOUND
- 84. BUGS FOUND
- 85. Simulator Bugs • Low hanging fruits first (predictable) • BUG: simulator non-determinism (RNG ops) BUG FOUND
- 86. Simulator Bugs • BUG: faulty parameter distribution boundaries BUG FOUND
- 87. Simulator Bugs • BUG: faulty parameter distribution boundaries BUG FOUND
- 88. Simulator Bugs • BUG: faulty parameter distributions BUG FOUND BUG: 1/8000 chance of sum == 0 FIX: hack
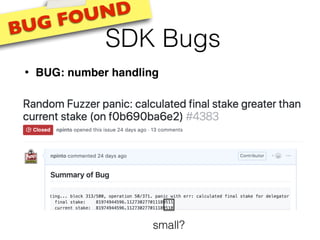
- 89. SDK Bugs • BUG: number handling BUG FOUND small?
- 90. SDK Bugs • BUG: number handling BUG FOUND small?
- 91. SDK Bugs • BUG: number handling BUG FOUND
- 92. Coverage • Coverage is trending down as devs add more features… MORE ! https://codecov.io/gh/cosmos/cosmos-sdk
- 93. Coverage • Brute force “AI” is already helping… MORE !
- 94. Coverage • Coverage optim (+test_cover.sh): from 56.5% to 61.6% • However, code coverage is easier and less valuable than state coverage… MORE !
- 95. Copper Cluster • Collaboration w/ Prof. Graham Taylor @ University of Guelph (AI friend but also Ethan’s M.S. advisor!) • Copper: a real SuperComputer • Compute: 577 CPUs / concurrent processes (12X more than before) • 24/7, just for us!? • 10Ks+ simulations per day • Maybe: academic paper with Graham’s research group? MORE !
- 96. Future? MORE !
- 97. 4. Discussion
- 98. Kaggle-like Competition? • Dataset sharing: 76,655 simulations with associated profiling data • Idea: Kaggle-style bounty-driven competition?
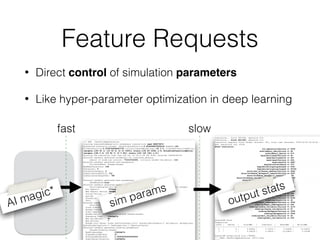
- 99. Feature Requests • Direct control of simulation parameters • Like hyper-parameter optimization in deep learning sim params output stats fast slow AI magic*
- 100. Feature Requests • Direct control of simulation parameters DONE
- 101. Feature Requests
- 102. Feature Requests • Bug “Bubbles”: • ways to parametrize sim around critical bugs? • and use these as seeds to explore around…
- 103. Future Work • Full transaction control during the simulation • “AI” Bugs to “AI” Fixes? • Semi-automated bug reports • Problem: reports are (human) time consuming to “manicure” • Solution: attention model for highlights / insights
- 104. Getting you involved! • A lot of surface area to cover: F(X) = Y ~ Z • Engage you as well as the AI community • Come make Cosmos the most tested/robust project in blockchain software ever !
- 105. Thanks • Thomas France • ICF, Tendermint: Ethan, Jae, Chris, Alex, Rigel, Zaki, Anton, Jessy • Interviewees: Adrian, Gautier, Hendrik, Hyung, Anil • Current collaborators: Graham Taylor, Fernand Pajot • Future collaborators: Joseph Turian*, Nicolas Poilvert, Edouard Oyallon • BouBou(Node)
- 106. Outcome
- 107. COME