All about XML, JSON and related topics..
- 2. JSON stands for JavaScript object notation. JSON has been derived from javascript, where javascript is a programming language. It was originally created to hold the structured data that could be used in javascript. JSON became so popular that it is used for data for all kinds of applications. It is the most popular way of sending the data for Web APIs. Basic data types supported by JSON are: 1. Strings: Characters that are enclosed in single or double quotation marks. 2. Number: A number could be integer or decimal, positive or negative. 3. Booleans: The Boolean value could be either true or false without any quotation marks. 4. Null: Here, null means nothing without any quotation marks.
- 3. WHAT IS XML? XML stands for an extensible markup language. It is like HTML, where HTML stands for Hypertext Markup language. HTML is used for creating websites, whereas XML can be used for any kind of structured data. XML has two ways of handling data, i.e., Tags and Attributes. The tags work as HTML. The start tags start with the <_> and end with the </_>. The start and end tags must match. The names must only be letters, numbers, and underscore, and the tag name must start with a letter only.
- 4. SIMILARITIES BETWEEN THE JSON AND XML. 1. Self-describing: Both json and xml are self-describing as both xml data and json data are human-readable text. 2. Hierarchical: Both json and xml support hierarchical structure. Here hierarchical means that the values within values. 3. Data interchange format: JSON and XML can be used as data interchange formats by many different programming languages. 4. Parse: Both the formats can be easily parsed. 5. Retrieve: Both formats can be retrieved by using HTTP requests. The methods used for retrieving the data are GET, PUT, POST.
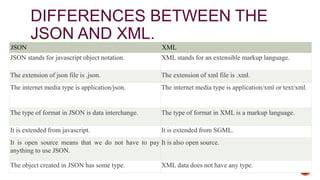
- 5. DIFFERENCES BETWEEN THE JSON AND XML. JSON XML JSON stands for javascript object notation. XML stands for an extensible markup language. The extension of json file is .json. The extension of xml file is .xml. The internet media type is application/json. The internet media type is application/xml or text/xml. The type of format in JSON is data interchange. The type of format in XML is a markup language. It is extended from javascript. It is extended from SGML. It is open source means that we do not have to pay anything to use JSON. It is also open source. The object created in JSON has some type. XML data does not have any type.
- 6. he data types supported by JSON are strings, numbers, Booleans, null, array. XML data is in a string format. It does not have any capacity to display the data. XML is a markup language, so it has the capacity to display the content. JSON has no tags. XML data is represented in tags, i.e., start tag and end tag. XML file is larger. If we want to represent the data in XML then it would create a larger file as compared to JSON. JSON is quicker to read and write. XML file takes time to read and write because the learning curve is higher. JSON can use arrays to represent the data. XML does not contain the concept of arrays. It can be parsed by a standard javascript function. It has to be parsed before use. XML data which is used to interchange the data, must be parsed with respective to their programming language to use that. It can be easily parsed and little bit code is required to parse the data. It is difficult to parse.
- 7. File size is smaller as compared to XML. File size is larger. JSON is data-oriented. XML is document-oriented. It is less secure than XML. It is more secure than JSON.
- 8. The JSON syntax is a subset of the JavaScript syntax. JSON Syntax Rules 1. JSON syntax is derived from JavaScript object notation syntax: 2. Data is in name/value pairs 3. Data is separated by commas 4. Curly braces hold objects 5. Square brackets hold arrays
- 9. JSON DATA - A NAME JSON data is written as name/value pairs (aka key/value pairs). A name/value pair consists of a field name (in double quotes), followed by a colon, followed by a value: Example "name":"John"
- 10. JSON VALUES In JSON, values must be one of the following data types: 1. a string 2. a number 3. an object 4. an array 5. a boolean 6. null
- 11. In JavaScript values can be all of the above, plus any other valid JavaScript expression, including: 1. a function 2. a date 3. undefined In JSON, string values must be written with double quotes: JSON {"name":"John"} In JavaScript, you can write string values with double or single quotes: JavaScript {name:'John'}
- 12. JSON OBJECT LITERALS This is a JSON string: '{"name":"John", "age":30, "car":null}' Inside the JSON string there is a JSON object literal: {"name":"John", "age":30, "car":null} JSON object literals are surrounded by curly braces {}. JSON object literals contains key/value pairs. Keys and values are separated by a colon. Keys must be strings, and values must be a valid JSON data type: 1. string 2. number 3. object 4. array 5. boolean 6. null Each key/value pair is separated by a comma.
- 13. JSON ARRAY LITERALS This is a JSON string: '["Ford", "BMW", "Fiat"]' Inside the JSON string there is a JSON array literal: ["Ford", "BMW", "Fiat"] Arrays in JSON are almost the same as arrays in JavaScript. In JSON, array values must be of type string, number, object, array, boolean or null. In JavaScript, array values can be all of the above, plus any other valid JavaScript expression, including functions, dates, and undefined.











![JSON ARRAY LITERALS
This is a JSON string:
'["Ford", "BMW", "Fiat"]'
Inside the JSON string there is a JSON array literal:
["Ford", "BMW", "Fiat"]
Arrays in JSON are almost the same as arrays in JavaScript.
In JSON, array values must be of type string, number, object, array, boolean or null.
In JavaScript, array values can be all of the above, plus any other valid JavaScript expression,
including functions, dates, and undefined.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitvjson-240223042148-c59d955d/85/All-about-XML-JSON-and-related-topics-13-320.jpg)