Android development tutorial
- 1. Android Development Tutorial Yi Huang
- 2. Contents 2 What’s Android Android architecture Android software development ‘Hello World’ on Android More…
- 4. Android Phones 4 Motorola Cliq HTC G1 HTC Hero Samsung i7500 Samsung Moment Motorola Droid HTC Magic HTC Tattoo Sony X10
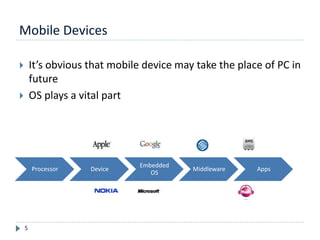
- 5. Mobile Devices 5 It’s obvious that mobile device may take the place of PC in future OS plays a vital part Processor Device Embedded OS Middleware Apps
- 6. 6
- 7. OHA and Android 7 OHA(Open Handset Alliance) is a group of 71 technology and mobile companies, including Google, Intel, Dell, HTC and China Mobile… OHA’s aim: accelerate innovation in mobile phones offer consumers a richer, less expensive, and better mobile experience OHA developed Android™, the first complete, open, and free mobile platform OHA was initially called up by Google, and Google is the ‘captain’
- 8. What’s Android 8 Generally, Android is a software stack for mobile devices that includes an operating system, middleware and key applications Android is based on JAVA and all its applications are developed in JAVA The JAVA VM, known as Dalvik, is highly customized and optimized for mobile devices Android SDK offers rich tools for android application development and many useful APIs。 The core of Android
- 9. Android Features #1 9 Application framework enabling reuse and replacement of components Optimized Java virtual machine: Dalvik Optimized Graphics Processing, supporting 2D and 3D graphics(OpenGL ES 1.0 ) Integrated open source web browser: WebKit SQLite for structured data storage
- 10. Android Features #2 10 Multimedia capability, supporting varieties of audio, video and still image formats GSM Telephony Bluetooth, EDGE, 3G and Wi-Fi support Camera, GPS, compass, accelerometer and other sensors support Rich development environment, including an emulator, debugging tools, memory probe tools, log tools and powerful eclipse plugins Hardware dependent
- 12. 12
- 13. Linux Kernel 13 Note that Android based on a Linux kernel not a Linux OS Supplies Security, Memory management, Process management, Network stack and Driver model Acts as an abstraction layer between the hardware and the rest of the software stack
- 14. Libraries 14 Run in system background Using C/C++ Language 4 types of Libraries Bionic Libc, system C libraries Function Libraries, supporting multimedia, web browser, SQLite... Native Servers Hardware Abstraction Libraries
- 15. Core Libraries 15 System C library, the standard C system library, tuned for embedded Linux-based devices Media Libraries, support playback and recording of many popular audio and video formats, as well as image files, including MPEG4, H.264, MP3, AAC, AMR, JPG, and PNG Surface Manager, manages access to the display subsystem and seamlessly composites 2D and 3D graphic layers from multiple applications WebKit, a modern web browser engine which powers both the Android browser and an embeddable web view SGL, the underlying 2D graphics engine 3D libraries, an implementation based on OpenGL ES 1.0 APIs FreeType , bitmap and vector font rendering SQLite , a powerful and lightweight relational database engine
- 16. Andoid Runtime 16 The core of Android platform Dalvik Virtual Machine Register-based Executes files in the Dalvik Executable (.dex) format Java core Libraries Provides most of the functionality of the Java programming language.
- 17. Android Runtime (cont.) 17 The functions of Java core libraries rely on the Dalvik VM and the underlying Linux kernel Multiple Dalvik VMs may run at the same time Every Android application runs in its own process, with its own instance of the Dalvik virtual machine The "dx" tool in Android SDK can transform compiled JAVA class into the .dex format
- 18. Dalvik Virtual Machine 18 Android custom implementation virtual machine Provides application portability and runtime consistency Runs optimized file format (.dex) and Dalvik bytecode Java .class / .jar files converted to .dex at build time Designed for embedded environment Supports multiple virtual machine processes per device Highly CPU-optimized bytecode interpreter Efficiently Using runtime memory Core Libraries Core APIs for Java language provide a powerful, yet simple and familiar development platform
- 19. DVM vs. JVM 19 DVM Google Dalvik executable Only supports a subset of standard Java Library JVM Sun Java bytecode Some worries that Java world may be divided into different communities, each has its own Java standard
- 20. Application Framework 20 Simplify the reuse of components Applications can publish their capabilities and any other application may then make use of those capabilities Applications is a set of services and systems, include Views system, content providers, resources manager and so on
- 21. Application Framework (cont.) 21 Activity Manager, manages the lifecycle of applications and provides a common navigation backstack Notification Manager, enables all applications to display custom alerts in the status bar Resource Manager, providing access to non-code resources such as localized strings, graphics, and layout files Content Providers, access data from other applications (such as Contacts), or to share their own data Views, used to build an application, including lists, grids, text boxes, buttons, and even an embeddable web browser
- 22. Applications 22 A set of core applications shipped with Android platform an email client, SMS program, calendar, maps, browser, contacts, and others All written in Java Our applications are in the same level as these applications
- 24. Development Environment IDE – Eclipse Eclipse plug-in - ADT Software Development Kit (SDK) Android Emulator Debugger
- 25. Setup Android SDK 25 Download Android SDK and extract the zip file to an arbitrary folder http://androidappdocs.appspot.com/sdk/index.html E.g.: extract to C: The SDK will be used by ADT in eclipse
- 26. Setup ADT plugin 26 Install Eclipse ADT plugin Eclipse must be J2EE edition, 3.5 recommended Update site: https://dl- ssl.google.com/android/eclip se/ Install all the plugins in the repository Restart needed after installation
- 27. Configure ADT Plugin 27 Open eclipse Window->Preferences, select Android Setup the SDK location as the folder where you extracted the downloaded SDK zip file
- 28. Setup SDK APIs 28 Open Window->Android SDK and AVD Manager Click Available Packages and then choose proper APIs to install, the latest may be the best
- 29. Setup Emulators 29 After SDK APIs installation, click Virtual Devices Click new, there will be a dialog input a name choose a running target and a skin specify the SD card size
- 30. Ready… 30 Now you may start the AVD Click start to start the new AVD First start-up may take a very long time
- 31. ‘Hello World’ on Android 31
- 32. Create a new Android Project 32 Open File->New- >Android project Project name Build Target Application name Package name Create Activity
- 33. Hello World Project 33 src: source folder gen: SDK generated file android 2.2: reference lib assets: binary resources res: resource files and resource description files AndroidManifest.xml: application description file default.properties: project properties file
- 34. Say Hello World 34 modify HelloWorld.java
- 35. Run Hello World 35 Select HelloWorld Project, Run->Run as->Android Application ADT will start a proper AVD and run HelloWorld app on it
- 36. Behind HelloWorld #1 36 R.java, generated by Android SDK, represents all the resources of the app. resources are all in res folder resources are pre-compiled into binary format /* AUTO-GENERATED FILE. DO NOT MODIFY. * * This class was automatically generated by the * aapt tool from the resource data it found. It * should not be modified by hand. */ package sample.hello; public final class R { public static final class attr { } public static final class drawable { public static final int icon=0x7f020000; } public static final class layout { public static final int main=0x7f030000; } public static final class string { public static final int app_name=0x7f040001; public static final int hello=0x7f040000; } }
- 37. Linear Layout Behind HelloWorld #2 37 res/layout , contains layout declarations of the app, in XML format, UIs are built according to the layout file main.xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android=http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"> <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/hello" /> </LinearLayout> TextView, display static text A reference to String resource ‘hello’
- 38. referenced in res/layout/mai n.xml Behind HelloWorld #3 38 res/values, contains string declarations or other values(e.g.:colors) of the app string.xml, contains string resources <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <string name="hello">Hello World, HelloWorld!</string> <string name="app_name">HelloWorld</string> </resources> referenced in AndroidManifest.xml
- 39. Behind HelloWorld #4 39 res/drawable, contains all image resources folders may have suffixes, app will choose the most suitable one, so do the other resources three folders: drawable-ldpi, drawable-hdpi, drawable-mdpi, each contains an icon.png file app will choose the proper icon according to the device DPI reference name:@drawable/icon other folders we may use in future menu, anim (animation), xml ( preference and searchable)
- 40. Behind HelloWorld #5 40 AndroidManifest.xml describe the application declare app’s name, version, icon, permission, etc… declare the application's components: activity, service ,receiver or provider <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="sample.hello" android:versionCode="1" android:versionName="1.0"> <application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name"> <activity android:name=".HelloWorld" android:label="@string/app_name"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER”/> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> <uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="8" /> </manifest>
- 41. Core Components-Activity #1 41 Basically, An activity presents a visual user interface for one focused endeavor the user can undertake An application might consist of just one activity or several, each Activity is derived from android.app.Activity and should be declared in AndroidManifest.xml file Each activity is given a default window to draw in, the window may be full screen or smaller and on top of other window The visual content of the window is provided by a hierarchy of views — objects derived from the base View class Activity.setContentView() method is used to set a certain hierarchy of view objects
- 42. Core Components-Activity #2 42 Activities are activated by asynchronous messages called intents An intent is an Intent object that holds the content of the message The action being requested or the URI of the data to act on The <intent-filter> label in AndroidManifest.xml file specifies the Intent that can start the Activity declares the main activity, it will be started automatically when the app starts An activity is launched (or given something new to do) by passing an Intent object to Context.startActivity() or Activity.startActivityForResult()
- 44. Other Core Components 44 Service A service doesn't have a visual user interface, runs in the background for a period of time Broadcast receivers a component that does nothing but receive and react to broadcast announcements Content providers A content provider makes a specific set of the application's data available to other applications. The data can be stored in the file system, in an SQLite database, or in any other manner that makes sense
- 45. Beyond HelloWorld #1 45 Build up an app that you can input your greetings and display your greetings Input: EditText Display: TextView Of course, we have to add an button Edit res/layout/main.xml file to add these components each has an android:id property, used to reference it in code
- 46. Beyond HelloWorld #2 46 modify HelloWorld.java firstly get the references declared in main.xml then add event response for Button
- 47. Beyond HelloWorld #3 47 Finished! Run->Run as->Android Application Quite easy, isn’t it?
- 48. More… 48
- 49. Useful Materials 49 Android Official Site • http://www.android.com Android SDK, Tutorial, Concepts and API docs • http://androidappdocs.appspot.com/index.html Android Development Community • http://www.anddev.org/ 30 Days Android Apps Development • http://bakhtiyor.com/category/30-days-of-android-apps/
- 50. Thank U so much! 50