Android overview
- 1. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY ANDROID AN OPEN HANDSET ALLIANCE Submitted By: Shubhangi Arora 10ECTCS111 Submitted To: Mrs.Sunita Choudhary (H.O.D. ) 1
- 2. INDEX What is Android? Features of Android Android versions Technology used Setup Emulator AVD Activity Creating a project Project components Xml R class ListView Intent SharedPrefrences Gallery SQLite Database 2
- 3. WHAT IS ANDROID……..? Android is an open source operating system Mobile apps Linux based (2.6 kernel) Create by Google and Open Handset Alliance. 3
- 4. FEATURES OF ANDROID Messaging Web browser Multi-touch Multitasking Video calling Multiple language support Connectivity Bluetooth Media support External storage Java support 4
- 5. ANDROID VERSIONS Android 1.5 Cupcake(API Level 3) Android 1.6 Donut(API Level 4) Android 2.0 Eclair(API Level 5) Android 2.0.1 Eclair(API Level 6) Android 2.1 Eclair(API Level 7) Android 2.2 Froyo(API Level 8) Android 2.3 Gingerbread(API Level 9) Android 2.3.3 Gingerbread(API Level 10) Android 3.0 Honeycomb(API Level 11) Android 3.1 Honeycomb (API Level 12) Android 3.2 Honeycomb (API Level 13) Android 4.0 Ice Cream Sandwich(API Level 14) Android 4.0.3 Ice Cream Sandwich (API Level 15) Android 4.1 Jelly Bean(API Level 16) Android 4.2 Jelly Bean (API Level 17) Android 4.3 Jelly Bean (API Level 18) Android 4.4 Kit Kat(API Level 19) 5
- 6. TECHNOLOGY & TOOLS USED DataBase used: SQLite Programming Languages: XML && java IDE :Eclipse,ADT 6
- 7. SETUP Download the Android SDK. Install the ADT plugin for Eclipse (if you’ll use the Eclipse IDE). Download the latest SDK tools and platforms using the SDK Manager. 7
- 8. EMULATOR A virtual mobile device. Develop and test Android applications without using a physical device. 8
- 10. AVD Creation of AVD Default AVD 10
- 11. Activity An Activity is an application component that provides a screen with which users can interact in order to do something, such as dial the phone, take a photo, send an email. Each activity is gives a window in which to draw its user interface. An Application usually consists of multiple activities that are loosely bounded to each other. 11
- 12. 12
- 14. PROJECT COMPONENTS src – your source code gen – auto-generated code (usually just R.java) Included libraries Resources Drawables (like .png images) Layouts Values (like strings) Manifest file 14
- 15. XML Used to define some of the resources Layouts (UI) Strings Manifest file Shouldn’t usually have to edit it directly, Eclipse can do that for you Preferred way of creating UIs Separates the description of the layout from any actual code that controls it Can easily take a UI from one platform to another 15
- 16. R CLASS Auto-generated: you shouldn’t edit it Contains IDs of the project resources Enforces good software engineering Use findViewById and Resources object to get access to the resources Ex. Button b = (Button)findViewById(R.id.button1) Ex. getResources().getString(R.string.hello)); 16
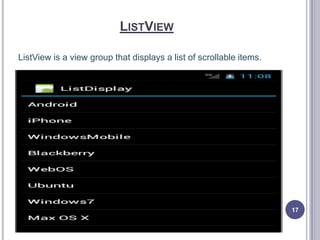
- 17. LISTVIEW ListView is a view group that displays a list of scrollable items. 17
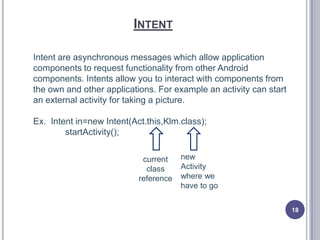
- 18. INTENT Intent are asynchronous messages which allow application components to request functionality from other Android components. Intents allow you to interact with components from the own and other applications. For example an activity can start an external activity for taking a picture. Ex. Intent in=new Intent(Act.this,Klm.class); startActivity(); current class reference new Activity where we have to go 18
- 19. 19
- 20. SHAREDPREFERENCES For any particular set of preferences, there is a single instance of this class that all clients share. Modifications to the preferences must go through an SharedPreferences.Editor object to ensure the preference values remain in a consistent state and control when they are committed to storage. 20
- 21. ABOUT SQLITE SQLite is an embedded SQL database engine. SQLite does not have a separate server process. SQLite reads and writes directly to ordinary disk files. 21
- 22. SQLITE DATABASE SQLiteDatabase has methods to create, delete, execute SQL commands, and perform other common database management tasks. Database names must be unique within an application, not across all applications. 22
- 23. 23