Android Workshop Part 1
- 1. Android Development Workshop Part - 1 Ritesh Ambastha Rajnikant Joshi 12th March
- 2. What is Android? • Android is a mobile phone operating system developed by Google. • Android is unique because Google is actively developing the platform by giving it away for free to hardware manufacturers and phone carriers who want to use Android on their devices.
- 3. Open Handset Alliance (OHA) • Google formed a group of hardware, software, and telecommunication companies called the Open Handset Alliance with the goal of contributing to Android development. • Most members also have the goal of making money from Android, either by selling phones, phone service, or mobile applications.
- 4. SDK and Android Market Place • Anyone can download the SDK (software development kit) and write applications for Android phones. Google doesn't take part of the profits. • These apps can be downloaded from the Android Market Place. If the app costs money, you pay for it using Google Checkout.
- 5. Google Services • Because Google developed Android, it comes with a lot of Google services installed right out of the box. • Gmail, Google Calendar, and Google Web search are all pre- installed, and Google is also the default Web page for the Web browser.
- 6. Introduction to Android Platform • Android is an open software platform for mobile development. It’s intended to be a complete stack that includes everything from the Operating System through middleware up through applications.
- 7. Android Architecture • If I'm going to talk about architecture, we need to start with a diagram covered with a lot of little boxes.
- 8. Linux Kernel • The architecture is based on the Linux 2.6 kernel. Android use Linux kernel as its hardware abstraction layer. • The reason they're using Linux is because it provides a proven driver model in a lot of cases existing drivers. • It also provides memory management, process management, a security model, and networking, a lot of core operating system infrastructures that are robust and have been proven over time.
- 9. Native Libraries • The next level up is the native libraries. Everything that you see here in green is written in C and C++. • It's at this level where a lot of the core power of the Android platform comes from.
- 10. Native Libraries: Surface Manager • The surface manager is responsible for composing different drawing surfaces onto the screen. • So it's the surface manager that's responsible for taking different windows that are owned by different applications that are running in different processes and all drawing at different times and making sure the pixels end up on the screen when they're supposed to.
- 11. Native Libraries: OpenGL|ES and SGL • OpenGL/ES is a 3D library. • They have a software implementation that is hardware acceleratable if the device has a 3D chip on it. • The SGL graphics are for 2D graphics and that is what most of the application drawing is based on. • One interesting thing about the Android graphics platform is that you can combine 3D and 2D graphics in the same application.
- 12. Native Libraries: Media Framework • The Media Framework was provided by PacketVideo, one of the members of the open handset alliance and that contains the entire codex that make up the core of the media experiences. • So, in there you'll find IMPEG 4, H.264, MP3, AAC, all the audio and video codex you need to build a rich media experience.
- 13. Native Libraries: FreeType & SQLite • FreeType • They use FreeType to render our fonts. FreeType is a free, high-quality and portable font engine. • SQLite • They have an implementation of SQLite, it uses that as the core of most of its data storage.
- 14. Native Libraries: WebKit • They have WebKit which is the open source browser engine, that's what they're using as a core of Android’s browser. • It's the same browser that's powering Safari from Apple and they’ve worked with that engine to make it render well on small screens and on mobile devices.
- 15. Android Run Time • The Android Runtime was designed specifically for Android to meet the needs of running in an embedded environment where you have limited battery, limited memory, limited CPU. • The DVM runs something called dex files, D-E-X. and these are bytecodes that are the results of converting at build time .Class and .JAR Files. • So, these files when they are converted to .dex, become a much more efficient bytecode that can run very well on small processors. They use memory very efficiently.
- 16. Android Run Time • The next level up from that is the Core Libraries. • This is in blue, meaning that it's written in the Java programming language. • And the core library contains all of the collection classes, utilities, IO, all the utilities and tools that you’ve come to expected to use.
- 17. Application Framework • This is all written in a Java programming language and the application framework is the toolkit that all applications use. • These applications include the ones that come with a phone like the home applications, or the phone application. • It includes applications written by Google, and it includes apps that will be written by you. • So, all apps use the same framework and the same APIs.
- 18. Application Framework • Activity Manager • The Activity manager is what manages the life cycle of the applications. It also maintains a common backstack so that application that is running in different processes can have a smoothly integrated navigation experience. • Package Manager • The package manager is what keeps track of which applications are installed on your device. So, if you download new applications over the air or otherwise install apps, it's the package manager that's responsible for keeping track of what you have and what the capabilities of each of your applications are.
- 19. Application Framework • Window Manager • The window manager manages Windows. It's mostly a java programming language abstraction on top of lower level services that are provided by the surface manager. • Telephony Manager • The telephony manager contains the APIs that we use to build the phone application that's central to the phone experience.
- 20. Application Framework • Content Providers • Content providers are a unique piece of the Android platform. That's the framework that allows applications to share their data with other applications. • The View system • View System contains things like buttons and lists, all the building blocks of the UI. It also handles things like event dispatching, layout drawing, .
- 21. Application Framework • The resource manager is what they use to store local iStrings, bitmaps, layout file descriptions, all of the external parts of an application that aren't code. • Location manager, notification manager and XMPP service are some APIs that I think will allow developers to create really innovative and exciting applications.
- 22. Applications • And the final layer on top is Applications. • This is where all the applications get written. • It includes the home application, the contacts application, the browser, and your apps. • And everything at this layer is, again, using the same app framework provided by the layers below.
- 24. Application Building Blocks • Now, if you're going to write an app, the first step is to decompose it into the components that are supported by the Android platform. • UI component typically corresponding to one Activity screen. • Responds to notification or status changes. Can Intent Receiver wake up your process. Service • Faceless task that runs in the background. Content Provider • Enable applications to share data
- 25. Application Building Blocks Activity • An activity is essentially just a piece of UI typically corresponding to one screen. • So if you think of something like the mail application, that would be decomposed into maybe three major activities, something that lists your mail, something that shows you what an individual message and a compose screen to put together an outgoing email.
- 26. Application Building Blocks Intent Receiver • An intent receiver is a way for which your application to register some code that won't be running until it's triggered by some external event. • And the set of external events that triggers your code is open and extensible.
- 27. Application Building Blocks Service • A service is a task that doesn't have any UI, that's long lived, that's running in the background. • A good example is a music player. You may start playing music from an activity, from a piece of UI, but once the music is playing, you'd want it to keep playing even if you're navigating to other parts of the user experience.
- 28. Application Building Blocks Content Provider • It is a component that allows you to share some of your data with other processes and other applications. • Now, any application can store data in whatever may-way it makes sense for that application. • They can store it in the files. • They can store it in Android’s super light database, whatever makes sense.
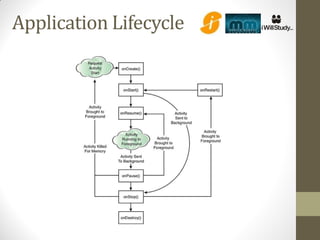
- 29. Application Lifecycle • Applications run in their own processes • Processes are started and stopped as needed to run an application's components • Processes may be killed to reclaim resources • In android, every application runs in its own process. There's a lot of benefits to this. It gives you security, protected memory. It means that an application is doing something CPU intensive, won't block other critical activities, like, answering a phone. • So all applications are running in their own processes and the Android System itself is responsible for starting these proecesses and shutting them down as necessary to reclaim resources.
- 31. Installations & Configuration Next PPT…