Approximate Bayesian computation for the Ising/Potts model
- 1. Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion an introduction to Approximate Bayesian Computation Matt Moores Research Fellow Department of Statistics University of Warwick Warwick ML Club June 12, 2017
- 2. Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion Motivation Inference for a parameter θ when it is: impossible or very expensive to evaluate the likelihood p(y|θ) ABC is a likelihood-free method for approximating the posterior distribution π(θ|y) by generating pseudo-data from the model: w ∼ f(·|θ)
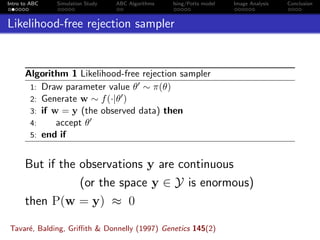
- 3. Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion Likelihood-free rejection sampler Algorithm 1 Likelihood-free rejection sampler 1: Draw parameter value θ ∼ π(θ) 2: Generate w ∼ f(·|θ ) 3: if w = y (the observed data) then 4: accept θ 5: end if But if the observations y are continuous (or the space y ∈ Y is enormous) then P(w = y) ≈ 0 Tavar´e, Balding, Griffith & Donnelly (1997) Genetics 145(2)
- 4. Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion ABC tolerance accept θ if δ(w, y) < where > 0 is the tolerance level δ(·, ·) is a distance function (for an appropriate choice of norm) Inference is more exact when is close to zero. but more proposed θ are rejected (tradeoff between accuracy & computational cost) Pritchard, Seielstad, Perez-Lezaun & Feldman (1999) Mol. Biol. Evol. 16(12)
- 5. Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion Summary statistics Computing δ(w, y) for w1, . . . , wn and y1, . . . , yn can be very expensive for large n Instead, compute summary statistics s(y) e.g. sufficient statistics (only available for exponential family)
- 6. Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion Sufficient statistics Fisher-Neyman factorisation theorem: if s(y) is sufficient for θ then p(y|θ) = f(y) g (s(y)|θ) only applies to Potts, Ising, exponential random graph models (ERGM) otherwise, selection of suitable summary statistics can be a very difficult problem
- 7. Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion ABC rejection sampler Algorithm 2 ABC rejection sampler 1: for all iterations t ∈ 1 . . . T do 2: Draw independent proposal θ ∼ π(θ) 3: Generate w ∼ f(·|θ ) 4: if s(w) − s(y) < then 5: set θt ← θ 6: else 7: set θt ← θt−1 8: end if 9: end for Approximates π(θ|y) by π (θ | s(w) − s(y) < ) Marin, Pudlo, Robert & Ryder (2012) Stat. Comput. 22(6) Marin & Robert (2014) Bayesian Essentials with R §8.3
- 8. Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion A trivial example Gaussian with unknown variance: y ∼ N(1, σ2 ) normalising constant: Z(σ2 ) = (2πσ2 )−n 2 natural conjugate prior: π 1 σ2 ∼ Ga ν0 2 , ν0ψ2 0 2 sufficient statistic: s(y) = 1 n n i=1 (yi − 1)2 posterior is analytically tractable: π 1 σ2 | y ∼ Ga ν0+n 2 , ν0ψ2 0+ns(y) 2 ∴ no need for ABC (nor MCMC) in practice
- 9. Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion R code π(τ|y) Density 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0.00.10.20.30.4 § y ← rnorm (n=5, mean=1, sd=2/3) n ← length ( y ) s sq ← sum(( y −1)ˆ2)/n post nu ← nu0 + n post ssd ← ( nu0 ∗ s0 ˆ2 + n∗ s sq )/2
- 10. Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion now with ABC π(τ) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0.00.51.01.5 πε(τ | δ(s(w), s(y)) < ε) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0.00.10.20.30.4 § prop tau ← rgamma(10000 , nu0/2 , 0.5 ∗nu0∗ s0 ˆ2) pseudo ← rnorm (n∗ 10000 , 1 , 1/ sqrt ( prop tau )) pseudoMx ← matrix ( pseudo , nrow=10000, ncol=n) pseudoSSD ← rowSums (( pseudoMx − 1)ˆ2)/n ps norm ← abs ( pseudoSSD − s sq ) e p s i l o n ← sort ( ps norm ) [ 2 0 0 0 ] prop keep ← prop tau [ ps norm <= e p s i l o n ]
- 11. Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion choice of 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0.00.20.40.6 (a) = 8.430 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0.00.10.20.30.4 (b) = 1.427 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0.00.20.40.6 (c) = 0.011 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0.00.40.8 (d) = 0.001
- 12. Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion concentration of measure 0 1 2 3 4 0.00.40.8 (a) n = 25, = 0.149 0 1 2 3 4 0.01.02.03.0 (b) n = 500, = 0.025 0 1 2 3 4 02468 (c) n = 104 , = 0.011 0 1 2 3 4 020406080100 (d) n = 106 , = 0.001
- 13. Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion Metropolis-Hastings proposals Algorithm 3 ABC-MCMC 1: Initialise θ0 ∼ π(θ) 2: for all iterations t ∈ 1 . . . T do 3: Draw proposal θ ∼ q(· | θt−1) 4: Generate w ∼ f(·|θ ) 5: Draw u ∼ Unif(0, 1) 6: if u < π(θ )q(θt−1|θ ) π(θt−1)q(θ |θt−1) and s(w) − s(y) < then 7: set θt ← θ 8: else 9: set θt ← θt−1 10: end if 11: end for Unfortunately, this algorithm is prone to getting ”stuck” Marjoram, Molitor, Plagnol & Tavar´e (2003) PNAS 100(26) Lee & Latuszy´nski (2014) Biometrika 101(3)
- 14. Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion Sequential Monte Carlo Algorithm 4 ABC-SMC 1: Draw N particles θi ∼ π0(θ) 2: Draw N × M sets of pseudo-data wi,m ∼ f(·|θi) 3: repeat 4: Adaptively select ABC tolerance t 5: Update importance weights λi for each particle 6: if effective sample size (ESS) < Nmin then 7: Resample particles according to their weights 8: end if 9: Update particles using Metropolis-Hastings step (with adaptive proposal bandwidth σ2 t ) 10: until naccept N < 0.015 or t < 10−9 or t ≥ 100 Targets a sequence of distributions π t (θ | s(w) − s(y) < t) such that 1 > 2 > · · · > T Drovandi & Pettitt (2011) Biometrics 67(1) Del Moral, Doucet & Jasra (2012) Stat. Comput. 22(5)
- 15. Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion hidden Markov random field Joint distribution of observed pixel intensities y = (y1, . . . , yn) ∈ Rn and latent labels z = (z1, . . . , zn) ∈ {1, . . . , k}n: Pr(y, z | µ, σ2 , β) = L(y|µ, σ2 , z)π(z|β) (1) Additive Gaussian noise: yi | zi =j iid ∼ N µj, σ2 j (2) Potts model: π(zi | zi, β) = exp {β i∼ δ(zi, z )} k j=1 exp {β i∼ δ(j, z )} (3) Potts (1952) Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society 48(1) Winkler (2003) Image Analysis, Random Fields and MCMC Methods, 2nd ed.
- 16. Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion Inverse Temperature (e) β = 0.1 (f) β = 0.5 (g) β = 0.85 (h) β = 0.95 (i) β = 1.005 (j) β = 1.15
- 17. Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion Doubly-intractable posterior p(β|z) = C−1(β)eβS(z)π(β) β C−1(β)eβS(z)π(dβ) (4) The normalising constant has computational complexity O(nkn), since it involves a sum over all possible combinations of the labels z ∈ Z: C(β) = z∈Z eβS(z) (5) S(z) is the sufficient statistic of the Potts model: S(z) = i∼ ∈E δ(zi, z ) (6) where E is the set of all unique neighbour pairs.
- 18. Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion bayesImageS An R package for Bayesian image segmentation using the hidden Potts model: RcppArmadillo for fast computation in C++ OpenMP for parallelism § l i b r a r y ( bayesImageS ) p r i o r s ← l i s t ("k"=3,"mu"=rep (0 ,3) , "mu.sd"=sigma , "sigma"=sigma , "sigma.nu"=c (1 ,1 ,1) , "beta"=c (0 ,3)) mh ← l i s t ( algorithm="pseudo" , bandwidth =0.2) r e s u l t ← mcmcPotts ( y , neigh , block ,NULL, 55000 ,5000 , p r i o r s ,mh) Eddelbuettel & Sanderson (2014) RcppArmadillo: Accelerating R with high-performance C++ linear algebra. CSDA 71
- 19. Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion Bayesian computational methods bayesImageS supports methods for updating the latent labels z: Chequerboard updating (Winkler 2003) Swendsen-Wang (1987) and also methods for updating the inverse temperature β: Pseudolikelihood (Ryd´en & Titterington 1998) Path Sampling (Gelman & Meng 1998) Exchange Algorithm (Murray, Ghahramani & MacKay 2006) Approximate Bayesian Computation (Grelaud et al. 2009) Sequential Monte Carlo (SMC-ABC) (Del Moral, Doucet & Jasra 2012)
- 20. Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion Lake Menteith, Scotland 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 0.00.20.40.60.81.0
- 21. Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion ABC-SMC for the hidden Potts model § l i b r a r y ( bayess ) data ( Menteith ) y ← as . matrix ( Menteith ) l i b r a r y ( bayesImageS ) mask ← matrix (1 , nrow=nrow( y ) , ncol=ncol ( y )) neigh ← getNeighbors (mask , c (2 ,2 ,0 ,0)) block ← getBlocks (mask , 2) p r i o r s ← l i s t ( k=6, mu=rep (256/2 , 6) , mu. sd=rep (256/ 6 ,6) , sigma=rep (256/ 6 ,6) , sigma . nu=rep (6 , 6) , beta ← c (0 ,2)) r e s ← smcPotts ( as . vector ( y ) , neigh , block , param=l i s t ( npart =2000, nstat =5) , p r i o r s=p r i o r s ) 6h 15min for 100 SMC iterations (N=2000, M=5)
- 22. Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion ABC tolerance SMC iteration εt 0 20 40 60 80 100 02000400060008000100001200014000
- 23. Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion approximate posterior ( t = 37.5) β Density 1.280 1.285 1.290 1.295 1.300 1.305 1.310 1.315 0204060 Equivalent to 120,801 iterations of the ABC rejection sampler
- 24. Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion Effective Sample Size SMC iteration ESS 0 20 40 60 80 100 800100012001400160018002000
- 25. Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion image segmentation (a) Original image (b) Potts labels
- 26. Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion Summary ABC is a method for likelihood-free inference It enables inference for models that are otherwise computationally intractable Main components of ABC: π(θ) proposal density for θ f(·|θ) generative model for w tolerance level δ(·, ·) distance function s(y) summary statistics
- 27. Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion References I M. Moores, A. N. Pettitt & K. Mengersen Scalable Bayesian inference for the inverse temperature of a hidden Potts model. arXiv:1503.08066 [stat.CO], 2015. M. Moores, C. C. Drovandi, K. Mengersen & C. P. Robert Pre-processing for approximate Bayesian computation in image analysis. Statistics & Computing 25(1): 23–33, 2015. J.-M. Marin, P. Pudlo, C. P. Robert & R. Ryder Approximate Bayesian computational methods. Statistics & Computing, 22(6): 1167–80, 2012. A. Grelaud, C. P. Robert, J.-M. Marin, F. Rodolphe & J.-F. Taly ABC likelihood-free methods for model choice in Gibbs random fields. Bayesian Analysis, 4(2): 317–36, 2009. J.-M. Marin & C. P. Robert Bayesian Essentials with R Springer-Verlag, 2014.
- 28. Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion References II A. Lee & K. Latuszy´nski Variance bounding and geometric ergodicity of Markov chain Monte Carlo kernels for approximate Bayesian computation Biometrika 101(3): 655–671, 2014. P. Del Moral, A. Doucet & A. Jasra An adaptive sequential Monte Carlo method for approximate Bayesian computation. Statistics & Computing, 22(5): 1009–20, 2012. C. C. Drovandi & A. N. Pettitt Estimation of Parameters for Macroparasite Population Evolution Using Approximate Bayesian Computation Biometrics 67(1): 225–233, 2011. P. Marjoram, J. Molitor, V. Plagnol & S. Tavar´e Markov chain Monte Carlo without likelihoods. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 100(26): 15324–15328, 2003.
- 29. Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion References III J. Pritchard, M. Seielstad, A. Perez-Lezaun & M. Feldman Population Growth of Human Y Chromosomes: A Study of Y Chromosome Microsatellites. Mol. Biol. Evol. 16(12): 1791–98, 1999. S. Tavar´e, D. Balding, R, Griffiths & P. Donnelly Inferring coalescence times from DNA sequence data. Genetics, 145(2): 505–18, 1997. R. B. Potts Some generalized order-disorder transformations. Proc. Cambridge Philosophical Society, 48(1): 106–109, 1952. G. Winkler Image analysis, random fields and Markov chain Monte Carlo methods 2nd ed., Springer-Verlag, 2003. D. Eddelbuettel Seamless R and C++ integration with Rcpp Springer-Verlag, 2013.









![Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion
now with ABC
π(τ)
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
0.00.51.01.5
πε(τ | δ(s(w), s(y)) < ε)
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
0.00.10.20.30.4
§
prop tau ← rgamma(10000 , nu0/2 , 0.5 ∗nu0∗ s0 ˆ2)
pseudo ← rnorm (n∗ 10000 , 1 , 1/ sqrt ( prop tau ))
pseudoMx ← matrix ( pseudo , nrow=10000, ncol=n)
pseudoSSD ← rowSums (( pseudoMx − 1)ˆ2)/n
ps norm ← abs ( pseudoSSD − s sq )
e p s i l o n ← sort ( ps norm ) [ 2 0 0 0 ]
prop keep ← prop tau [ ps norm <= e p s i l o n ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/warwickmlabc-170612065718/85/Approximate-Bayesian-computation-for-the-Ising-Potts-model-10-320.jpg)
















![Intro to ABC Simulation Study ABC Algorithms Ising/Potts model Image Analysis Conclusion
References I
M. Moores, A. N. Pettitt & K. Mengersen
Scalable Bayesian inference for the inverse temperature of a hidden Potts
model.
arXiv:1503.08066 [stat.CO], 2015.
M. Moores, C. C. Drovandi, K. Mengersen & C. P. Robert
Pre-processing for approximate Bayesian computation in image analysis.
Statistics & Computing 25(1): 23–33, 2015.
J.-M. Marin, P. Pudlo, C. P. Robert & R. Ryder
Approximate Bayesian computational methods.
Statistics & Computing, 22(6): 1167–80, 2012.
A. Grelaud, C. P. Robert, J.-M. Marin, F. Rodolphe & J.-F. Taly
ABC likelihood-free methods for model choice in Gibbs random fields.
Bayesian Analysis, 4(2): 317–36, 2009.
J.-M. Marin & C. P. Robert
Bayesian Essentials with R
Springer-Verlag, 2014.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/warwickmlabc-170612065718/85/Approximate-Bayesian-computation-for-the-Ising-Potts-model-27-320.jpg)

