Aray in Programming
- 2. So far this semester all input has been from keyboard all output has been to computer screen these are just two examples of where to retrieve/send data
- 3. ifstream – Input File Stream reads input from the location of your choice ifstream is a type declare variables of type ifstream use variable for file input
- 4. Steps to read from a file: 1. declare a variable infile of type ifstream 2. call infile.open, and send the filename as its parameter 3. check to see if the open command worked with infile.fail 4. use infile to read in data 5. call infile.close to close the stream ifstream infile; infile.open("prices.dat"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } // read data from infile infile.close();
- 5. ifstream variable declared like any other variable ifstream infile; can use any legal variable name that you like I will use infile for all of my examples ifstream kev; // legal, but not a good choice kev.open("kev.txt"); requires #include<fstream>
- 6. .open takes a null-terminated character array as input string literal: infile.open("prices.dat"); character array variable char filename[] = "prices.dat"; infile.open(filename); will a string variable work? string filename = "prices.dat"; infile.open(filename);
- 7. c_str a string variable does not hold a null-terminated character array string data type provides a member function called c_str() returns a null-terminated character array representing the string to use, just affix .c_str() to the variable name string filename = "prices.dat"; infile.open(filename.c_str());
- 8. .fail returns true if the file has been opened, false otherwise if (infile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } exit terminates the program, and returns its argument value to the operating system must #include<cstdlib> to use exit
- 9. .close closes the current file stream good programming practice to close files when you're done with them O/S only allows finite number of open files infile.close();
- 10. Example 1: Open a file called "prices.dat". If the file opens, print the message "File successfully opened!". If not, print "File failed to open".
- 11. #include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <cstdlib> using namespace std; int main() { ifstream infile; infile.open("prices.dat"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } cout << "File successfully opened!" << endl; infile.close(); return 0; } Example 1: Open a file called "prices.dat". If the file opens, print the message "File successfully opened!". If not, print "File failed to open".
- 12. #include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <cstdlib> using namespace std; int main() { ifstream infile; infile.open("prices.dat"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } cout << "File successfully opened!" << endl; infile.close(); return 0; } Example 1: Open a file called "prices.dat". If the file opens, print the message "File successfully opened!". If not, print "File failed to open". Steps to read from a file: 1. declare a variable infile of type ifsteam 2. call infile.open, and send the filename as its parameter 3. check to see if the open command worked with infile.fail 4. use infile to read in data 5. call infile.close to close the stream
- 13. #include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <cstdlib> using namespace std; int main() { ifstream infile; infile.open("prices.dat"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } cout << "File successfully opened!" << endl; infile.close(); return 0; } Example 1: Open a file called "prices.dat". If the file opens, print the message "File successfully opened!". If not, print "File failed to open". Steps to read from a file: 1. declare a variable infile of type ifsteam 2. call infile.open, and send the filename as its parameter 3. check to see if the open command worked with infile.fail 4. use infile to read in data 5. call infile.close to close the stream
- 14. #include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <cstdlib> using namespace std; int main() { ifstream infile; infile.open("prices.dat"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } cout << "File successfully opened!" << endl; infile.close(); return 0; } Example 1: Open a file called "prices.dat". If the file opens, print the message "File successfully opened!". If not, print "File failed to open". Steps to read from a file: 1. declare a variable infile of type ifsteam 2. call infile.open, and send the filename as its parameter 3. check to see if the open command worked with infile.fail 4. use infile to read in data 5. call infile.close to close the stream
- 15. #include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <cstdlib> using namespace std; int main() { ifstream infile; infile.open("prices.dat"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } cout << "File successfully opened!" << endl; infile.close(); return 0; } Example 1: Open a file called "prices.dat". If the file opens, print the message "File successfully opened!". If not, print "File failed to open". Steps to read from a file: 1. declare a variable infile of type ifsteam 2. call infile.open, and send the filename as its parameter 3. check to see if the open command worked with infile.fail 4. use infile to read in data 5. call infile.close to close the stream
- 16. #include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <cstdlib> using namespace std; int main() { ifstream infile; infile.open("prices.dat"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } cout << "File successfully opened!" << endl; infile.close(); return 0; } Example 1: Open a file called "prices.dat". If the file opens, print the message "File successfully opened!". If not, print "File failed to open". Steps to read from a file: 1. declare a variable infile of type ifsteam 2. call infile.open, and send the filename as its parameter 3. check to see if the open command worked with infile.fail 4. use infile to read in data 5. call infile.close to close the stream
- 17. #include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <cstdlib> using namespace std; int main() { ifstream infile; infile.open("prices.dat"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } cout << "File successfully opened!" << endl; infile.close(); return 0; } Example 1: Open a file called "prices.dat". If the file opens, print the message "File successfully opened!". If not, print "File failed to open". Steps to read from a file: 1. declare a variable infile of type ifsteam 2. call infile.open, and send the filename as its parameter 3. check to see if the open command worked with infile.fail 4. use infile to read in data 5. call infile.close to close the stream
- 18. Example 2: Read a filename from the user, and open that file for reading. If the file opens, print the message "File successfully opened!". If not, print "File failed to open".
- 19. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib, string int main() { string filename; cout << "Please enter the name of the file: "; cin >> filename; ifstream infile; infile.open(filename.c_str()); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } cout << "File successfully opened!" << endl; infile.close(); return 0; } Read a filename from the user, and open that file for reading. If the file opens, print the message "File successfully opened!". If not, print "File failed to open".
- 20. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib, string int main() { string filename; cout << "Please enter the name of the file: "; cin >> filename; ifstream infile; infile.open(filename.c_str()); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } cout << "File successfully opened!" << endl; infile.close(); return 0; } Read a filename from the user, and open that file for reading. If the file opens, print the message "File successfully opened!". If not, print "File failed to open".
- 21. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib, string int main() { string filename; cout << "Please enter the name of the file: "; cin >> filename; ifstream infile; infile.open(filename.c_str()); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } cout << "File successfully opened!" << endl; infile.close(); return 0; } Read a filename from the user, and open that file for reading. If the file opens, print the message "File successfully opened!". If not, print "File failed to open".
- 22. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib, string int main() { string filename; cout << "Please enter the name of the file: "; cin >> filename; ifstream infile; infile.open(filename.c_str()); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } cout << "File successfully opened!" << endl; infile.close(); return 0; } Read a filename from the user, and open that file for reading. If the file opens, print the message "File successfully opened!". If not, print "File failed to open".
- 23. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib, string int main() { string filename; cout << "Please enter the name of the file: "; cin >> filename; ifstream infile; infile.open(filename.c_str()); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } cout << "File successfully opened!" << endl; infile.close(); return 0; } Read a filename from the user, and open that file for reading. If the file opens, print the message "File successfully opened!". If not, print "File failed to open".
- 24. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib, string int main() { string filename; cout << "Please enter the name of the file: "; cin >> filename; ifstream infile; infile.open(filename.c_str()); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } cout << "File successfully opened!" << endl; infile.close(); return 0; } Read a filename from the user, and open that file for reading. If the file opens, print the message "File successfully opened!". If not, print "File failed to open".
- 25. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib, string int main() { string filename; cout << "Please enter the name of the file: "; cin >> filename; ifstream infile; infile.open(filename.c_str()); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } cout << "File successfully opened!" << endl; infile.close(); return 0; } Read a filename from the user, and open that file for reading. If the file opens, print the message "File successfully opened!". If not, print "File failed to open".
- 26. How to read from a file ifstream is a subtype of istream this means that anything you can do with an istream, you can do with an ifstream cin is an istream hence, any operation supported by cin, is also supported by infile the >> operator getline
- 27. Example: Read in three values from a file called "data.txt", and print out the average of those three values.
- 28. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib int main() { ifstream infile; infile.open("data.txt"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } double val1, val2, val3; infile >> val1 >> val2 >> val3; cout << "The average of these values is: " << (val1 + val2 + val3)/3 << endl; infile.close(); return 0; Example: Read in three values from a file called "data.txt", and print out the average of those three values. Code for reading in values goes here!
- 29. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib int main() { ifstream infile; infile.open("data.txt"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } double val1, val2, val3; cin >> val1 >> val2 >> val3; cout << "The average of these values is: " << (val1 + val2 + val3)/3 << endl; infile.close(); return 0; Example: Read in three values from a file called "data.txt", and print out the average of those three values. If we were reading from the keyboard, code would look like this:
- 30. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib int main() { ifstream infile; infile.open("data.txt"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } double val1, val2, val3; cin >> val1 >> val2 >> val3; cout << "The average of these values is: " << (val1 + val2 + val3)/3 << endl; infile.close(); return 0; Example: Read in three values from a file called "data.txt", and print out the average of those three values. Replace cin with infile, and you'll read from the file, instead of the keyboard.
- 31. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib int main() { ifstream infile; infile.open("data.txt"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } double val1, val2, val3; infile >> val1 >> val2 >> val3; cout << "The average of these values is: " << (val1 + val2 + val3)/3 << endl; infile.close(); return 0; Example: Read in three values from a file called "data.txt", and print out the average of those three values. Replace cin with infile, and you'll read from the file, instead of the keyboard.
- 32. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib int main() { ifstream infile; infile.open("data.txt"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } double val1, val2, val3; infile >> val1 >> val2 >> val3; cout << "The average of these values is: " << (val1 + val2 + val3)/3 << endl; infile.close(); return 0; Example: Read in three values from a file called "data.txt", and print out the average of those three values.
- 33. File Input: Unknown file size Example: read in all of the numbers from a file, and print their average.
- 34. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib int main() { ifstream infile; infile.open("test.txt"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } double val1, val2, val3; infile >> val1 >> val2 >> val3; cout << "The average of these values is: " << (val1 + val2 + val3)/3 << endl; infile.close(); return 0; Example: Read in three values from a file called "data.txt", and print out the average of those three values. This accommodates exactly three values. • if "test.txt" contains more than 3 values, they are ignored • if "test.txt" contains less than 3 values, program doesn't fill val3.
- 35. Solution: loop through all values in the file add each value read to a variable total count the number of values read divide total by the number of values read
- 36. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib int main() { ifstream infile; infile.open("test.txt"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } double total = 0; int count = 0; infile >> val; while ( ) { total += val; count++; infile >> val; } if (count == 0) { cout << "No values to average!" << endl; } else { cout << "The average of these values is: " << total / count << endl; } infile.close(); What goes here?
- 37. .eof() .eof() returns true when the file has been read past its end typical format for .eof() loops Step 1: read a value from filestream Step 2: while ( filestream.eof() is not true) Step 2.1 Do something with value Step 2.2 read another value from filestream
- 38. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib int main() { ifstream infile; infile.open("test.txt"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } double total = 0; int count = 0; infile >> val; while ( ) { total += val; count++; infile >> val; } if (count == 0) { cout << "No values to average!" << endl; } else { cout << "The average of these values is: " << total / count << endl; } infile.close(); Step 1: read a value from filestream Step 2: while ( filestream.eof() is not true) Step 2.1 Do something with value Step 2.2 read another value from filestream
- 39. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib int main() { ifstream infile; infile.open("test.txt"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } double val, total = 0; int count = 0; infile >> val; while ( ) { total += val; count++; infile >> val; } if (count == 0) { cout << "No values to average!" << endl; } else { cout << "The average of these values is: " << total / count << endl; } infile.close(); Step 1: read a value from filestream Step 2: while ( filestream.eof() is not true) Step 2.1 Do something with value Step 2.2 read another value from filestream
- 40. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib int main() { ifstream infile; infile.open("test.txt"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } double val, total = 0; int count = 0; infile >> val; while ( !infile.eof() ) { total += val; count++; infile >> val; } if (count == 0) { cout << "No values to average!" << endl; } else { cout << "The average of these values is: " << total / count << endl; } infile.close(); Step 1: read a value from filestream Step 2: while ( filestream.eof() is not true) Step 2.1 Do something with value Step 2.2 read another value from filestream
- 41. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib int main() { ifstream infile; infile.open("test.txt"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } double val, total = 0; int count = 0; infile >> val; while ( !infile.eof() ) { total += val; count++; infile >> val; } if (count == 0) { cout << "No values to average!" << endl; } else { cout << "The average of these values is: " << total / count << endl; } infile.close(); Step 1: read a value from filestream Step 2: while ( filestream.eof() is not true) Step 2.1 Do something with value Step 2.2 read another value from filestream
- 42. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib int main() { ifstream infile; infile.open("test.txt"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } double val, total = 0; int count = 0; infile >> val; while ( !infile.eof() ) { total += val; count++; infile >> val; } if (count == 0) { cout << "No values to average!" << endl; } else { cout << "The average of these values is: " << total / count << endl; } infile.close(); Step 1: read a value from filestream Step 2: while ( filestream.eof() is not true) Step 2.1 Do something with value Step 2.2 read another value from filestream
- 43. File Output so far, all of our information has gone to the screen we can redirect this to a file, in a similar manner as redirecting input from a file use ofstream variable ofstream is a type, of subtype ostream cout is an ostream variable anything you can do with cout, you can do with an ofstream variable this includes <<, and all formatting flags
- 44. Steps to write to a file: 1. declare a variable outfile of type ofstream 2. call outfile.open, and send the filename as its parameter 3. check to see if the open command worked with outfile.fail 4. use outfile to output data 5. call outfile.close to close the stream ofstream outfile; outfile.open("prices.dat"); if (outfile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } // write data to outfile outfile.close();
- 45. Example: Write your name, address, and phone number to a file called "name.txt"
- 46. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib int main() { ofstream outfile; outfile.open("name.txt"); if (outfile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } cout << "Kevin Grant" << endl; cout << "1234 Main Street" << endl; cout << "Disneyland, California, 90210" << endl; cout << "(123) 456-7890" << endl; outfile.close(); return 0; } If we were writing to the screen, we would do this.
- 47. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib int main() { ofstream outfile; outfile.open("name.txt"); if (outfile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } cout << "Kevin Grant" << endl; cout << "1234 Main Street" << endl; cout << "Disneyland, California, 90210" << endl; cout << "(123) 456-7890" << endl; outfile.close(); return 0; } Replace cout with outfile
- 48. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib int main() { ofstream outfile; outfile.open("name.txt"); if (outfile.fail()) { cout << "File failed to open" << endl; exit(1); } outfile << "Kevin Grant" << endl; outfile << "1234 Main Street" << endl; outfile << "Disneyland, California, 90210" << endl; outfile << "(123) 456-7890" << endl; outfile.close(); return 0; }
- 49. Kevin Grant 1234 Main Street Disneyland, California, 90210 (123) 456-7890 name.txt
- 50. Example: Copy the contents of a file called "input.txt" to a file called "output.txt" Steps: 1) Open a file called input.txt for reading 2) Open a file called output.txt for writing 3) Write each line in input.txt to output.txt 4) Close files
- 51. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib, string int main() { 1) Open a file called input.txt for reading 2) Open a file called output.txt for writing 3) Write each line in input.txt to output.txt 4) Close files return 0; }
- 52. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib, string int main() { 1) Open a file called input.txt for reading 2) Open a file called output.txt for writing 3) Write each line in input.txt to output.txt 4) Close files return 0; }
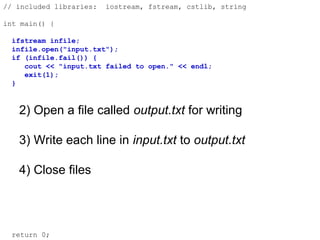
- 53. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib, string int main() { ifstream infile; infile.open("input.txt"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "input.txt failed to open." << endl; exit(1); } 2) Open a file called output.txt for writing 3) Write each line in input.txt to output.txt 4) Close files return 0;
- 54. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib, string int main() { ifstream infile; infile.open("input.txt"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "input.txt failed to open." << endl; exit(1); } 2) Open a file called output.txt for writing 3) Write each line in input.txt to output.txt 4) Close files return 0;
- 55. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib, string int main() { ifstream infile; infile.open("input.txt"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "input.txt failed to open." << endl; exit(1); } ofstream outfile; outfile.open("output.txt"); if (outfile.fail()) { cout << "output.txt failed to open." << endl; exit(1); } 3) Write each line in input.txt to output.txt 4) Close files return 0; }
- 56. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib, string int main() { ifstream infile; infile.open("input.txt"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "input.txt failed to open." << endl; exit(1); } ofstream outfile; outfile.open("output.txt"); if (outfile.fail()) { cout << "output.txt failed to open." << endl; exit(1); } 3) Write each line in input.txt to output.txt 4) Close files return 0; }
- 57. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib, string int main() { ifstream infile; infile.open("input.txt"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "input.txt failed to open." << endl; exit(1); } ofstream outfile; outfile.open("output.txt"); if (outfile.fail()) { cout << "output.txt failed to open." << endl; exit(1); } 3) For each line in input.txt 3.1) Write line to output.txt 4) Close files return 0; }
- 58. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib, string int main() { ifstream infile; infile.open("input.txt"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "input.txt failed to open." << endl; exit(1); } ofstream outfile; outfile.open("output.txt"); if (outfile.fail()) { cout << "output.txt failed to open." << endl; exit(1); } 3) For each line in input.txt 3.1) Write line to output.txt 4) Close files return 0; } Step 1: read a value from filestream Step 2: while ( filestream.eof() is not true) Step 2.1 Do something with value Step 2.2 read another value from filestream
- 59. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib, string int main() { ifstream infile; infile.open("input.txt"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "input.txt failed to open." << endl; exit(1); } ofstream outfile; outfile.open("output.txt"); if (outfile.fail()) { cout << "output.txt failed to open." << endl; exit(1); } string buffer; getline(infile, buffer); while ( !infile.eof() ) { 3.1) Write line to output.txt getline(infile, buffer); } 4) Close files return 0; }
- 60. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib, string int main() { ifstream infile; infile.open("input.txt"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "input.txt failed to open." << endl; exit(1); } ofstream outfile; outfile.open("output.txt"); if (outfile.fail()) { cout << "output.txt failed to open." << endl; exit(1); } string buffer; getline(infile, buffer); while ( !infile.eof() ) { 3.1) Write line to output.txt getline(infile, buffer); } 4) Close files return 0; }
- 61. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib, string int main() { ifstream infile; infile.open("input.txt"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "input.txt failed to open." << endl; exit(1); } ofstream outfile; outfile.open("output.txt"); if (outfile.fail()) { cout << "output.txt failed to open." << endl; exit(1); } string buffer; getline(infile, buffer); while ( !infile.eof() ) { outfile << buffer << endl; getline(infile, buffer); } 4) Close files return 0; }
- 62. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib, string int main() { ifstream infile; infile.open("input.txt"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "input.txt failed to open." << endl; exit(1); } ofstream outfile; outfile.open("output.txt"); if (outfile.fail()) { cout << "output.txt failed to open." << endl; exit(1); } string buffer; getline(infile, buffer); while ( !infile.eof() ) { outfile << buffer << endl; getline(infile, buffer); } 4) Close files return 0; }
- 63. // included libraries: iostream, fstream, cstlib, string int main() { ifstream infile; infile.open("input.txt"); if (infile.fail()) { cout << "input.txt failed to open." << endl; exit(1); } ofstream outfile; outfile.open("output.txt"); if (outfile.fail()) { cout << "output.txt failed to open." << endl; exit(1); } string buffer; getline(infile, buffer); while ( !infile.eof() ) { outfile << buffer << endl; getline(infile, buffer); } infile.close(); outfile.close(); return 0; }





![.open
takes a null-terminated character array as
input
string literal:
infile.open("prices.dat");
character array variable
char filename[] = "prices.dat";
infile.open(filename);
will a string variable work?
string filename = "prices.dat";
infile.open(filename);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/19fileio-180908091319/85/Aray-in-Programming-6-320.jpg)