Arduino程式快速入門
- 1. Arduino程式快速入門 Revised on September 10, 2019 程式基本架構 程式語法 資料型別 變數與常數 運算子 條件敘述 迴圈敘述
- 2. 選單命令「File/New」 檢視預設的程式框架 void setup() { // put your setup code here, to run once: } void loop() { // put your main code here, to run repeatedly: } Arduino程式基本架構 2
- 3. 選單命令File> New 編輯以下程式碼 void setup() { // put your setup code here, to run once: Serial.begin(9600); Serial.println("setup"); } void loop() { // put your main code here, to run repeatedly: Serial.println("loop"); delay(2500); } Lab 測試Arduino程式運行 1/2 3
- 4. 選單命令Tools> Serial Monitor開啟序列埠監控視窗 檢視輸出結果 按⼀下Arduino Reset按鈕,檢視輸出結果 Lab 測試Arduino程式運行 2/2 按下Arduino Reset按鈕 Arduino開始執行 4 必須與Serial.begin(9600);指令設定相符
- 5. /* 註解區 (block comment) 通常在程式檔開頭,簡述程式之功能、作者、設計日期、程式版本等訊息 ShyiShiou Wu; November 5, 2017 */ //單行註解 (single line comment) //標頭檔區,如有使用擴充函式庫時,須在此指定擴充函式庫之標頭檔 #include <Servo.h> //自行定義的標頭檔使用雙引號 #include "config.h" //全域變數宣告區,程式中使用的全域變數或常數 #define RED_LED 12 Servo myservo; //系統設置函式,Arduino重置時,會先執行設置函式,且只會執行一次 void setup(){ //put your setup code here, to run once: } Arduino程式框架 1/2 5
- 6. //程式主廻圈,Arduino會循環執行loop函式 void loop() { //put your main code here, to run repeatedly: } //其它自訂函式,依功能需求自行設計之函式 void mySub() { // put your subroutine code here } Arduino程式框架 2/2 6
- 7. 前置處理指令 #include 用來引入標頭檔(header file) 專案資料夾(儲存*.ino的目錄)下的自訂標頭檔 #include "config.h" libraries資料夾下的函式庫標頭檔 #include <Servo.h> #define 用來定義常數(constant) #define RED_LED 12 //不用等號與分號,通常使用大寫字母 宣告變數(variable) int lightness = 0; //變數型別 變數名稱 = 初始值; Arduino程式基本語法 1/3 7
- 8. 每行指令敘述以分號結尾(前置處理指令不可加分號) int lightness = 0; 程式碼區分大小寫(case sensitive) lightness ≠ Lightness 程式區塊,左右大括弧必須成對 void setup() { ... } Arduino程式基本語法 2/3 8
- 9. 自訂副程式(subroutine) 沒有回傳值 //void 副程式名稱(參數1, 參數2, ...) void showMessage(){ //副程式程式碼 ... } 自訂函式(function) 使用return回傳資料 //傳回值型別 函式名稱(參數1, 參數2, ...) int function_name(int arg1, int arg2){ //函式程式碼 ... return (expression); //傳回值 } Arduino程式基本語法 3/3 9
- 10. 資料型別決定資料變數的格式與容量 boolean 只有true或false二種值(HIGH或LOW) char 字元資料,佔1 byte 使用單引號標記字元,例如'A' 也可使用ACSII code,例如65 做為數值資料時,有效值-128~127 unsigned char 1 byte,數值0~255 Arduino Uno資料型別 1/4 10
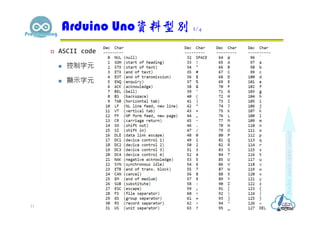
- 11. ASCII code 控制字元 顯示字元 Arduino Uno資料型別 2/4 11
- 12. byte 8-bit無號數,數值0~255 int 16-bit整數,-32,768~32,767 unsigned int 16-bit無號數,0~65,535 word 16-bit無號數,0~65,535 short 16-bit整數,-32,768~32,767 Arduino Uno資料型別 3/4 12
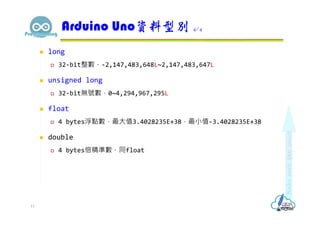
- 13. long 32-bit整數,-2,147,483,648L~2,147,483,647L unsigned long 32-bit無號數,0~4,294,967,295L float 4 bytes浮點數,最大值3.4028235E+38,最小值-3.4028235E+38 double 4 bytes倍精準數,同float Arduino Uno資料型別 4/4 13
- 14. 十進制(decimal) 123 二進制(binary) B1111011 限用於表示8位元數值 (0 to 255) 八進制(octal) 0173 十六進制(hexadecimal) 0x7B 數值資料表示法 1/2 14
- 15. 浮點數 10.0 10.0 10.0 2.34E5 2.34 * 10^5 234000 67e-12 67.0 * 10^-12 0.000000000067 數值資料表示法 2/2 15
- 16. 在程式中用來暫存資料 宣告變數 (declaring variables) 語法:資料型別 變數名稱 [= 初始值]; int count; float temperature = 25.0; 變數 1/4 16
- 17. 變數命名規則 只能包含字⺟、數字及底線 開頭字元不能是數字 不能使用保留字 arduino IDE中保留字會標示顏色(arduino目錄libkeywords.txt) 變數注意事項 區分大小寫 使用有意義的文字組合 clock_pin clockPin 小駝峰式命名法 (lower camel case) ClockPin 大駝峰式命名法 (upper camel case) 變數 2/4 17
- 18. 有效範圍(scope) 全域變數(global variable),宣告在#include指令之後,提供整份 Arduino程式使用 區域變數(local variable),宣告在程式區塊中,只能在所宣告的程式 區塊中使用;每次執行時變數會被動態創建(create)和銷毁(destroy) int gPWMval; //整個程式檔都可使用gPWMval變數 void setup() { //... } void loop() { int i, j; //在loop程式區塊中可使用變數i與j //... for (int k = 0; k < 100; k++){ //變數k只能在for程式區塊中使用 //... } } 變數 3/4 18
- 19. 靜態變數 (static variable) 在區域變數宣告前加上static關鍵字 程式執行期間變數內容會保留 void walk(int steps){ static int a; //每次執行walk()函式,變數a會保留上一次執行結果 int b; //每次執行walk()函式,變數b會重置 a = a + steps; b = b + steps; } 變數 4/4 19
- 20. int a = 0; //全域變數 void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); a = a + 1; Serial.print("a = "); Serial.println(a); func1(); func2(); a = a + 1; Serial.print("a = "); Serial.println(a); func1(); func1(); func2(); func2(); } void loop() { } Lab 測試變數Scope 1/2 20
- 21. void func1() { int b = 0; b = a + b; Serial.print("b in func1 = "); Serial.println(b); } void func2(){ static int b = 0; b = a + b; Serial.print("b in func2 = "); Serial.println(b); } Lab 測試變數Scope 2/2 21
- 22. 程式執行過程中不會變更的數 常數名稱通常使用大寫字⺟ #define RED_LED 12 編譯時,RED_LED會被替換成數字12 const byte RED_LED = 12; 保留RED_LED變數,但限定內容不可變動 內建常數 INPUT, OUTPUT HIGH, LOW true, false 常數 22
- 23. ⼀般的變數只能儲存⼀個值,陣列則可以用來存放多個值 陣列中的每個資料稱為陣列元素(element),程式中以索引值存取陣 列元素,索引值從0開始 byte ledPins[] = {2, 4, 8}; pinMode(ledPins[0], OUTPUT); pinMode(ledPins[1], OUTPUT); pinMode(ledPins[2], OUTPUT); 二維陣列 char keypad[4][4] = { //矩陣按鍵 {'1','2','3','A'}, {'4','5','6','B'}, {'7','8','9','C'}, {'*','0','#','D'}}; 陣列 (array) 23
- 24. 使用雙引號標記字串資料 char str1[] = "Arduino"; sizeof(str1)結果為8,會自動加上'0'(空字元)做為字串結束標記 字串就是⼀種字元陣列 (char array) char str2[] = {'A', 'r', 'd', 'u', 'i', 'n', 'o', '0'}; 字串 24 如果要把str2做為字串,必須自行加上字串結束字元
- 25. String物件比字元陣列提供更多便利的字串處理運算 建構元 String str1 = String(235, BIN); //"11101011" String str2 = String(45, HEX); //"2d" String str3 = "Hello String"; //"Hello String" 字串串接 int sensorValue=analogRead(A0); String msg$ = "Sensor value: " + sensorValue; 尋找特定字元位置索引 String html_str = "<HTML><HEAD><BODY>"; int i1 = html_str.indexOf('>'); //5 int i2 = html_str.indexOf('>', i1 + 1); //11 int lastOpeningBracket=html_str.lastIndexOf('<'); //12 String物件 1/4 25
- 26. 計算字串⻑度 String hello_str = "Hello! arduio "; Serial.println(hello_str.length()); //18 hello_str.trim(); //切除字串後面多餘空白 Serial.println(hello_str.length()); //14 大小寫轉換 String arduino_str = "Arduino programming"; Serial.println(arduino_str); //Arduino programming arduino_str.toUpperCase(); Serial.println(arduino_str); //ARDUINO PROGRAMMING arduino_str.toLowerCase(); Serial.println(arduino_str); //arduino programming String物件 2/4 26
- 27. 替換字串 String hello_str = "Hello! arduio"; Serial.println(hello_str); //Hello! arduino hello_str.replace("Hello","Hi"); Serial.println(hello_str); //Hi! arduino 子字串 String head_str = "Content-Type: text/html"; Serial.println(head_str.substring(14, 18)); //text 移除子字串 String hello_str = "Hi! arduio"; hello_str.remove(2, 6); //Hiino String物件 3/4 27
- 28. 比較字串 String cmd1_str = "Turn on"; String cmd2_str = "Turn off"; Serial.println(cmd1_str == "Turn on"); //1 Serial.println(cmd2_str.equals("Turn Off")); //0 Serial.println(cmd2_str.equalsIgnoreCase("Turn Off")); //1 String物件 4/4 28
- 29. 算術運算子(Arithmetic Operators) % (modulo) * (multiplication) + (addition) - (subtraction) / (division) = (assignment operator) float r = 3 / 2; //r=1.0 float r = 3 / 2.0; //r=1.5 float r = 3 / (float)2; //r=1.5 Arduino運算子 1/7 29
- 30. 比較運算子(Comparison Operators) != (not equal to) < (less than) <= (less than or equal to) == (equal to) > (greater than) >= (greater than or equal to) Arduino運算子 2/7 30
- 31. 位元運算子 (Bitwise Operators) & (bitwise and) << (bitshift left) LSB補0 >> (bitshift right) MSB補符號位元 ^ (bitwise xor) | (bitwise or) ~ (bitwise not) PORTD ^= (1 << PD3); //Toggle D3輸出 Arduino運算子 3/7 31
- 32. 布林運算子 (Boolean Operators) ! (logical not) && (logical and) || (logical or) Arduino運算子 4/7 32
- 33. 遞增運算 ++ (increment) x++; //等同x = x + 1; 遞減運算 -- (decrement) x--; //等同x = x - 1; Arduino運算子 5/7 33
- 34. 複合運算子(Compound Operators) 同時執行『算數運算子或位元運算子』及『指定運算子』兩件工作 += (compound addition) x += y; //等同x = x + y; -= (compound subtraction) x -= y; //等同x = x - y; *= (compound multiplication) x *= y; //等同x = x * y; /= (compound division) x /= y; //等同x = x / y; Arduino運算子 6/7 34
- 35. &= (compound bitwise and) x &= y; //等同x = x & y; |= (compound bitwise or) x |= y; //等同x = x | y; ^= (compound bitwise xor) x ^= y; //等同x = x ^ y; Arduino運算子 7/7 35
- 36. 優先序(Precedence) 決定運算的先後次序 a = b + c * d; 結合性(associativity) 決定相同優先序的運算同時存在時,是要由左向右運算,還是由右向左運算 a = b + c + d; 最好使用小括號明確設定運算優先序 Precedence & associativity 1/2 36
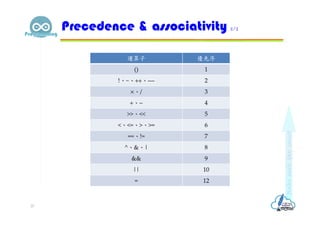
- 37. 運算子 優先序 () 1 !、~、++、−− 2 ×、/ 3 +、− 4 >>、<< 5 <、<=、>、>= 6 ==、!= 7 ^、&、| 8 && 9 || 10 = 12 Precedence & associativity 2/2 37
- 38. 循序結構(Sequence) 選擇結構(Selection) 程式的三種基本控制結構 1/2 truefalse 38
- 40. if … else if (condition1){ //do job A } else if (condition2){ //do job B } else if (condition3){ //do job C } else { //do job D } if敘述 40
- 41. X ? Y : Z 若X為true,執行Y,否則執行Z 範例 if (analogRead(CDS) < threshold) ledState = HIGH; else ledState = LOW; 上述程式碼可改寫如下: ledState = (analogRead(CDS) < threshold)? HIGH : LOW; 三元運算子 41
- 42. #define LED 13 void setup() { pinMode(LED, OUTPUT); Serial.begin(9600); } void loop() { byte cmd = Serial.read(); if (cmd == '1') { //從序列埠收到'1' digitalWrite(LED, HIGH); Serial.println("Turn LED on"); } if (cmd == '0') { //從序列埠收到'0' digitalWrite(LED, LOW); Serial.println("Turn LED off"); } } Lab if敘述 1/2 42
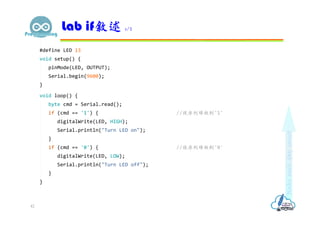
- 43. Lab if敘述 2/2 43
- 44. switch…case switch (var) { //var必須是整數或字元 case label1: // statements break; case label2: // statements break; default: // statements } switch…case敘述 case 比對1 default 其它敘述 程式區塊1 true false 程式區塊2case 比對2 switch (整數運算式) case 比對n true false non break 程式區塊n true non break non break break break break 結束 false 44
- 45. #define LED 13 void setup() { pinMode(LED, OUTPUT); Serial.begin(9600); } void loop() { byte cmd = Serial.read(); switch (cmd){ case '0': //從序列埠收到'0' digitalWrite(LED, LOW); Serial.println("Turn LED off"); break; case '1': //從序列埠收到'1' digitalWrite(LED, HIGH); Serial.println("Turn LED on"); break; } } Lab switch敘述 1/2 45
- 47. for迴圏 for (initialization; condition; increment) { //statement(s); } 範例 byte ledPins[] = {2, 4, 8, 3, 6}; for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ pinMode(ledPins[i], OUTPUT); } for迴圈敘述 條件運算式 重複作業區塊 true false 更新計數值 初始計數值 結束 47
- 48. void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); } void loop() { int i; for (i = 0; i <= 255; i += 5){ Serial.println(i); delay(500); } Serial.print("Finally, i = "); Serial.println(i); } Lab for迴圈敘述 48
- 49. while迴圏 while(condition){ // statement(s) } 範例 int i = 0; while (i <= 255){ analogWrite(pwmPin, i); delay(10); i++; } while迴圈敘述 條件運算式 重複作業區塊 true false 結束 49
- 50. void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); } void loop() { int i = 0; while (i <= 255){ Serial.println(i); delay(500); i += 5; } Serial.print("Finally, i = "); Serial.println(i); } Lab while迴圈敘述 50
- 51. do … while迴圏 do { // statement block } while (condition); ⾄少會執行⼀次 範例 #define pwmPin 3 ... int i = 0; do { analogWrite(pwmPin, i); delay(10); i++; } while (i <= 255); do迴圈敘述 條件運算式 重複作業區塊 true false 結束 51
- 52. void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); } void loop() { int i = 0; do { Serial.println(i); delay(500); i += 5; } while (i <= 255); Serial.print("Finally, i = "); Serial.println(i); } Lab do迴圈敘述 52














![ 在程式中用來暫存資料
宣告變數 (declaring variables)
語法:資料型別 變數名稱 [= 初始值];
int count;
float temperature = 25.0;
變數 1/4
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03arduinoprogram-190910122223/85/Arduino-16-320.jpg)






![ ⼀般的變數只能儲存⼀個值,陣列則可以用來存放多個值
陣列中的每個資料稱為陣列元素(element),程式中以索引值存取陣
列元素,索引值從0開始
byte ledPins[] = {2, 4, 8};
pinMode(ledPins[0], OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPins[1], OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPins[2], OUTPUT);
二維陣列
char keypad[4][4] = { //矩陣按鍵
{'1','2','3','A'},
{'4','5','6','B'},
{'7','8','9','C'},
{'*','0','#','D'}};
陣列 (array)
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03arduinoprogram-190910122223/85/Arduino-23-320.jpg)
![ 使用雙引號標記字串資料
char str1[] = "Arduino";
sizeof(str1)結果為8,會自動加上'0'(空字元)做為字串結束標記
字串就是⼀種字元陣列 (char array)
char str2[] = {'A', 'r', 'd', 'u', 'i', 'n', 'o', '0'};
字串
24
如果要把str2做為字串,必須自行加上字串結束字元](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03arduinoprogram-190910122223/85/Arduino-24-320.jpg)




















![ for迴圏
for (initialization; condition; increment) {
//statement(s);
}
範例
byte ledPins[] = {2, 4, 8, 3, 6};
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
pinMode(ledPins[i], OUTPUT);
}
for迴圈敘述
條件運算式 重複作業區塊
true
false
更新計數值
初始計數值
結束
47](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03arduinoprogram-190910122223/85/Arduino-47-320.jpg)