ARM Micro-controller
- 1. Introduction toIntroduction to ARM Micro-controllersARM Micro-controllers Ravikumar Tiwari Assistant Professor Dept. of Electronics, GHRCE [email protected] www.facebook.com/rravik www.twitter.com/Ravi6096
- 2. ARM family of micro-controllersARM family of micro-controllers “ARM” architecture: designed by Advance RISC Machines Ltd., U.K. (www.arm.com) Designs the ARM range of RISC processor cores Many versions exist with backward compatibility. ARM does not fabricate silicon itself ARM7TDMI is one popular ARM version. Several manufacturers.
- 4. ARM architecture basicsARM architecture basics Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC). 32 bit architecture Optional 16 bit THUMB mode in ARM7TDMI Pipeline architecture Data-processing operations only on registers. “Accumulator” register not provided and not required. 32 bit arithmetic operations in 1 instruction (except division). Various modes of operation: user, supervisor … Exceptions such as interrupt, memory abort … Other special features to support Operating Systems.
- 5. ARM7TDMI architectureARM7TDMI architecture One of the most popular ARM variant architectures. Offers very good price/performance ratio. 2 Operating States: ◦ 32 bit ARM ◦ 16 bit THUMB. ARM state offers very high performance (speed). THUMB state offers tight code density (size). Operating State can be changed by software. Instruction length is 32 bit (ARM) or 16 bit (THUMB)
- 6. Pipelining The ARM7TDMI core uses a pipeline to increase the speed of the flow of instructions to the processor. This enables several operations to take place simultaneously. The processing and memory systems to operate continuously A three-stage pipeline is used, so instructions are executed in three stages:.
- 7. Fig. ARM7TDMI processor block diagram
- 8. Fig. ARM7TDMI main processor logic
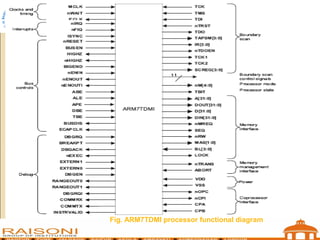
- 9. Fig. ARM7TDMI processor functional diagram
- 10. ARM7TDMI modesARM7TDMI modes 7 modes of operation: User (usr): normal program execution mode. FIQ (fiq): to support DMA kind of operations. IRQ (irq): for general purpose interrupt handling. Supervisor (svc): protected mode for OS. Abort (abt): to handle memory access abort. System (sys): Privileged user mode for OS. Undefined (und): Entered when undefined instruction is executed.
- 11. ARM7TDMI registersARM7TDMI registers Total 31 registers – each 32 bit. At any time, 16 general registers and 1 or 2 status registers are visible in ARM state. General registers are named R0 to R15. R15 is same as Program Counter (PC). R14 is same as Link Register (LR). When a sub-routine is called, return address is automatically saved in LR. R13 is often used as Stack Pointer (SP).
- 12. ARM7TDMI registers …ARM7TDMI registers … CPSR (Current Program Status Register) contains condition code flags (like Z, C) and current mode bits. SPSR (Saved Program Status Register) holds saved copy of previous CPSR. A subset of ARM registers is visible in THUMB state. Only R0 to R7 and PC, LR, SP are directly visible in THUMB state.
- 13. ThumbThumb Thumb is a 16-bit instruction set ◦ Optimised for code density from C code (~65% of ARM code size) ◦ Improved performance from narrow memory ◦ Subset of the functionality of the ARM instruction set Core has additional execution state - Thumb ◦ Switch between ARM and Thumb using BX instruction 015 31 0 ADDS r2,r2,#1 ADD r2,#1 32-bit ARM Instruction 16-bit Thumb Instruction For most instructions generated by compiler: Conditional execution is not used Source and destination registers identical Only Low registers used Constants are of limited size Inline barrel shifter not used
- 14. ARM / THUMB advantageARM / THUMB advantage Many ARM operations can be done in 1 THUMB instruction; some need 2 or more THUMB instructions. Using THUMB instructions results in 30-40% reduction in code size. Using ARM instructions provides faster performance. Intermixing of ARM and THUMB code results in optimum solution in terms of code size and speed.
- 15. ARM Instruction SetARM Instruction Set All instructions are conditionally executed. Conditions can be “if Z flag set”, “if C flag clear” etc. “Always” is a valid condition. Many instructions are of the form: “ADD R1,R2,R3” – add contents of R2 with contents of R3 and store result in R1. Instructions to add, subtract, multiply 8/16/32 bit numbers. Instructions for logical operations AND, OR, EXOR…
- 16. ARM Instruction Set …ARM Instruction Set … Instructions for comparison of 32 bit numbers. MOV instructions to move contents of registers and constants. Immediate addressing mode supported, but not all values of constants are legal. Special Multiply-Accumulate instruction. Load / store instructions to move data between registers and memory.
- 17. ARM Instruction Set …ARM Instruction Set … Load / store instructions support various addressing modes like indexed, pre/post increment/decrement of base, write-back of base and so on. Special SWAP instruction to exchange contents of a register and a memory location. Branch (B) instruction to transfer control. Branch and Link (BL) instruction to call a sub-routine. BX instruction to branch and change state (ARM / THUMB).
- 18. Applications of ARM Micro-controllersApplications of ARM Micro-controllers Any application desiring 32 bit performance. 3.3 V (or even lower voltage) ARM micro-controllers – suitable for battery operation. Applications requiring faster performance at lower power consumption. Applications requiring higher performance at not-so- high prices.
- 19. Some ARM7TDMI family membersSome ARM7TDMI family members LPC21xx family (Philips). ADuC7026 (Analog Devices). AT91RM42800A (Atmel).
- 20. Future of ARMFuture of ARM ARM is already most popular among 32 bit micro- controllers. Competes equally well with 16 bit micro-controllers, due to THUMB architecture. Competes with 8 bit micro-controllers due to better price/performance ratio. Newer ARM architectures include DSP capabilities to compete with DSP processors. ARM is likely to stay popular for long time.
- 21. Links for more information:Links for more information: www.arm.com www.semiconductors.philips.com www.analogdevices.com www.atmel.com www.spjsystems.com/armboards.htm www.spjsystems.com/scarm.htm Thanks for your time!
- 22. ?
Editor's Notes
- #14: The Thumb instruction set was designed by looking at the instructions produced by the ARM C compiler from real application code to see which instructions were most often used. This subset of instructions was then compressed into 16-bit opcodes to give better code density and better performance from narrow memory A Thumb compatible processor is still a 32-bit processor, but it has the ability to execute either sections of ARM code or sections of Thumb code. The two instruction sets cannot be interleaved though, a special form of branch has to be used to change “state”. The diagram then shows the way that a typical 32-bit ARM instruction might be “compressed” into a 16-bit Thumb one.