Bankers algorithm
- 1. Bankers Algorithm The banker’s algorithm which is also known as avoidance algorithm is a deadlock detection algorithm. It was developed by Edsger Dijkstra. It is designed to check the safe state whenever a resource is requested. It takes analogy of bank, where customer request to withdraw cash. Based on some data the cash is lent to the customer. The banker can’t give more cash than what the customer has requested for, and the total available cash. As this algorithm uses bank analogy so named as banker’s algorithm Following data structures are used to implement the Banker’s Algorithm: Let ‘n’ be the number of processes in the system and ‘m’ be the number of resources types. Available: It is a 1-d array of size ‘m’ indicating the number of available resources of each type. Available[ j ] = k means there are ‘k’ instances of resource type Rj Max: It is a 2-d array of size ‘n*m’ that defines the maximum demand of each process in a system. Max[ i, j ] = k means process Pi may request at most ‘k’ instances of resource type Rj. Allocation: It is a 2-d array of size ‘n*m’ that defines the number of resources of each type currently allocated to each process. Allocation[ i, j ] = k means process Pi is currently allocated ‘k’ instances of resource type Rj Need: It is a 2-d array of size ‘n*m’ that indicates the remaining resource need of each process. Need [ i, j ] = k means process Pi currently allocated ‘k’ instances of resource type Rj Need [ i, j ] = Max [ i, j ] – Allocation [ i, j ] Banker’s Algorithm 1. Let Work and Finish be vectors of length ‘m’ and ‘n’ respectively. Initialize: Work = Available Finish [i] = false; for i=1,2,……,n 2. Find an i such that both a) Finish [i] = false b) Need_i <= work if no such i exists goto step (4) 3. Work = Work + Allocation_i Finish[i] = true goto step(2) 4. If Finish[i] = true for all i, then the system is in safe state.
- 2. Sample Code #include<stdio.h> int main() { int allocation[20][20],max[20][20],available[20]; int i,j,process,flag = 1,sq[20],index = 0,flag2, resource,need[20][20],work[20],finish[20]; printf("Enter the number of process:"); scanf("%d",&process); printf("Enter the number of resource:"); scanf("%d",&resource); printf("Enter the allocation matrix:"); for(i = 0; i<process; i++) for(j = 0; j<resource; j++) scanf("%d",&allocation[i][j]); printf("Enter the max matrix:"); for(i = 0; i<process; i++) for(j = 0; j<resource; j++) scanf("%d",&max[i][j]); printf("Enter available:"); for(j = 0; j<resource; j++) scanf("%d",&available[j]); for(i = 0; i<process; i++)
- 3. for(j = 0; j<resource; j++) need[i][j] = max[i][j]-allocation[i][j]; for(i = 0; i<resource; i++) work[i] = available[i]; for(i = 0; i<process; i++) finish[i] = 0; while(flag) { flag = 0; for(i = 0; i<process; i++) { if(!finish[i]) { flag2 = 1; for(j = 0; j<resource; j++) if(need[i][j]>work[j]) flag2 = 0; if(flag2) { flag = 1; for(j = 0; j<resource; j++) work[j]+=allocation[i][j]; finish[i] = 1; sq[index++] = i; }
- 4. } } } flag = 1; for(i = 0; i<process;i++) { if(!finish[i]) flag = 0; } if(flag) { printf("ntTHE SQUENCE OF SAFE STATE IS :n"); for(i = 0; i<index; i++) printf("t%d",sq[i]); } else printf("ntIT IS IN UNSAFE STATE ."); } Sample Output Case 1: Enter the number of process:5 Enter the number of resource:3 Enter the allocation matrix: 0 1 0 2 0 0 3 0 2 2 1 1 0 0 2
- 5. Enter the max matrix: 7 5 3 3 2 2 9 0 2 2 2 2 4 3 3 Enter available: 3 3 2 THE SQUENCE OF SAFE STATE IS : 1 3 4 0 2 Case 2: Enter the number of process:3 Enter the number of resource:4 Enter the allocation matrix: 1 2 5 1 1 1 3 3 1 2 1 0 Enter the max matrix: 3 3 2 2 1 2 3 4 1 3 5 0 Enter available: 3 0 1 2 IT IS IN UNSAFE STATE .
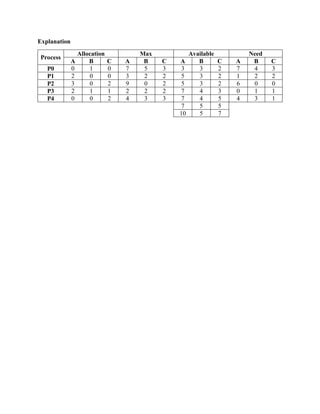
- 6. Explanation Process Allocation Max Available Need A B C A B C A B C A B C P0 0 1 0 7 5 3 3 3 2 7 4 3 P1 2 0 0 3 2 2 5 3 2 1 2 2 P2 3 0 2 9 0 2 5 3 2 6 0 0 P3 2 1 1 2 2 2 7 4 3 0 1 1 P4 0 0 2 4 3 3 7 4 5 4 3 1 7 5 5 10 5 7

![Bankers Algorithm
The banker’s algorithm which is also known as avoidance algorithm is a deadlock detection
algorithm. It was developed by Edsger Dijkstra. It is designed to check the safe state whenever a
resource is requested. It takes analogy of bank, where customer request to withdraw cash. Based
on some data the cash is lent to the customer. The banker can’t give more cash than what the
customer has requested for, and the total available cash. As this algorithm uses bank analogy so
named as banker’s algorithm
Following data structures are used to implement the Banker’s Algorithm:
Let ‘n’ be the number of processes in the system and ‘m’ be the number of resources types.
Available:
It is a 1-d array of size ‘m’ indicating the number of available resources of each type.
Available[ j ] = k means there are ‘k’ instances of resource type Rj
Max:
It is a 2-d array of size ‘n*m’ that defines the maximum demand of each process in a
system.
Max[ i, j ] = k means process Pi may request at most ‘k’ instances of resource type Rj.
Allocation:
It is a 2-d array of size ‘n*m’ that defines the number of resources of each type currently
allocated to each process.
Allocation[ i, j ] = k means process Pi is currently allocated ‘k’ instances of resource
type Rj
Need:
It is a 2-d array of size ‘n*m’ that indicates the remaining resource need of each process.
Need [ i, j ] = k means process Pi currently allocated ‘k’ instances of resource type Rj
Need [ i, j ] = Max [ i, j ] – Allocation [ i, j ]
Banker’s Algorithm
1. Let Work and Finish be vectors of length ‘m’ and ‘n’ respectively.
Initialize: Work = Available
Finish [i] = false; for i=1,2,……,n
2. Find an i such that both
a) Finish [i] = false
b) Need_i <= work
if no such i exists goto step (4)
3. Work = Work + Allocation_i
Finish[i] = true
goto step(2)
4. If Finish[i] = true for all i, then the system is in safe state.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bankersalgorithm-210706152335/85/Bankers-algorithm-1-320.jpg)
![Sample Code
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int allocation[20][20],max[20][20],available[20];
int i,j,process,flag = 1,sq[20],index = 0,flag2,
resource,need[20][20],work[20],finish[20];
printf("Enter the number of process:");
scanf("%d",&process);
printf("Enter the number of resource:");
scanf("%d",&resource);
printf("Enter the allocation matrix:");
for(i = 0; i<process; i++)
for(j = 0; j<resource; j++)
scanf("%d",&allocation[i][j]);
printf("Enter the max matrix:");
for(i = 0; i<process; i++)
for(j = 0; j<resource; j++)
scanf("%d",&max[i][j]);
printf("Enter available:");
for(j = 0; j<resource; j++)
scanf("%d",&available[j]);
for(i = 0; i<process; i++)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bankersalgorithm-210706152335/85/Bankers-algorithm-2-320.jpg)
![for(j = 0; j<resource; j++)
need[i][j] = max[i][j]-allocation[i][j];
for(i = 0; i<resource; i++)
work[i] = available[i];
for(i = 0; i<process; i++)
finish[i] = 0;
while(flag)
{
flag = 0;
for(i = 0; i<process; i++)
{
if(!finish[i])
{
flag2 = 1;
for(j = 0; j<resource; j++)
if(need[i][j]>work[j])
flag2 = 0;
if(flag2)
{
flag = 1;
for(j = 0; j<resource; j++)
work[j]+=allocation[i][j];
finish[i] = 1;
sq[index++] = i;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bankersalgorithm-210706152335/85/Bankers-algorithm-3-320.jpg)
![}
}
}
flag = 1;
for(i = 0; i<process;i++)
{
if(!finish[i])
flag = 0;
}
if(flag)
{
printf("ntTHE SQUENCE OF SAFE STATE IS :n");
for(i = 0; i<index; i++)
printf("t%d",sq[i]);
}
else
printf("ntIT IS IN UNSAFE STATE .");
}
Sample Output
Case 1:
Enter the number of process:5
Enter the number of resource:3
Enter the allocation matrix:
0 1 0
2 0 0
3 0 2
2 1 1
0 0 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bankersalgorithm-210706152335/85/Bankers-algorithm-4-320.jpg)