Basic synthesis flow and commands in digital VLSI
- 1. Logic Synthesis Page 61 Introduction to Digital VLSI Basic Synthesis Flow and Commands • Technology Libraries • Design Read/Write • Design Objects • Timing Paths • Constraints • Compile • Wire Load Models • Multiple Instances • Integration • Advanced Commands • Check Before Compile • Check After Compile
- 2. Logic Synthesis Page 62 Introduction to Digital VLSI Synthesis Script Flow 1. Configuration variables, e.g. bus_naming_style, verilogout_no_tri 2. Library variables 3. Read design 4. Constraints 5. Compile 6. Reports 7. Write design
- 3. Logic Synthesis Page 63 Introduction to Digital VLSI Some Tcl Syntax dc_shell-t> set a 5 5 dc_shell-t> set b {c d $a [list $a z]} c d $a [list $a z] dc_shell-t> set b [list c d $a [list $a z]] c d 5 {5 z} dc_shell-t> set delay [expr .5 * $base_delay] • [cmd] — returns the result of the command: like ‘cmd‘ in csh. • {} — creates a list without variable or command substitution • Use the list command when variable and/or command subtitution is required. • Use the expr command for all arithmetic expressions. Many Tcl resources (for advanced scripts): http://tcl.activestate.com
- 4. Logic Synthesis Page 64 Introduction to Digital VLSI Technology Libraries Target Library • The target library is the technology library you want to map to during synthesis. It is also known as the destination library. • Specify the target library with the pointer variable target_library. set target_library {"cdr2synPwcslV300T125.db" "scanff.db"} Target Library Design Compiler Optimized Netlist Design is mapped to gates from target_library.
- 5. Logic Synthesis Page 65 Introduction to Digital VLSI Link Library • The link library is a technology library that is used to describe the function of mapped cells prior to optimization. • Specify the link library with the variable pointer link_library. • Typically, the link and target library are set to the same technology library. • The first entry in the list should be "*" to use designs currently in memory. Target Library Design Compiler Optimized Netlist Design is mapped to gates from target_library. Link Library HDL Code RTL + manually instantiated gates Netlist from earlier synthesis
- 6. Logic Synthesis Page 66 Introduction to Digital VLSI Physical Technology Libraries (PC Flow) Physical Library • The physical library is the technology library which inbclues the physical design rules and physical view of the standard cells. • Specify the physical library with the pointer variable physical_library. set physical_library {"cmos090gp_h8hp_tech.pdb" "cmos090gp_h8hp_stdcells.pdb"} Target Library Physical Compiler Optimized (mapped and placed) Netlist HDL Code RTL + manually instantiated gates Netlist from earlier synthesis Link Library Physical LibraryFloorplan Design mapped to gates from target library Output: Verilog GLV and layout pdef/def format Design placed according to physical library
- 7. Logic Synthesis Page 67 Introduction to Digital VLSI Example of Libraries include file set search_path [concat $search_path /usr/cad/library/udr2/synopsys_1998.02 ~ppcec/synopsys/lib_1998.02] set target_library { adv_lib_3state_udr2_85_wcs_v3t135_3c.db adv_lib_comb_udr2_85_wcs_v3t135_3c.db adv_lib_dff_udr2_85_wcs_v3t135_3c.db adv_lib_latch_udr2_85_wcs_v3t135_3c.db msil_udr2_85_wcs_v3t150.db ppcec_prv_udr2_85_wcs_v3t135.db clock_driver.db wire_load_models.db } set link_library { "*" adv_lib_3state_udr2_85_wcs_v3t135_3c.db adv_lib_comb_udr2_85_wcs_v3t135_3c.db adv_lib_dff_udr2_85_wcs_v3t135_3c.db adv_lib_latch_udr2_85_wcs_v3t135_3c.db adv_lib_latch_old_udr2_85_wcs_v3t135_3c.db msil_udr2_85_wcs_v3t150.db ppcec_prv_udr2_85_wcs_v3t135.db clock_driver.db wire_load_models.db }
- 8. Logic Synthesis Page 68 Introduction to Digital VLSI Design Read read_file [-format input_format] [-define macro_names] file_list • -format input_format • db — Synopsys internal database format (smaller and loads faster than netlist) • verilog — RTL or gate-level Verilog netlist • -define macro_names: enables setting defined values used in the Verilog source code. If you code uses ‘ifdef statements, you should set: hdlin_enable_vpp=”true” • read_db or read_verilog are equivalent to read_file -format xxx Example: read_file -format verilog -define BLOCK_A_DEF { block_a.v block_b.v } current_design [design] • returns or sets the current working design • Note: The read command sets the last module read as the current design.
- 9. Logic Synthesis Page 69 Introduction to Digital VLSI Design Read by Analyze and Elaborate analyze & elaborate flow can be for power compiler clock gating, or for set- ting a parametric design selection analyze [-format input_format] [-update] [-define macro_names] file_list • Analyzes HDL files and stores the intermediate format for the HDL description in the specified library. Similar to first stage of read_file. Example: analyze -f verilog -update { block_a.v block_b.v } elaborate top_design [-parameters param_list] [-architecture arch_name] [-update] [-gate_clock] Example: elaborate -update mult -parameters "N=8,M=3" -gate_clock
- 10. Logic Synthesis Page 70 Introduction to Digital VLSI Design Write write_file [-format output_format] [-hierarchy] [-output output_file_name] [design_list] • output_format can be db or verilog as above • -hierarchy writes the entire hierarchy from the named design down; otherwise, only the top-level module is saved • The default for design_list is the current design.
- 11. Logic Synthesis Page 71 Introduction to Digital VLSI Design Objects module m (i1, i2, i3, i4, clk, out1); input i1, i2, i3, i4, clk; output out1; wire int1, int0; kuku U1 (.a(i1), .b(i2), .c(i3), .d(in4), .q1(int1), .q0(int0)); ind3f U2 (.IN1(int1), .IN2(int0), .IN3(clk), .OUT1(out1)); endmodule Design Cell Port Reference Pin Net
- 12. Logic Synthesis Page 72 Introduction to Digital VLSI Design Objects (cont.) • Design: A circuit description that performs one or more logical functions (i.e Verilog module). • Cell: An instantiation of a design within another design (i.e Verilog instance). • Reference:The original design that a cell "points to" (i.e Verilog sub- module) • Port: The input, output or inout port of a Design. • Pin: The input, output or inout pin of a Cell in the Design. • Net: The wire that connects Ports to Pins and/or Pins to each other. • Clock: Port of a Design or Pin of a Cell explicitly defined as a clock source.
- 13. Logic Synthesis Page 73 Introduction to Digital VLSI Design Objects Exercise dffrpc ind2c INPUT1 INPUT2 OUTPUT1 D C RB Q in1 in2 clk reset int1 out1 (i1) (i8) • all_inputs {"clk", "in1", "in2", "reset"} • all_outputs {"out1"} • all_clocks /* works only after clocks are defined */ {"clk"} • all_registers {"i8"} • all_connected int1 {"i1/OUTPUT1", "i8/D"}
- 14. Logic Synthesis Page 74 Introduction to Digital VLSI Timing Paths • Timing paths are usually: • input port -> output port • input port -> register • register -> output port • register -> register • The startpoint from a FF is the clock pin. • The endpoint at a FF is a data pin. • Timing paths do not go through FFs (except for asynchronous set/ reset).
- 15. Logic Synthesis Page 75 Introduction to Digital VLSI Timing Paths Example clk dffp dffp dffp oe reset out[2:0] aoi211 aoi211 aoi21iand2 trinv trinv trinv d d d q q q qb qb qb 2 1 0 (synnchonous)
- 16. Logic Synthesis Page 76 Introduction to Digital VLSI Timing Path - Input Port to Output Port d q c d q c clk in1 in2 out rst rst rst (async) Comb1 Comb2 set_input_delay set_output_delay set_max_delaycreate_clock possible clock tree
- 17. Logic Synthesis Page 77 Introduction to Digital VLSI Timing Path - Input Port to Register d q c d q c clk in1 in2 out rst rst rst (async) Comb1 Comb2set_input_delay create_clock possible clock tree
- 18. Logic Synthesis Page 78 Introduction to Digital VLSI Timing Path - Register to Output Port d q c d q c clk in1 in2 out rst rst rst (async) Comb1 Comb2 set_output_delay create_clock possible clock tree
- 19. Logic Synthesis Page 79 Introduction to Digital VLSI Timing Path - Register to Register d q c d q c clk in1 in2 out rst rst rst (async) Comb1 Comb2 create_clock possible clock tree
- 20. Logic Synthesis Page 80 Introduction to Digital VLSI Timing Path - Transparent Latch, Input to Output d q en d q c clk in1 in2 out rst rst rst (async) Comb1 Comb2 create_clock possible clock tree Latch DFF set_output_delay set_input_delay clock is active when in2 changes
- 21. Logic Synthesis Page 81 Introduction to Digital VLSI False Timing Path - from Async Set/Reset (not checked) d q c d q c clk in1 in2 out rst rst rst (async) Comb1 Comb2 create_clock possible clock tree
- 22. Logic Synthesis Page 82 Introduction to Digital VLSI Constraints Defining Clocks create_clock [port_pin_list] [-name clock_name] [-period period_value] [-waveform edge_list] • Creating a clock with a specified period automatically constrains the internal (FF -> FF) paths. • -name can be used to give the clock a different name or to create a virtual clock • The edge_list consists of an even number (usually 2) of rising and falling edges; the default is {0 period_value/2} to produce a 50% duty cycle. Example: set cg_host_clk54_period 18 create_clock -period $cg_host_clk54_period cg_host_clk54
- 23. Logic Synthesis Page 83 Introduction to Digital VLSI Defining Clocks (cont.) • An ideal clock uses the specified propagation delays between the clock source and the register clock pins. An ideal clock is used when the actual clock tree has not yet been inserted (pre-layout). The estimated parameters of the clock tree are specified using the following commands. set_clock_latency delay object_list set_clock_uncertainty uncertainty object_list set_clock_transition transition clock_list • A propagated clock uses the calculated propagation delays between the clock source and the register clock pins. This is appropriate when the actual clock tree is included in the model (post-layout). set_propagated_clock object_list
- 24. Logic Synthesis Page 84 Introduction to Digital VLSI Defining Clocks (cont.) set_dont_touch_network object_list • The "dont_touch" attribute is applied to cells and nets in the fanout of the object until register pins are reached. • This is intended for preserving clock trees. set_propagated_clock [all_clocks] set_dont_touch_network [all_clocks]
- 25. Logic Synthesis Page 85 Introduction to Digital VLSI Defining Clocks create_generated_clock -source master_pin [port_pin_list] [-name clock_name] [-divide_by divide_factor] • Defines a clock that is derived within the module from another clock. • Insertion latency is calculated automatically; no need to specify timing explicitly. • -name can be used to give the clock a different name • -divide_by specifis the division factor Example: (divide by 2) create_generated_clock -source clka -divide_by 2 -name clkb [get_pins clkb_reg/q] clka clkb clkb_reg
- 26. Logic Synthesis Page 86 Introduction to Digital VLSI Input Constraints • All input ports (except clocks) should have 2 types of constraints: load and timing set_driving_cell [-cell library_cell_name] port_list • This command specifies the drive capability of the input port in terms of a library cell. It indirectly limits the load seen on the input port. set_max_fanout fanout_value object_list • This command limits the number of components that can be driven by the input port. It is useful for signals that drive many blocks (e.g. global buses, reset). Example: set_driving_cell -cell inv_6 [all_inputs] remove_driving_cell {cg_host_clk54} set normal_fanout 6 set_max_fanout $normal_fanout [all_inputs] set_max_fanout 1 {g_reset}
- 27. Logic Synthesis Page 87 Introduction to Digital VLSI Input Constraints (cont.) set_input_delay -max delay_value [-clock clock_name] port_pin_list set_input_delay -min delay_value_hold [-clock clock_name] port_pin_list • The delay_value is the external delay from the clock edge. This leaves (clock_period - delay_value) for the input signal in the current design. clk clock_period in1 0.5 set_input_delay -max 7.2 -clock clk {in1}7.2 set_input_delay -min 0.5 -clock clk {in1}
- 28. Logic Synthesis Page 88 Introduction to Digital VLSI Output Constraints • All output ports should have 2 types of constraints: load and timing set_load load_value object_list • This command specifies the external load that the output port must drive. Example: # standard load definition of inverter 8X drive according to synopsys library set std_gate_load [load_of $library_name/inv_8/a] # capacitance of 1u from wire_load model parameters in synopsys library set u_wire_load 0.00016 # load variables definition for normal signals set normal_load [expr ($normal_fanout * $std_gate_load) + (1000 * $u_wire_load)] set_load $normal_load [all_outputs]
- 29. Logic Synthesis Page 89 Introduction to Digital VLSI Output Constraints (cont.) set_output_delay -max delay_value_setup [-clock clock_name] port_pin_list set_output_delay -mix delay_value_hold [-clock clock_name] port_pin_list • The delay_value is the external delay to the clock edge. This leaves (clock_period - delay_value) for the output signal in the current design (max path). • 3-state disable not supported well. clk clock_period 5500ps out1 set_output_delay 5500 -max -clock clk {out1} set_output_delay -500 -min -clock clk {out1} 500ps
- 30. Logic Synthesis Page 90 Introduction to Digital VLSI Path Constraints set_max_delay delay_value [-rise | -fall] [-from from_list] [-through through_list] [-to to_list] set_min_delay delay_value [-rise | -fall] [-from from_list] [-through through_list] [-to to_list] • Path start points are usually input ports or register clock pins. • Path end points are usually output ports or register data pins. • Using -from and/or -to with points along a path splits the path into two shorter paths. Use with care! • -rise and -fall select paths whose end point is rising or falling • -through can be used to select among multiple paths with the same start and end points
- 31. Logic Synthesis Page 91 Introduction to Digital VLSI Timing Exceptions set_false_path [-rise | -fall] [-from from_list] [-through through_list] [-to to_list] • Disables timing constraints on specific paths. • Used for paths from signals that are stable during circuit operation: set_false_path -from cg_scan_test • Used for paths between clock domains. (The timing of signals between asynchronous clocks should be correct by design: synchronizers, etc.!) set_false_path -from [get_clocks ig_tsiclk] -to [get_clocks cg_host_clk54]
- 32. Logic Synthesis Page 92 Introduction to Digital VLSI Timing Exceptions (cont.) set_multicycle_path path_multiplier [-rise | -fall] [-setup | -hold] [-from from_list] [-to to_list] [-through through_list] [-start | -end] • Overrides the clock-to-clock timing for paths that may use more than one clock cycle. • To allow N clock cycles for the path, use -setup N and -hold (N-1): set_multicycle_path 2 -setup -from {cg_adr} -to {nx_adr nx_write_en} set_multicycle_path 1 -hold -from {cg_adr} -to {nx_adr nx_write_en} • Details are somewhat complex. Use the manual for other cases.
- 33. Logic Synthesis Page 93 Introduction to Digital VLSI Default - Multicycle setup=1, hold=0 endpoint startpoint setup relationhold relation endpoint startpoint setup relationhold relation Same Clock Shifted Clock
- 34. Logic Synthesis Page 94 Introduction to Digital VLSI Multicycle Path setup=2, hold=0 endpoint startpoint setup relation hold relation endpoint startpoint setup relation hold relation Same Clock Shifted Clock
- 35. Logic Synthesis Page 95 Introduction to Digital VLSI Multicycle Path setup=2, hold=1 endpoint startpoint setup relationhold relation endpoint startpoint setup relation hold relation Same Clock Shifted Clock
- 36. Logic Synthesis Page 96 Introduction to Digital VLSI Multicycle Path, Multi Frequency, Default Setup=1, Hold=1 endpoint startpoint setup relation hold relation endpoint startpoint setup relation hold relation Fast to Slow Slow to Fast By default - setup timing is related to the Endpoint clock and hold timing related to the Startpoint clock
- 37. Logic Synthesis Page 97 Introduction to Digital VLSI Multicycle Path, Multi Frequency, Setup=2, Hold=0, 3 endpoint startpoint setup relation hold relation Fast to Slow, Step 1 set_multicycle_path 2 -from Start -to End endpoint startpoint setup relation hold relation Fast to Slow, Step 2 set_multicycle_path 3 -hold -from Start -to End (implicitly hold becomes zero since no -setup flag used) 0 1 2 3 (hold reference point) Can alse be: set_multicycle_path 1 -hold -end -from Start -to End
- 38. Logic Synthesis Page 98 Introduction to Digital VLSI Multicycle Path, Multi Frequency, Setup by Startpoint endpoint startpoint setup relation hold relation Fast to Slow set_multicycle_path 2 -setup -start -from Start -to End Similarily - hold can be moved from Startpoint (default) to Endpoint: set_multicycle_path 1 -hold -end -from Start -to End endpoint startpoint setup relation hold relation Fast to Slow set_multicycle_path 2 -setup -start -from Start -to End
- 39. Logic Synthesis Page 99 Introduction to Digital VLSI Timing Exceptions (cont.) Using ’-through’ set_multicycle_path 2 -setup -through {a b c} -through {d e} • Selects all paths that pass through (a OR b OR c) AND THEN (d OR e)
- 40. Logic Synthesis Page 100 Introduction to Digital VLSI Area Optimization set_max_area [-ignore_tns] area • If the max_area is not defined, DC will do minimal area optimization. This is appropriate if the area is not important since it reduces the compile time. set_max_area 0 • This command will cause DC to reduce the area as much as possible w/o increasing any timing violation (1998.02-). This is recommended for most designs at MSIL where the optimization priority is: (1) timing and (2) area set_max_area -ignore_tns 0 • This command will cause DC to reduce the area as much as possible w/o increasing the worst timing violation of a path group, but may increase delay violations below the worst timing violations. Not Recommended.
- 41. Logic Synthesis Page 101 Introduction to Digital VLSI Compile compile [-map_effort low | medium | high] [-incremental_mapping] [-verify] [-scan] • The compile command performs the mapping and optimization of the current design taking into account the constraints. • The map_effort specifies which algorithms should be used. Higher effort produces better results, but requires more run time. - Low effort can be used to check constraints. Medium effort is the default. High effort should be used for final synthesis to take full advantage of the tool. • -incremental_mapping starts with the current mapping and optimizes where there are violations. Otherwise, an additional compile re-maps the design. • -verify checks the logic of the netlist vs. the equations derived from the RTL (sometimes may take very long time !) • -scan inserts scan registers - generate a “scan-ready” design. SDI is tied to Q, and SE is tied to 0. Scan chain is not stiched. • More options will be discussed later.
- 42. Logic Synthesis Page 102 Introduction to Digital VLSI Compile Strategy • Top-Down: Use top level constraints and get internally the sub- design to sub-design constaints in one pass. May need flattening the design or uniquifying blocks. • Bottom-up: compile a sub-design with its own constraints, then go to the top level, apply top level constraints and compile incrementally (set_dont_touch attribute on identical compiled sub- blocks or uniquify them. In case of dont_touch, top level compile may not be incremental). How do we choose the compilation strategy ? >> There is no “Golden” script for that.
- 43. Logic Synthesis Page 103 Introduction to Digital VLSI Sample Synopsys Scripts set company "MSIL"; echo "Running ptec_synopsys_dc.setup" alias h history set verilogout_no_tri "true" set_fix_multiple_port_nets -all set bus_naming_style "%s_%d" set compile_instance_name_prefix "z"
- 44. Logic Synthesis Page 104 Introduction to Digital VLSI Sample Synopsys Scripts (cont.) source -echo -verbose ../../examples/general_tcl/ppcec_libs.include.tcl set suppress_errors {"EQN-19" "UID-109" "UID-101"} read_verilog try.verilog source -echo -verbose ../../examples/general/ppcec_general.include source -echo -verbose try.constraints set_max_transition 4000 out1 set_dont_use {adv_lib_comb_udr2_85_wcs_v3t135_3c/*a} set_dont_use {adv_lib_latch_udr2_85_wcs_v3t135_3c/*b} remove_attribute {adv_lib_latch_udr2_85_wcs_v3t135_3c/dff*b} dont_use set_max_area 5500000 compile -map_effort medium -verify -verify_effort medium compile -incremental_mapping -map_effort high -verify -verify_effort medium source -echo -verbose ../../examples/general/report.include.tcl write_file -format verilog -output try.ver quit
- 45. Logic Synthesis Page 105 Introduction to Digital VLSI Sample Synopsys Scripts (cont.) Example of Synopsys constraints file current_design try create_clock cl_xt1 -period 14000 -waveform {0 7000} create_clock cl_xt2 -period 14000 -waveform {7000 14000} create_clock cl_xt3 -period 14000 -waveform {10500 17500} remove_driving_cell {cl_xt1 cl_xt2} set_propagated_clock {cl_xt1 cl_xt2} set_dont_touch_network {cl_xt1 cl_xt2} set_false_path -from {cx_reset} # no paths start on the block’s async. reset set_multicycle_path 2 -from in1 -to [get_clocks cl_xt1] set_load 0.2 [all_outputs] group_path -weight 50 -name LATEARRIVAL -critical_range 10000 -to clr set_input_delay 1000 -clock cl_xt1 {cl_lb_data_sel} set_input_delay 6500 -clock cl_xt2 {cl_iq_fld_sng cl_iq_l_fp_wr} set_output_delay 3000 -clock cl_xt2 -clock_fall {cl_dl_fp_snorm cl_dl_ld_dnorm} set_dont_touch { z_cell_* } set_input_delay 6500 -clock cl_xt2 {cl_iq_l_fp_wr}
- 46. Logic Synthesis Page 106 Introduction to Digital VLSI Wire Load Models set_wire_load_model -name wire_load_model_name • Wire load models are used to estimate capacitance, resistance, and area of nets prior to layout. library (wire_load_models_90) { pulling_resistance_unit : "1ohm" ; capacitive_load_unit (1, pf) ; wire_load ( small_block ) { resistance : 0 ; capacitance : 0.0000250 ; area : 9 ; fanout_length (1, 500) ; fanout_length (2, 950) ; slope : 500 ; } wire_load ( medium_block ) { resistance : 0 ; capacitance : 0.0000250 ; area : 9 ; fanout_length (1, 1000) ; slope : 1000 ; } }
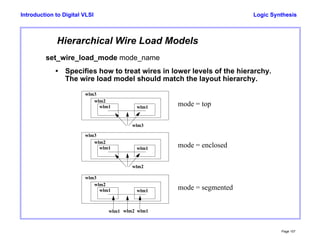
- 47. Logic Synthesis Page 107 Introduction to Digital VLSI Hierarchical Wire Load Models set_wire_load_mode mode_name • Specifies how to treat wires in lower levels of the hierarchy. The wire load model should match the layout hierarchy. wlm1 wlm1 wlm2 wlm3 mode = top wlm3 wlm1 wlm1 wlm2 wlm3 mode = enclosed wlm2 wlm1 wlm1 wlm2 wlm3 mode = segmented wlm1 wlm1wlm2
- 48. Logic Synthesis Page 108 Introduction to Digital VLSI Automatic Wire Load Selection • DC can automatically select the wire load model according to block size. • A table of models as a function of size is included in the library. • set auto_wire_load_selection true library (cdr2_70a_wlm) { wire_load_selection(CDR2_15_AREA) { wire_load_from_area( 0 , 50000, "CDR2_15_0Kto50K_DW01" ); wire_load_from_area( 50000 , 75000, "CDR2_15_50Kto75K" ); wire_load_from_area( 75000 , 100000, "CDR2_15_75Kto100K" ); wire_load_from_area( 100000 , 150000, "CDR2_15_100Kto150K" ); wire_load_from_area( 150000 , 200000, "CDR2_15_150Kto200K" ); wire_load_from_area( 200000 , 300000, "CDR2_15_200Kto300K" ); wire_load_from_area( 300000 , 600000, "CDR2_15_300Kto600K" ); wire_load_from_area( 600000 , 700000, "CDR2_15_600Kto700K" ); wire_load_from_area( 700000 , 800000, "CDR2_15_700Kto800K" ); wire_load_from_area( 800000 , 3000000, "CDR2_15_800Kto3000K" ); wire_load_from_area( 3000000 , 5500000, "CDR2_15_3000Kto5500K" ); wire_load_from_area( 5500000 , 8000000, "CDR2_15_5500Kto8000K" ); wire_load_from_area( 8000000 , 10000000, "CDR2_15_8000Kto10000K" ); wire_load_from_area( 10000000 , 20000000, "CDR2_15_10000Kto20000K" ); } default_wire_load_selection : "CDR2_15_AREA" ; default_wire_load_mode : enclosed ; }
- 49. Logic Synthesis Page 109 Introduction to Digital VLSI Design Rule Constraints • set_max_transition Set the maximal transition time (low-high and high-low) for a port or a design. The library defines the transition measure points (i.e: 10%- 90%, 20%-80%). Delay of library cells as well as their output transition depends on this value. Also, setup and hold time of sequential cells is affected by it. • set_max_fanout In all libraries a cell input has a fanout load value. In most cases it’s 1, but can be a different value. Compile attempts to ensure that the sum of the fanout_load attributes for input pins on nets driven by the specified ports or all nets in the specified design is less than the given value. • set_max_capacitance Limits the allowed capacitance on input, output or bidirectional ports and/or designs.
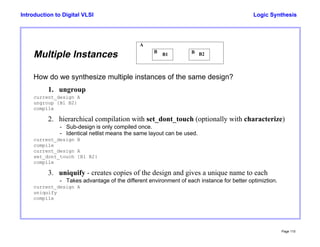
- 50. Logic Synthesis Page 110 Introduction to Digital VLSI Multiple Instances How do we synthesize multiple instances of the same design? 1. ungroup current_design A ungroup {B1 B2} compile 2. hierarchical compilation with set_dont_touch (optionally with characterize) - Sub-design is only compiled once. - Identical netlist means the same layout can be used. current_design B compile current_design A set_dont_touch {B1 B2} compile 3. uniquify - creates copies of the design and gives a unique name to each - Takes advantage of the different environment of each instance for better optimiztion. current_design A uniquify compile B B A B1 B2
- 51. Logic Synthesis Page 111 Introduction to Digital VLSI Integration How do we integrate blocks that were synthesized separately? propagate_constraints [-false_path] [-multicycle_path] [-gate_clock] [-all] [-verbose] [-dont_apply] [-design <design_list>] [-output <file_name>] • This command translates the constraints that were applied to a lower-level instance and applies them to the current design. Clock definitions should not be propagated if they occur on multiple blocks. • -verbose option shows each constraint and its source • -dont_apply option checks for problems, but doesn’t apply the constraints • -output option writes the constraints to file_name • -gate_clock required in power compiler flow to move clock setup and hold check previously specified with the set_clock_gating_check command.
- 52. Logic Synthesis Page 112 Introduction to Digital VLSI Integration (cont.) compile -top • The -top option does a compile that only fixes design rule violations and timing violations that cross the top level. No mapping or area optimization is performed. • set compile_top_all_paths true can be used to fix all timing violations
- 53. Logic Synthesis Page 113 Introduction to Digital VLSI Integration (cont.) current_design B source B.con current_design C source C.con current_design A create_clock ... propagate_constraints -verbose compile -top Example: set_false_path -from cg_scan_test # in n_mem.con is changed to: set_false_path -through [get_pins "n_mem/cg_scan_test"] • -from/to <port> is changed to -through <pin> A B C
- 54. Logic Synthesis Page 114 Introduction to Digital VLSI Advanced Commands The get_* Commands • Returns a collection of objects when used standalone: ({item1 item2 ...}). • Should be used when several object types have the same name (e.g. same reference and net names).
- 55. Logic Synthesis Page 115 Introduction to Digital VLSI get_* Command Syntax get_xxx [patterns] • xxx: • Specifies the type of object to be found. The value of type can be: designs clocks ports references cells nets pins libs lib_cells ib_pins • patterns (optional): • List of names (including wildcards: *) of the design or library objects in dc_shell to be found. • If name_list is not specified, then all objects of the specified type are returned. • If no matches are found, returns an empty string (with a warning).
- 56. Logic Synthesis Page 116 Introduction to Digital VLSI get_* Function Examples dffrpc ind2c INPUT1 INPUT2 OUTPUT1 D C RB Q in1 in2 clk reset int1 out1 (i1) (i8) • get_ports {"clk", "in1", "in2", "reset", "out1"} • get_cells {"i1", "i8"} • get_references {"ind2c", "dffrpc"} • get_references dff* {"dffrpc"} • get_nets {"in1", "clk", "reset", "in2", "int1", "out1"} • set_dont_touch [get_designs]
- 57. Logic Synthesis Page 117 Introduction to Digital VLSI The filter_collection Command • The filter_collection command takes a collection of objects and a filter expression (a list of attribute-value relations), and returns a new collection containing only the objects that have the defined attribute values. • A filter expression is composed of conditional expressions, such as "@port_direction == inout", or "@rise_delay > 1.3". A filter expression is enclosed in double quotes (" "): @attribute_name operator value • -regexp flag enables the use of real regular expressions. -nocase make the regular expression case insensitive Example: set a [ filter_collection [ get_cells *] "is_hierarchical == true"] {"Adder1", "Adder2"}
- 58. Logic Synthesis Page 118 Introduction to Digital VLSI filter_collection Command Syntax filter_collection collection "filter_expression" • List all bidirectional ports: dc_shell-t> filter_collection [all_inputs] "@port_direction == inout" {INOUT0, INOUT1} • List all PLA designs in memory: dc_shell-t> filter_collection [get_designs] "@design_type == pla" {PLA_1, PLA_@} set_attribute command may be used to create user-defined attributes: • To add a numeric attribute to some cells: dc_shell> set_attribute {cell70 cell88 cell95} kuku 6.5 dc_shell> filter_collection [get_cells] "@kuku == 6.5" A collection can also be filtered when it is created: get_ports -filter "@port_direction == inout"
- 59. Logic Synthesis Page 119 Introduction to Digital VLSI Synopsys script using get_* and filter_collection • New commands: foreach_in_collection, if # add dont_touch attribute to all the instantiations of cl1rspoX latches foreach_in_collection mod [get_designs] { set current_design $mod set mashcell [get_cells "x_cell_*"] if {$mashcell != ""} { set_dont_touch [filter_collection $mashcell "@ref_name == cl1rspob || @ref_name == cl1rspoc || @ref_name == cl1rspod"] } } set current_design top
- 60. Logic Synthesis Page 120 Introduction to Digital VLSI Check Before Compile • report_port - check set_load, set_driving_cell, set_input_delay, set_output_delay Pin Wire Max Max Connection Port Dir Load Load Trans Cap Class Attrs -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ak_rx_req_b in 0.0000 0.0000 -- -- -- ca_clk27 in 0.0000 0.0000 -- -- -- ... ka_rx_clk out 1.8396 0.0000 2.00 -- -- ka_rx_data out 1.8396 0.0000 -- -- -- ka_rx_sync out 1.8396 0.0000 -- -- -- ... Input Delay Min Max Related Max Input Port Rise Fall Rise Fall Clock Fanout -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ak_rx_req_b 1.00 1.00 18.50 18.50 ca_clk27 6.00 ... Output Delay Min Max Related Fanout Output Port Rise Fall Rise Fall Clock Load -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ka_rx_sync 9.00 9.00 9.00 9.00 cg_host_clk54 0.00
- 61. Logic Synthesis Page 121 Introduction to Digital VLSI • report_design- check wire loads and operating conditions Library(s) Used: cdr2PwcsV300T120 (File: /home/mercy2/orion_home/projects/orion/01/uds/cdr2-70-ang/ synopsys/technology/cdr2PwcsV300T120.db) B000032W32D103B (File: /home/mercy2/orion_home/projects/orion/01/blocks/orion_mem/ des_rel/ram/cdr2/synopsys/technology/wcsV300T120/B000032W32D103B.db) Local Link Library: {cdr2PwcsV300T120.db} Wire Loading Model: Selected manually by the user. Name : DEMUX Location : demux_wlm Resistance : 7e-05 Capacitance : 0.00016 Area : 0 Slope : 120.88 Fanout Length Points Average Cap Std Deviation -------------------------------------------------------------- 1 96.73 2 215.06 ... Wire Loading Model Mode: segmented. ...
- 62. Logic Synthesis Page 122 Introduction to Digital VLSI • report_clocks- check that clocks were properly defined Attributes: d - dont_touch_network f - fix_hold p - propagated_clock Clock Period Waveform Attrs Sources -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ca_clk27 37.00 {0 18.5} d {ca_clk27} cg_host_clk54 18.00 {0 9} d {cg_host_clk54} cg_mem_clk 9.20 {0 4.6} d {cg_mem_clk} -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Rise Fall Min Rise Min fall Uncertainty Object Delay Delay Delay Delay Plus Minus -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- cg_mem_clk - - - - 0.60 0.60 cg_host_clk54 - - - - 0.60 0.60 ca_clk27 - - - - 0.60 0.60
- 63. Logic Synthesis Page 123 Introduction to Digital VLSI • report_attribute -design- lists all attributes set for the design Design Object Type Attribute Name Value -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- k_aout k_aout design hdl_canonical_params k_aout k_aout design hdl_parameters k_aout k_aout design hdl_template k_aout k_aout k_aout design _obj_name_type 0 k_aout k_aout design wire_load_selection_type 1 k_aout k_aout design wire_load_model_mode top k_aout k_aout design max_area 0.000000 k_aout k_aout design fix_multiple_port_nets feedthroughs constants outputs buffer_constants k_aout ak_rx_req_b port driving_cell_rise inv_6 k_aout ak_rx_req_b port driving_cell_fall inv_6 k_aout ak_rx_req_b port max_fanout 6.000000 k_aout cg_dmux_reset port driving_cell_rise inv_6 k_aout cg_dmux_reset port driving_cell_fall inv_6 k_aout cg_dmux_reset port max_fanout 1.000000 k_aout cg_scan_en port driving_cell_rise inv_6 k_aout cg_scan_en port driving_cell_fall inv_6 k_aout cg_scan_en port max_fanout 6.000000 k_aout cg_scan_test port driving_cell_rise inv_6 k_aout cg_scan_test port driving_cell_fall inv_6 k_aout cg_scan_test port max_fanout 6.000000 k_aout ka_rx_clk port max_transition 2.000000 ...
- 64. Logic Synthesis Page 124 Introduction to Digital VLSI • report_timing_requirements- lists all multicycle and false paths, max_delay and min_delay exceptions • report_timing_requirements -ignore- lists all ignored multicycle and false paths From Through To Setup Hold -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- cg_scan_en * * max=18 min=0 cg_scan_test * * FALSE FALSE cg_host_clk54 * cg_mem_clk FALSE FALSE cg_mem_clk * cg_host_clk54 FALSE FALSE ca_clk27 * cg_host_clk54 FALSE FALSE cg_host_clk54 * ca_clk27 FALSE FALSE
- 65. Logic Synthesis Page 125 Introduction to Digital VLSI Check After Compile • report_constraint -all_violators -verbose- all constraint violations • report_timing -path full -input_pins- detailed timing reports - check if paths are reasonable • Example after physical compiler placement: report_timing -path full -input_pins -physical -nets -trans -input_pins • Timing reports will be presented in detail in the next section.
- 66. Logic Synthesis Page 126 Introduction to Digital VLSI • report_net - check fanout and load on nets to see if they’re reasonable Attributes: d - dont_touch Net Fanout Fanin Load Resistance Pins Attributes -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ... ao_mem/DOi_26 1 1 0.13 0.05 2 ao_mem/DOi_27 1 1 0.13 0.05 2 ao_mem/DOi_28 1 1 0.13 0.05 2 ao_mem/DOi_29 1 1 0.13 0.05 2 ao_mem/DOi_30 1 1 0.13 0.05 2 ao_mem/DOi_31 1 1 0.13 0.05 2 ca_clk27 3 1 0.15 0.03 4 d cg_dmux_reset 1 1 0.08 0.01 2 cg_host_clk54 175 1 5.42 1.55 176 d cg_mem_clk 11 1 0.55 0.15 12 d ... -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total 1823 nets 4669 1823 245.21 56.04 6492 Maximum 175 1 5.42 1.55 176 Average 2.56 1.00 0.13 0.03 3.56
- 67. Logic Synthesis Page 127 Introduction to Digital VLSI • report_resources- check resource implementation (adder is rpl or cla) and sharing Resource Sharing Report for design k_aout =============================================================================== | | | | Contained | | | Resource | Module | Parameters | Resources | Contained Operations | =============================================================================== | r199 | DW01_add | width=15 | | | | | | k_54rnd/abrp_add_function_216/add_455 | | r205 | DW01_sub | width=14 | | | | | k_54rnd/abrp_add_function_223/abrp_add_function_216/sub_453 | | r421 | DW01_add | width=20 | | k_54rnd/add_372 | | r528 | DW01_cmp2 | width=15 | | | | | | k_54rnd/abrp_add_function_216/gt_464 | | r673 | DW01_sub | width=14 | | k_54rnd/sub_304 | ... Implementation Report ============================================================================= | | | Current | Set | | Cell | Module | Implementation | Implementation | ============================================================================= | k_54rnd/abrl_sub_function_245/gt_566 | DW01_cmp2 | rpl | | | k_54rnd/abrl_sub_function_245/gt_572 | DW01_cmp2 | rpl | | | k_54rnd/abrl_sub_function_245/sub_567 | DW01_sub | rpl | | | k_54rnd/abrl_sub_function_245/sub_573 | DW01_sub | rpl | |



![Logic Synthesis
Page 63
Introduction to Digital VLSI
Some Tcl Syntax
dc_shell-t> set a 5
5
dc_shell-t> set b {c d $a [list $a z]}
c d $a [list $a z]
dc_shell-t> set b [list c d $a [list $a z]]
c d 5 {5 z}
dc_shell-t> set delay [expr .5 * $base_delay]
• [cmd] — returns the result of the command: like ‘cmd‘ in csh.
• {} — creates a list without variable or command substitution
• Use the list command when variable and/or command subtitution is required.
• Use the expr command for all arithmetic expressions.
Many Tcl resources (for advanced scripts): http://tcl.activestate.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsynthesisflowandcommandsindigitalvlsi-200817143917/85/Basic-synthesis-flow-and-commands-in-digital-VLSI-3-320.jpg)



![Logic Synthesis
Page 67
Introduction to Digital VLSI
Example of Libraries include file
set search_path [concat $search_path
/usr/cad/library/udr2/synopsys_1998.02
~ppcec/synopsys/lib_1998.02]
set target_library {
adv_lib_3state_udr2_85_wcs_v3t135_3c.db
adv_lib_comb_udr2_85_wcs_v3t135_3c.db
adv_lib_dff_udr2_85_wcs_v3t135_3c.db
adv_lib_latch_udr2_85_wcs_v3t135_3c.db
msil_udr2_85_wcs_v3t150.db
ppcec_prv_udr2_85_wcs_v3t135.db
clock_driver.db
wire_load_models.db
}
set link_library { "*"
adv_lib_3state_udr2_85_wcs_v3t135_3c.db
adv_lib_comb_udr2_85_wcs_v3t135_3c.db
adv_lib_dff_udr2_85_wcs_v3t135_3c.db
adv_lib_latch_udr2_85_wcs_v3t135_3c.db
adv_lib_latch_old_udr2_85_wcs_v3t135_3c.db
msil_udr2_85_wcs_v3t150.db
ppcec_prv_udr2_85_wcs_v3t135.db
clock_driver.db
wire_load_models.db
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsynthesisflowandcommandsindigitalvlsi-200817143917/85/Basic-synthesis-flow-and-commands-in-digital-VLSI-7-320.jpg)
![Logic Synthesis
Page 68
Introduction to Digital VLSI
Design Read
read_file [-format input_format] [-define macro_names] file_list
• -format input_format
• db — Synopsys internal database format (smaller and loads faster than netlist)
• verilog — RTL or gate-level Verilog netlist
• -define macro_names: enables setting defined values used in the
Verilog source code. If you code uses ‘ifdef statements, you should
set: hdlin_enable_vpp=”true”
• read_db or read_verilog are equivalent to read_file -format xxx
Example:
read_file -format verilog -define BLOCK_A_DEF { block_a.v block_b.v }
current_design [design]
• returns or sets the current working design
• Note: The read command sets the last module read as the current
design.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsynthesisflowandcommandsindigitalvlsi-200817143917/85/Basic-synthesis-flow-and-commands-in-digital-VLSI-8-320.jpg)
![Logic Synthesis
Page 69
Introduction to Digital VLSI
Design Read by Analyze and Elaborate
analyze & elaborate flow can be for power compiler clock gating, or for set-
ting a parametric design selection
analyze [-format input_format] [-update] [-define macro_names] file_list
• Analyzes HDL files and stores the intermediate format for the HDL
description in the specified library. Similar to first stage of read_file.
Example:
analyze -f verilog -update { block_a.v block_b.v }
elaborate top_design
[-parameters param_list] [-architecture arch_name]
[-update] [-gate_clock]
Example:
elaborate -update mult -parameters "N=8,M=3" -gate_clock](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsynthesisflowandcommandsindigitalvlsi-200817143917/85/Basic-synthesis-flow-and-commands-in-digital-VLSI-9-320.jpg)
![Logic Synthesis
Page 70
Introduction to Digital VLSI
Design Write
write_file [-format output_format] [-hierarchy] [-output output_file_name]
[design_list]
• output_format can be db or verilog as above
• -hierarchy writes the entire hierarchy from the named design down;
otherwise, only the top-level module is saved
• The default for design_list is the current design.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsynthesisflowandcommandsindigitalvlsi-200817143917/85/Basic-synthesis-flow-and-commands-in-digital-VLSI-10-320.jpg)




![Logic Synthesis
Page 75
Introduction to Digital VLSI
Timing Paths Example
clk
dffp
dffp
dffp
oe
reset
out[2:0]
aoi211
aoi211
aoi21iand2
trinv
trinv
trinv
d
d
d q
q
q
qb
qb
qb
2
1
0
(synnchonous)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsynthesisflowandcommandsindigitalvlsi-200817143917/85/Basic-synthesis-flow-and-commands-in-digital-VLSI-15-320.jpg)






![Logic Synthesis
Page 82
Introduction to Digital VLSI
Constraints
Defining Clocks
create_clock [port_pin_list] [-name clock_name] [-period period_value]
[-waveform edge_list]
• Creating a clock with a specified period automatically constrains the
internal (FF -> FF) paths.
• -name can be used to give the clock a different name or to create a
virtual clock
• The edge_list consists of an even number (usually 2) of rising and
falling edges; the default is {0 period_value/2} to produce a 50% duty
cycle.
Example:
set cg_host_clk54_period 18
create_clock -period $cg_host_clk54_period cg_host_clk54](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsynthesisflowandcommandsindigitalvlsi-200817143917/85/Basic-synthesis-flow-and-commands-in-digital-VLSI-22-320.jpg)

![Logic Synthesis
Page 84
Introduction to Digital VLSI
Defining Clocks (cont.)
set_dont_touch_network object_list
• The "dont_touch" attribute is applied to cells and nets in the fanout
of the object until register pins are reached.
• This is intended for preserving clock trees.
set_propagated_clock [all_clocks]
set_dont_touch_network [all_clocks]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsynthesisflowandcommandsindigitalvlsi-200817143917/85/Basic-synthesis-flow-and-commands-in-digital-VLSI-24-320.jpg)
![Logic Synthesis
Page 85
Introduction to Digital VLSI
Defining Clocks
create_generated_clock -source master_pin [port_pin_list]
[-name clock_name] [-divide_by divide_factor]
• Defines a clock that is derived within the module from another clock.
• Insertion latency is calculated automatically; no need to specify
timing explicitly.
• -name can be used to give the clock a different name
• -divide_by specifis the division factor
Example: (divide by 2)
create_generated_clock -source clka -divide_by 2 -name clkb [get_pins clkb_reg/q]
clka
clkb
clkb_reg](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsynthesisflowandcommandsindigitalvlsi-200817143917/85/Basic-synthesis-flow-and-commands-in-digital-VLSI-25-320.jpg)
![Logic Synthesis
Page 86
Introduction to Digital VLSI
Input Constraints
• All input ports (except clocks) should have 2 types of constraints:
load and timing
set_driving_cell [-cell library_cell_name] port_list
• This command specifies the drive capability of the input port in
terms of a library cell. It indirectly limits the load seen on the input
port.
set_max_fanout fanout_value object_list
• This command limits the number of components that can be driven
by the input port. It is useful for signals that drive many blocks (e.g.
global buses, reset).
Example:
set_driving_cell -cell inv_6 [all_inputs]
remove_driving_cell {cg_host_clk54}
set normal_fanout 6
set_max_fanout $normal_fanout [all_inputs]
set_max_fanout 1 {g_reset}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsynthesisflowandcommandsindigitalvlsi-200817143917/85/Basic-synthesis-flow-and-commands-in-digital-VLSI-26-320.jpg)
![Logic Synthesis
Page 87
Introduction to Digital VLSI
Input Constraints (cont.)
set_input_delay -max delay_value [-clock clock_name] port_pin_list
set_input_delay -min delay_value_hold [-clock clock_name] port_pin_list
• The delay_value is the external delay from the clock edge. This
leaves (clock_period - delay_value) for the input signal in the current
design.
clk
clock_period
in1
0.5
set_input_delay -max 7.2 -clock clk {in1}7.2
set_input_delay -min 0.5 -clock clk {in1}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsynthesisflowandcommandsindigitalvlsi-200817143917/85/Basic-synthesis-flow-and-commands-in-digital-VLSI-27-320.jpg)
![Logic Synthesis
Page 88
Introduction to Digital VLSI
Output Constraints
• All output ports should have 2 types of constraints: load and timing
set_load load_value object_list
• This command specifies the external load that the output port must
drive.
Example:
# standard load definition of inverter 8X drive according to synopsys library
set std_gate_load [load_of $library_name/inv_8/a]
# capacitance of 1u from wire_load model parameters in synopsys library
set u_wire_load 0.00016
# load variables definition for normal signals
set normal_load [expr ($normal_fanout * $std_gate_load) + (1000 * $u_wire_load)]
set_load $normal_load [all_outputs]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsynthesisflowandcommandsindigitalvlsi-200817143917/85/Basic-synthesis-flow-and-commands-in-digital-VLSI-28-320.jpg)
![Logic Synthesis
Page 89
Introduction to Digital VLSI
Output Constraints (cont.)
set_output_delay -max delay_value_setup [-clock clock_name] port_pin_list
set_output_delay -mix delay_value_hold [-clock clock_name] port_pin_list
• The delay_value is the external delay to the clock edge. This leaves
(clock_period - delay_value) for the output signal in the current
design (max path).
• 3-state disable not supported well.
clk
clock_period
5500ps
out1
set_output_delay 5500 -max -clock clk {out1}
set_output_delay -500 -min -clock clk {out1}
500ps](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsynthesisflowandcommandsindigitalvlsi-200817143917/85/Basic-synthesis-flow-and-commands-in-digital-VLSI-29-320.jpg)
![Logic Synthesis
Page 90
Introduction to Digital VLSI
Path Constraints
set_max_delay delay_value [-rise | -fall]
[-from from_list] [-through through_list] [-to to_list]
set_min_delay delay_value [-rise | -fall]
[-from from_list] [-through through_list] [-to to_list]
• Path start points are usually input ports or register clock pins.
• Path end points are usually output ports or register data pins.
• Using -from and/or -to with points along a path splits the path into
two shorter paths. Use with care!
• -rise and -fall select paths whose end point is rising or falling
• -through can be used to select among multiple paths with the same
start and end points](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsynthesisflowandcommandsindigitalvlsi-200817143917/85/Basic-synthesis-flow-and-commands-in-digital-VLSI-30-320.jpg)
![Logic Synthesis
Page 91
Introduction to Digital VLSI
Timing Exceptions
set_false_path [-rise | -fall] [-from from_list] [-through through_list] [-to to_list]
• Disables timing constraints on specific paths.
• Used for paths from signals that are stable during circuit operation:
set_false_path -from cg_scan_test
• Used for paths between clock domains. (The timing of signals
between asynchronous clocks should be correct by design:
synchronizers, etc.!)
set_false_path -from [get_clocks ig_tsiclk] -to [get_clocks cg_host_clk54]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsynthesisflowandcommandsindigitalvlsi-200817143917/85/Basic-synthesis-flow-and-commands-in-digital-VLSI-31-320.jpg)
![Logic Synthesis
Page 92
Introduction to Digital VLSI
Timing Exceptions (cont.)
set_multicycle_path path_multiplier [-rise | -fall] [-setup | -hold]
[-from from_list] [-to to_list] [-through through_list]
[-start | -end]
• Overrides the clock-to-clock timing for paths that may use more than
one clock cycle.
• To allow N clock cycles for the path, use -setup N and -hold (N-1):
set_multicycle_path 2 -setup -from {cg_adr} -to {nx_adr nx_write_en}
set_multicycle_path 1 -hold -from {cg_adr} -to {nx_adr nx_write_en}
• Details are somewhat complex. Use the manual for other cases.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsynthesisflowandcommandsindigitalvlsi-200817143917/85/Basic-synthesis-flow-and-commands-in-digital-VLSI-32-320.jpg)







![Logic Synthesis
Page 100
Introduction to Digital VLSI
Area Optimization
set_max_area [-ignore_tns] area
• If the max_area is not defined, DC will do minimal area optimization.
This is appropriate if the area is not important since it reduces the
compile time.
set_max_area 0
• This command will cause DC to reduce the area as much as possible
w/o increasing any timing violation (1998.02-). This is recommended
for most designs at MSIL where the optimization priority is: (1) timing
and (2) area
set_max_area -ignore_tns 0
• This command will cause DC to reduce the area as much as possible
w/o increasing the worst timing violation of a path group, but may
increase delay violations below the worst timing violations.
Not Recommended.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsynthesisflowandcommandsindigitalvlsi-200817143917/85/Basic-synthesis-flow-and-commands-in-digital-VLSI-40-320.jpg)
![Logic Synthesis
Page 101
Introduction to Digital VLSI
Compile
compile [-map_effort low | medium | high] [-incremental_mapping] [-verify]
[-scan]
• The compile command performs the mapping and optimization of the
current design taking into account the constraints.
• The map_effort specifies which algorithms should be used. Higher
effort produces better results, but requires more run time.
- Low effort can be used to check constraints. Medium effort is the default. High effort
should be used for final synthesis to take full advantage of the tool.
• -incremental_mapping starts with the current mapping and optimizes
where there are violations. Otherwise, an additional compile re-maps
the design.
• -verify checks the logic of the netlist vs. the equations derived from
the RTL (sometimes may take very long time !)
• -scan inserts scan registers - generate a “scan-ready” design. SDI is
tied to Q, and SE is tied to 0. Scan chain is not stiched.
• More options will be discussed later.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsynthesisflowandcommandsindigitalvlsi-200817143917/85/Basic-synthesis-flow-and-commands-in-digital-VLSI-41-320.jpg)



![Logic Synthesis
Page 105
Introduction to Digital VLSI
Sample Synopsys Scripts (cont.)
Example of Synopsys constraints file
current_design try
create_clock cl_xt1 -period 14000 -waveform {0 7000}
create_clock cl_xt2 -period 14000 -waveform {7000 14000}
create_clock cl_xt3 -period 14000 -waveform {10500 17500}
remove_driving_cell {cl_xt1 cl_xt2}
set_propagated_clock {cl_xt1 cl_xt2}
set_dont_touch_network {cl_xt1 cl_xt2}
set_false_path -from {cx_reset} # no paths start on the block’s async. reset
set_multicycle_path 2 -from in1 -to [get_clocks cl_xt1]
set_load 0.2 [all_outputs]
group_path -weight 50 -name LATEARRIVAL -critical_range 10000 -to clr
set_input_delay 1000 -clock cl_xt1 {cl_lb_data_sel}
set_input_delay 6500 -clock cl_xt2 {cl_iq_fld_sng cl_iq_l_fp_wr}
set_output_delay 3000 -clock cl_xt2 -clock_fall {cl_dl_fp_snorm cl_dl_ld_dnorm}
set_dont_touch { z_cell_* }
set_input_delay 6500 -clock cl_xt2 {cl_iq_l_fp_wr}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsynthesisflowandcommandsindigitalvlsi-200817143917/85/Basic-synthesis-flow-and-commands-in-digital-VLSI-45-320.jpg)



![Logic Synthesis
Page 111
Introduction to Digital VLSI
Integration
How do we integrate blocks that were synthesized separately?
propagate_constraints [-false_path] [-multicycle_path] [-gate_clock]
[-all] [-verbose] [-dont_apply]
[-design <design_list>] [-output <file_name>]
• This command translates the constraints that were applied to a
lower-level instance and applies them to the current design. Clock
definitions should not be propagated if they occur on multiple
blocks.
• -verbose option shows each constraint and its source
• -dont_apply option checks for problems, but doesn’t apply the constraints
• -output option writes the constraints to file_name
• -gate_clock required in power compiler flow to move clock setup and hold
check previously specified with the set_clock_gating_check command.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsynthesisflowandcommandsindigitalvlsi-200817143917/85/Basic-synthesis-flow-and-commands-in-digital-VLSI-51-320.jpg)

![Logic Synthesis
Page 113
Introduction to Digital VLSI
Integration (cont.)
current_design B
source B.con
current_design C
source C.con
current_design A
create_clock ...
propagate_constraints -verbose
compile -top
Example:
set_false_path -from cg_scan_test # in n_mem.con
is changed to:
set_false_path
-through [get_pins "n_mem/cg_scan_test"]
• -from/to <port> is changed to -through <pin>
A
B C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsynthesisflowandcommandsindigitalvlsi-200817143917/85/Basic-synthesis-flow-and-commands-in-digital-VLSI-53-320.jpg)

![Logic Synthesis
Page 115
Introduction to Digital VLSI
get_* Command Syntax
get_xxx [patterns]
• xxx:
• Specifies the type of object to be found. The value of type can be:
designs
clocks
ports
references
cells
nets
pins
libs
lib_cells
ib_pins
• patterns (optional):
• List of names (including wildcards: *) of the design or library objects in dc_shell to be
found.
• If name_list is not specified, then all objects of the specified type are returned.
• If no matches are found, returns an empty string (with a warning).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsynthesisflowandcommandsindigitalvlsi-200817143917/85/Basic-synthesis-flow-and-commands-in-digital-VLSI-55-320.jpg)
![Logic Synthesis
Page 116
Introduction to Digital VLSI
get_* Function Examples
dffrpc
ind2c
INPUT1
INPUT2
OUTPUT1
D
C
RB
Q
in1
in2
clk
reset
int1
out1
(i1)
(i8)
• get_ports
{"clk", "in1", "in2", "reset", "out1"}
• get_cells
{"i1", "i8"}
• get_references
{"ind2c", "dffrpc"}
• get_references dff*
{"dffrpc"}
• get_nets
{"in1", "clk", "reset", "in2", "int1", "out1"}
• set_dont_touch [get_designs]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsynthesisflowandcommandsindigitalvlsi-200817143917/85/Basic-synthesis-flow-and-commands-in-digital-VLSI-56-320.jpg)
![Logic Synthesis
Page 117
Introduction to Digital VLSI
The filter_collection Command
• The filter_collection command takes a collection of objects and a
filter expression (a list of attribute-value relations), and returns a new
collection containing only the objects that have the defined attribute
values.
• A filter expression is composed of conditional expressions, such as
"@port_direction == inout", or "@rise_delay > 1.3". A filter
expression is enclosed in double quotes (" "):
@attribute_name operator value
• -regexp flag enables the use of real regular expressions. -nocase make
the regular expression case insensitive
Example:
set a [ filter_collection [ get_cells *]
"is_hierarchical == true"]
{"Adder1", "Adder2"}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsynthesisflowandcommandsindigitalvlsi-200817143917/85/Basic-synthesis-flow-and-commands-in-digital-VLSI-57-320.jpg)
![Logic Synthesis
Page 118
Introduction to Digital VLSI
filter_collection Command Syntax
filter_collection collection "filter_expression"
• List all bidirectional ports:
dc_shell-t> filter_collection [all_inputs] "@port_direction == inout"
{INOUT0, INOUT1}
• List all PLA designs in memory:
dc_shell-t> filter_collection [get_designs] "@design_type == pla"
{PLA_1, PLA_@}
set_attribute command may be used to create user-defined attributes:
• To add a numeric attribute to some cells:
dc_shell> set_attribute {cell70 cell88 cell95} kuku 6.5
dc_shell> filter_collection [get_cells] "@kuku == 6.5"
A collection can also be filtered when it is created:
get_ports -filter "@port_direction == inout"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsynthesisflowandcommandsindigitalvlsi-200817143917/85/Basic-synthesis-flow-and-commands-in-digital-VLSI-58-320.jpg)
![Logic Synthesis
Page 119
Introduction to Digital VLSI
Synopsys script using get_* and filter_collection
• New commands: foreach_in_collection, if
# add dont_touch attribute to all the instantiations of cl1rspoX latches
foreach_in_collection mod [get_designs] {
set current_design $mod
set mashcell [get_cells "x_cell_*"]
if {$mashcell != ""} {
set_dont_touch [filter_collection $mashcell "@ref_name == cl1rspob ||
@ref_name == cl1rspoc || @ref_name == cl1rspod"]
}
}
set current_design top](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsynthesisflowandcommandsindigitalvlsi-200817143917/85/Basic-synthesis-flow-and-commands-in-digital-VLSI-59-320.jpg)







