Basics of java 1
- 2. Course Objectives Create, compile, and run Java programs JAVA Anatomy I/O Java Collections Framework Methods Threads Reflection Serialization Networking RMI JDBC 2
- 3. Course Objectives, cont. You will be able to Write simple programs using primitive data types, control statements, methods, and arrays. Create and use methods Establish a firm foundation on Java concepts 3
- 4. Getting Started with Java Programming A Simple Java Application Compiling Programs Executing Applications 4
- 5. A Simple Application Example 1.1 //This application program prints Welcome //to Java! package chapter1; public class Welcome { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("Welcome to Java!"); } } 5 RunRunSourceSource NOTE: To run the program, install slide files on hard disk.
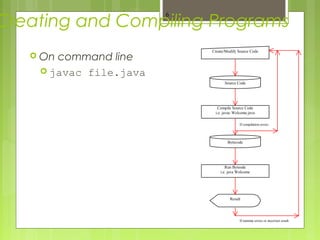
- 6. Creating and Compiling Programs On command line javac file.java 6 Source Code Create/Modify Source Code Compile Source Code i.e. javac Welcome.java Bytecode Run Byteode i.e. java Welcome Result If compilation errors If runtime errors or incorrect result
- 7. Executing Applications On command line java classname 7 Java Interpreter on Windows Java Interpreter on Sun Solaris Java Interpreter on Linux Bytecode ...
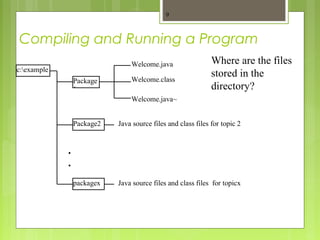
- 9. Compiling and Running a Program 9 Where are the files stored in the directory? c:example Package 1 Welcome.class Welcome.java Package2 . . . Java source files and class files for topic 2 packagex Java source files and class files for topicx Welcome.java~
- 10. Anatomy of a Java Program Comments Package Reserved words Modifiers Statements Blocks Classes Methods The main method 10
- 11. Comments In Java, comments are preceded by two slashes (//) in a line, or enclosed between /* and */ in one or multiple lines. When the compiler sees //, it ignores all text after // in the same line. When it sees /*, it scans for the next */ and ignores any text between /* and */. 11
- 12. Package The second line in the program (package chapter1;) specifies a package name, chapter1, for the class Welcome. Forte compiles the source code in Welcome.java, generates Welcome.class, and stores Welcome.class in the chapter1 folder. 12
- 13. Reserved Words Reserved words or keywords are words that have a specific meaning to the compiler and cannot be used for other purposes in the program. For example, when the compiler sees the word class, it understands that the word after class is the name for the class. Other reserved words in Example 1.1 are public, static, and void. 13
- 14. Modifiers Java uses certain reserved words called modifiers that specify the properties of the data, methods, and classes and how they can be used. Examples of modifiers are public and static. Other modifiers are private, final, abstract, and protected. A public datum, method, or class can be accessed by other programs. A private datum or method cannot be accessed by other programs. 14
- 15. Statements A statement represents an action or a sequence of actions. The statement System.out.println("Welcome to Java!") in the program in Example 1.1 is a statement to display the greeting "Welcome to Java!" Every statement in Java ends with a semicolon (;). 15
- 16. Blocks 16 A pair of braces in a program forms a block that groups components of a program. public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("Welcome to Java!"); } } Class block Method block
- 17. Classes The class is the essential Java construct. A class is a template or blueprint for objects. To program in Java, you must understand classes and be able to write and use them. The mystery of the class will continue to be unveiled throughout this book. For now, though, understand that a program is defined by using one or more classes. 17
- 18. Methods What is System.out.println? It is a method: a collection of statements that performs a sequence of operations to display a message on the console. It can be used even without fully understanding the details of how it works. It is used by invoking a statement with a string argument. The string argument is enclosed within parentheses. In this case, the argument is "Welcome to Java!" You can call the same println method with a different argument to print a different message. 18
- 19. main Method The main method provides the control of program flow. The Java interpreter executes the application by invoking the main method. The main method looks like this: public static void main(String[] args) { // Statements; } 19
- 20. The exit Method Use Exit to terminate the program and stop all threads. NOTE: When your program starts, a thread is spawned to run the program. When the showMessageDialog is invoked, a separate thread is spawned to run this method. The thread is not terminated even you close the dialog box. To terminate the thread, you have to invoke the exit method. 20
Editor's Notes
- #2: First Class: Introduction, Prerequisites, Advices, Syllabus Lab 1: Create a Java Project, Compile, and Run. Show syntax errors Print program Capture screen shots, and save it in Word, and print it. Homework One: Check in the class randomly.





![A Simple Application
Example 1.1
//This application program prints Welcome
//to Java!
package chapter1;
public class Welcome {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Welcome to Java!");
}
}
5
RunRunSourceSource
NOTE: To run the program,
install slide files on hard
disk.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsofjava1-190725180023/85/Basics-of-java-1-5-320.jpg)








![Blocks
16
A pair of braces in a program forms a block that
groups components of a program.
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Welcome to Java!");
}
}
Class block
Method block](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsofjava1-190725180023/85/Basics-of-java-1-16-320.jpg)


![main Method
The main method provides the control of program
flow. The Java interpreter executes the application by
invoking the main method.
The main method looks like this:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Statements;
}
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsofjava1-190725180023/85/Basics-of-java-1-19-320.jpg)
